Identifying Abusive Clauses in Romanian Consumer Contracts for Better Protection
Identifying Abusive Clauses in Romanian Consumer Contracts for Better Protection
Do you know that hidden, unfair terms in contracts could risk your consumer rights?
In Romania, the fight against these clauses is getting stronger.
Courts are dealing with more cases related to this issue.
This shows how important it is to be careful when signing agreements.
This is true, but even more so in banking and finance.
The Romanian civil code and consumer protection laws protect you from unfair terms.
But, many people don’t know their rights or how to spot these clauses.
Knowing the law is your best defense against unfair practices that could harm your finances.
Recently, the European Court of Justice made a big change.
Now, Romanian judges must check agreements for unfairness on their own.
This is a big step to make things fairer for consumers.
When dealing with consumer agreements, knowing is key.
By learning about common abusive clauses and your legal rights, you can make better choices.
You can also challenge unfair terms when needed.
For help with consumer rights and contract reviews, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Key Takeaways
- Romanian courts are seeing an increase in cases related to abusive clauses;
- The European Court of Justice mandates ex officio assessment of unfair terms;
- Law no. 193/2000 defines abusive clauses in consumer contracts;
- Judges are required to restore contractual balance in unfair agreements;
- Consumers should be aware of their rights under Romanian consumer protection laws;
- Legal assistance is available for reviewing and challenging unfair contract terms.
Understanding Romanian Consumer Protection Framework
Romania’s consumer protection has grown a lot after joining the EU.
It aims to protect consumers from unfair contracts and ensure clear terms.
Let’s look at the main points of this framework.
Key Legislative Acts and Regulations
The Romanian consumer credit market has seen big changes to protect consumers better.
In 2021, 10 new rules were added to make contracts clearer.
These laws help make sure contracts are fair for everyone.
Scope of Consumer Protection Laws
Consumer laws in Romania cover many areas, like credit and financial services.
Yet, a 2023 survey found that 40% of consumers don’t know their rights.
This shows we need to teach more about the legal help available to consumers.
Regulatory Bodies and Enforcement Agencies
The National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) and the Financial Supervisory Authority (ASF) are key in enforcing laws.
The ANPC said 25% of complaints in 2021 were about unfair contract terms.
The ASF works to prevent and solve problems, helping to educate consumers.
| Aspect | Data |
|---|---|
| Consumers encountering abusive clauses | 30% |
| Contracts with unclear terms | 35% |
| Consumers seeking legal advice | 15% |
| Consumers reading terms before signing | 20% |
Legal Definition of Abusive Clauses under Romanian Law
Romanian law says abusive clauses are terms that make deals unfair.
These clauses often sneak into contracts without the consumer’s say.
The law, no. 193/2000, helps protect consumers from these unfair practices.
Predatory lending often uses these unfair terms.
These terms usually favor the business a lot.
For instance, clauses that let one side change the deal or impose huge penalties are seen as unfair.
- Lack of direct negotiation with the consumer;
- Significant imbalance in rights and obligations;
- Violation of good faith principles.
Knowing this law helps you spot unfair terms in contracts.
If you find terms that seem unfair or one-sided, they might be abusive.
Always check agreements well and get legal help if you think there are unfair clauses.
Abusive Clauses in Romanian Consumer Contracts
The Romanian legal system has become tougher on abusive clauses in consumer contracts.
Recent changes aim to protect consumers from unfair practices.
The Emergency Government Ordinance no. 58/2022, which took effect on May 28, 2022, brought significant updates to regulatory enforcement.
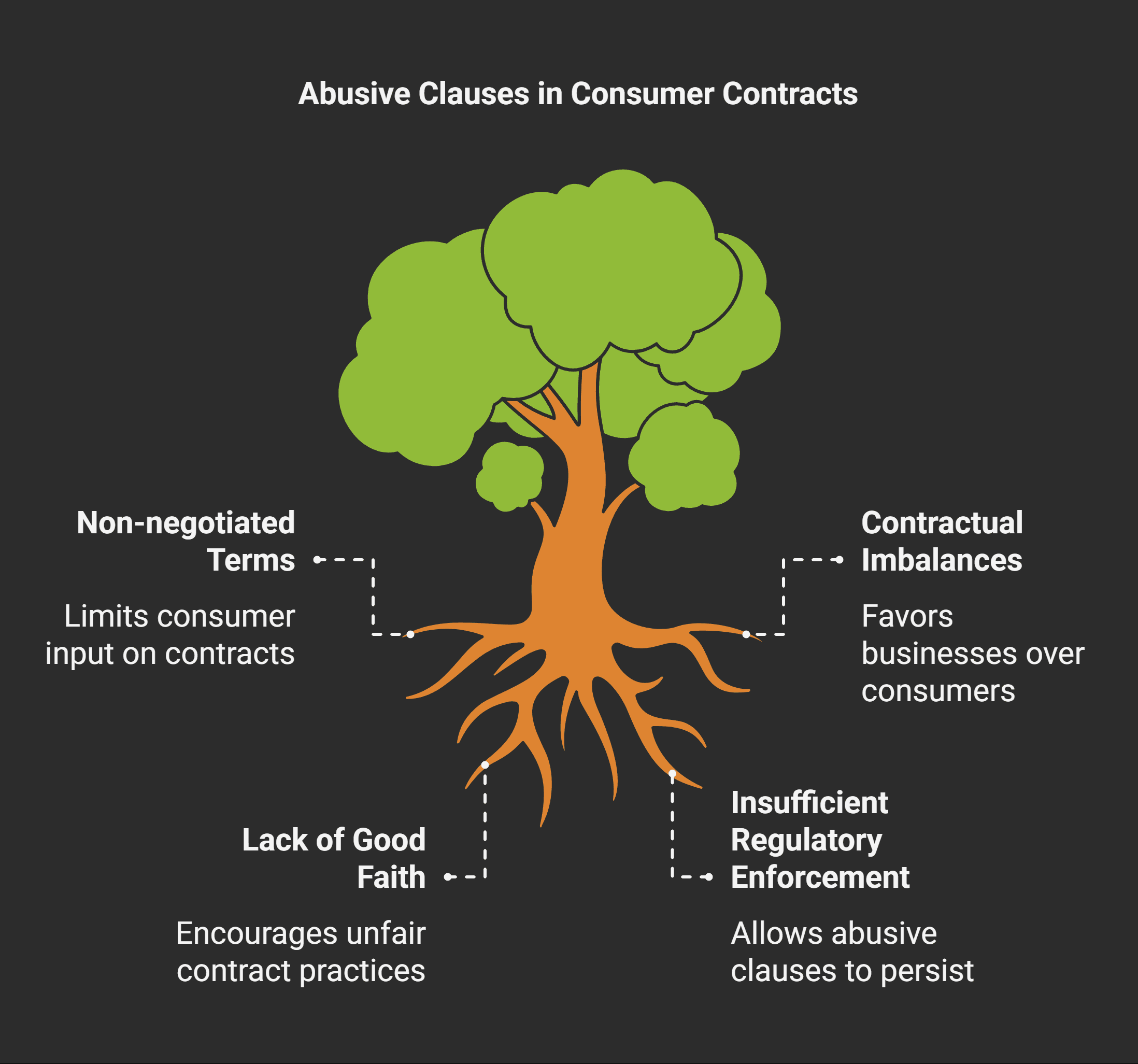
Non-negotiated Contract Terms
Non-negotiated terms often appear in standard form contracts.
These clauses can be problematic for consumers who have little say in their content.
The Romanian legal system now requires courts to analyze potentially abusive clauses as soon as they have enough legal and factual evidence.
Significant Contractual Imbalances
Contractual imbalances that heavily favor businesses over consumers are now subject to stricter scrutiny.
Sanctions for abusive clauses range from RON 20,000 to RON 100,000.
For large-scale violations, fines can reach up to 4% of a company’s turnover in Romania.
Good Faith Requirements
Businesses must act in good faith when drafting contracts.
The new regulations address issues like dual-quality products, with fines doubling if more than 100 consumers are affected.
Courts now have the power to order the removal of abusive clauses from all current contracts.
| Violation Type | Fine Range (RON) | Maximum Fine for Large-scale Violations |
|---|---|---|
| Abusive Clauses | 20,000 – 100,000 | Up to 4% of annual turnover |
| Dual-quality Products | 20,000 – 100,000 | Up to 4% of annual turnover |
| Non-fulfillment of Court Orders | 5,000 – 200,000 | N/A |
These changes reflect Romania’s commitment to aligning with EU standards and protecting consumers from unfair practices.
The increased fines and stricter enforcement measures aim to deter businesses from including abusive clauses in their contracts.
Common Types of Predatory Clauses in Consumer Agreements
Many consumer contracts have clauses that are unfair.
These clauses can harm consumer rights and lead to unfair practices.
Let’s look at some common types found in Romanian consumer agreements.
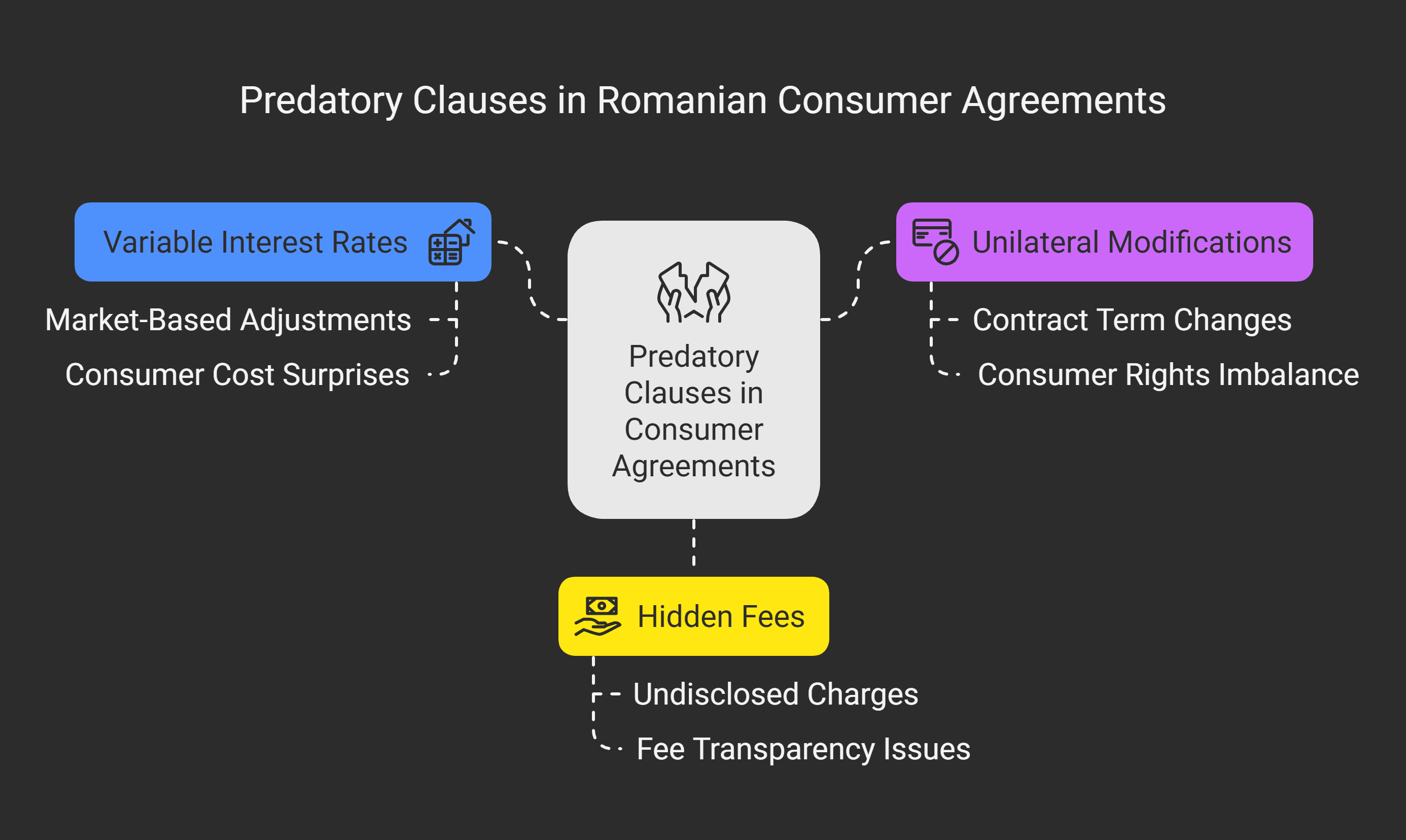
Variable Interest Rate Provisions
Variable interest rate clauses let lenders change rates based on the market.
They seem fair but can surprise consumers with higher costs.
Banks might use this to their advantage, violating consumer rights and needing legal action.
Unilateral Contract Modifications
Some agreements let companies change terms without asking the consumer.
This creates a big imbalance, usually in favor of the business.
It’s important for regulators to watch out for this to protect consumer rights.
Hidden Fees and Charges
Many contracts hide extra costs in small print or hard-to-understand language.
These hidden fees can make things much more expensive.
Consumers should watch out and seek legal help if they find these tricks.
| Clause Type | Potential Impact | Consumer Protection Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Variable Interest Rates | Unexpected cost increases | Interest rate caps |
| Unilateral Modifications | Unfavorable contract changes | Mandatory notification periods |
| Hidden Fees | Higher than advertised costs | Clear fee disclosure requirements |
The National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) has been cracking down on hidden fees and changes in consumer contracts.
This includes actions in the banking sector.
Their goal is to make sure consumer rights are respected and to fix unfair contract terms in different industries.
Consumer Rights and Legal Protections
Romanian consumers have strong legal protections against unfair terms and predatory practices.
The Consumer Protection Law No. 21/1992 is key to these safeguards.
It aims to balance the relationship between traders and consumers.
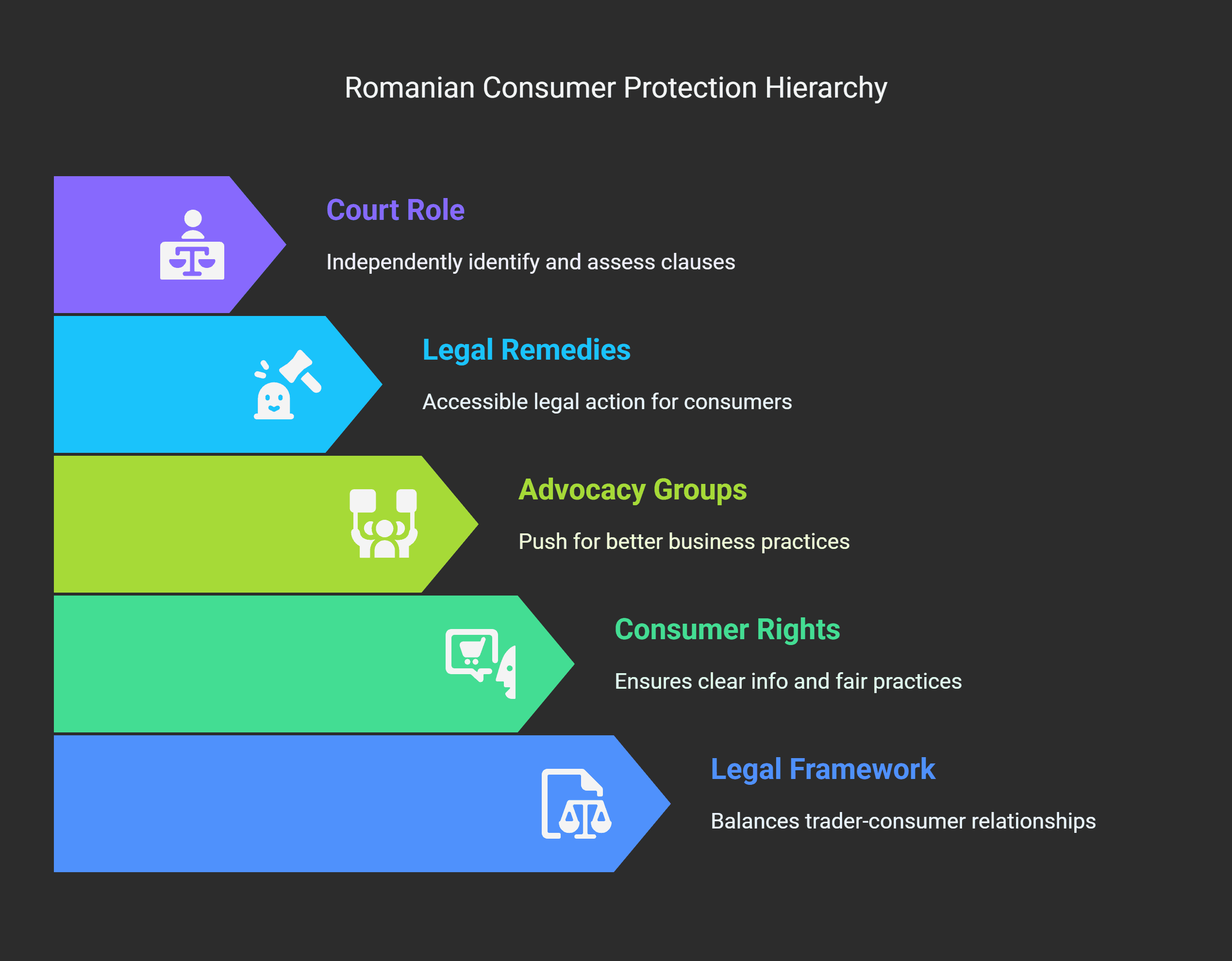
Your rights as a consumer in Romania include:
- Clear information about products and services;
- Compensation for damages;
- Safety from harmful goods;
- Protection against unfair trading practices;
- Shield from abusive contract clauses.
Consumer rights advocacy groups are vital in pushing for better business practices.
They offer support and guidance when dealing with unfair contract terms.
Legal remedies for consumers have been improved.
Fines for unfair terms now range from RON 20,000 to RON 100,000.
In cases affecting over 100 consumers, these fines can double.
If you face predatory practices, you can challenge them.
Consumer associations can publish final court judgments within 45 days.
This increases transparency.
You’re also exempt from court bond payments if your monthly income is below two minimum wages.
This makes legal action more accessible.
| Consumer Right | Legal Basis | Protection Offered |
|---|---|---|
| Right to Information | Law No. 21/1992 | Clear, comprehensible contract terms |
| Right to Negotiate | Emergency Ordinance No. 58/2022 | Protection against non-negotiated terms |
| Right to Challenge | Law No. 193/2000 | Ability to contest unfair clauses |
Role of Courts in Identifying Abusive Clauses
Romanian courts are key in protecting consumers from unfair terms.
They can check if contract clauses are abusive, even if no one complains.
This power comes from EU laws and helps protect consumers.
Ex Officio Assessment Powers
Romanian courts can find and fix unfair terms in contracts on their own.
This helps keep consumers safe, even if they don’t know they’re being taken advantage of.
The courts look closely at contracts to make sure they’re fair.
Judicial Interpretation Guidelines
Romanian courts have rules to follow when checking contracts.
They look at who gets what, if the contract is clear, and how it affects consumers.
They also watch out for clauses that change things without notice and hidden fees.
Legal Precedents and Case Law
Important court decisions guide how Romanian courts deal with contracts. For example, the European Court of Justice said courts must check if terms are unfair on their own. This has made Romanian courts more careful with consumer contracts.
| Key Aspect | Court’s Role |
|---|---|
| Ex Officio Assessment | Independently identify abusive clauses |
| Interpretation Guidelines | Evaluate balance, clarity, and economic impact |
| Legal Precedents | Apply ECJ rulings to national cases |
Banking and Financial Contract Protections
Romania has strong laws for banking and financial contracts.
These laws protect consumers by making sure contracts are clear and fair.
The Romanian Civil Code and laws like O.U.G. no. 50/2010 and O.U.G. no. 52/2016 are key to these protections.
Foreign Currency Loan Agreements
Foreign currency loans can be risky for consumers.
The Civil Code says borrowers must pay back the full amount, no matter the currency’s value.
This can be tough when currency values change.
The case of Șerban vs. Banca Transilvania SA showed the challenges of foreign currency loans.
It highlighted the need for better consumer protection.
Credit Agreement Safeguards
Credit agreements in Romania must follow strict rules.
O.U.G. no. 50/2010 makes sure interest rates, fees, and repayment terms are fair.
For mortgage loans, O.U.G. no. 52/2016 adds extra protections based on EU rules.
Risk Disclosure Requirements
Transparency is very important in financial contracts.
Banks must tell consumers about the risks of their products.
The Financial Supervisory Authority (A.S.F.) makes sure this happens, so consumers know what they’re getting into.
| Law | Purpose | Key Provisions |
|---|---|---|
| Civil Code | General loan regulation | Nominal amount repayment, interest rules |
| O.U.G. no. 50/2010 | Consumer credit agreements | Interest rates, fees, repayment terms |
| O.U.G. no. 52/2016 | Mortgage loans | Residential property credit protections |
Knowing about these protections helps you make better choices when dealing with financial agreements.
Always check the contract terms and ask for help if something is unclear.
This way, you can make sure your rights are looked after under Romanian contract law.
Remedies and Legal Actions Available to Consumers
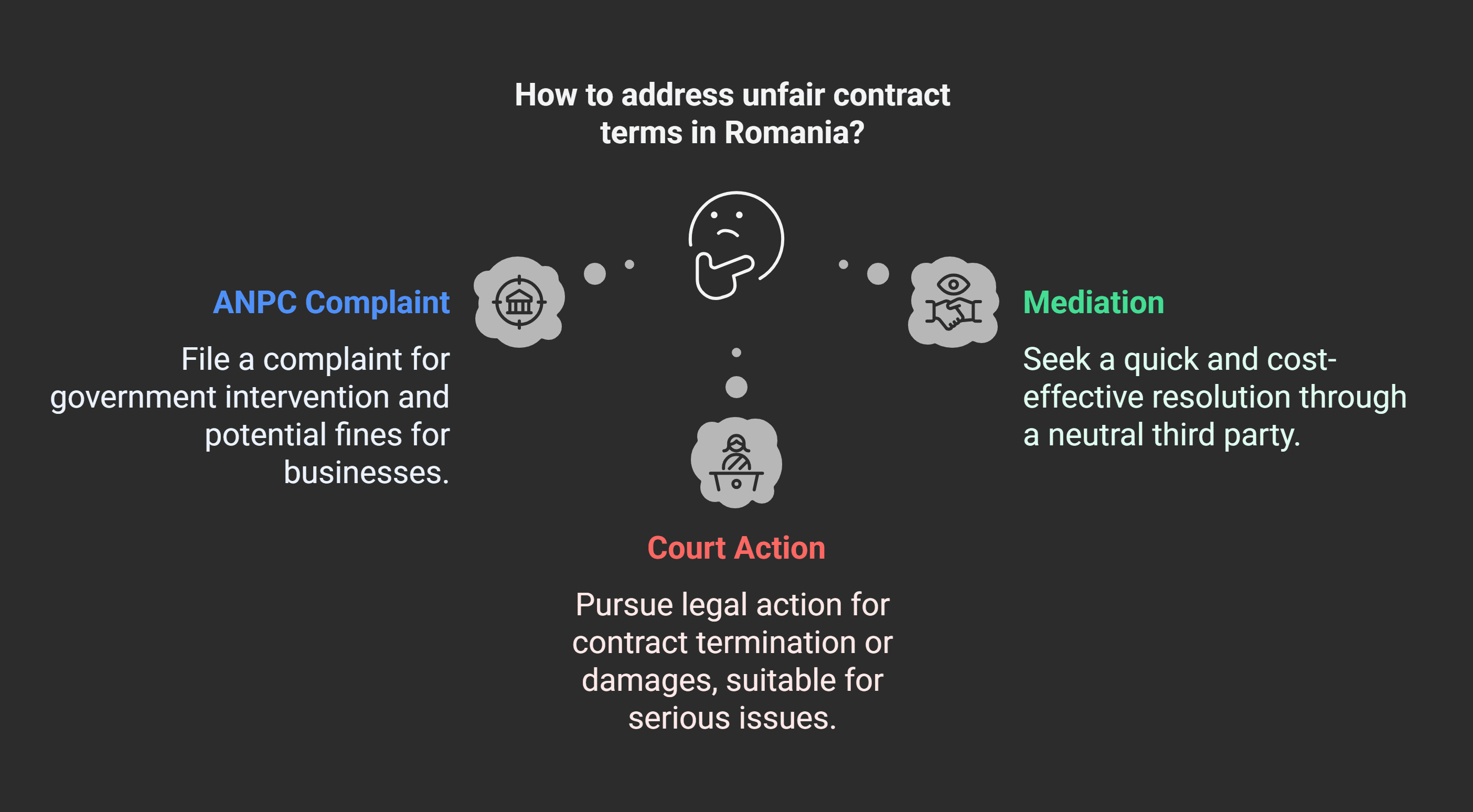
Romanian laws help consumers deal with unfair contract terms.
The National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) is key in keeping things fair.
It protects your rights as a consumer.
If you find unfair terms, you can report it to ANPC.
They check businesses and can fine them if they break the law.
In 2022, they even fined hotels for not being clean or serving bad food.
Mediation is another way to solve problems without going to court.
It’s quicker and cheaper than legal battles.
For bigger issues, you can go to court.
Romanian law lets you ask for fixes, refunds, or to cancel the contract.
Consumer groups can also sue on your behalf.
| Remedy | Description | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| ANPC Complaint | File a complaint with the National Authority for Consumer Protection | 15-30 days for initial response |
| Mediation | Seek resolution through a neutral third party | Varies, typically 1-3 months |
| Court Action | File a lawsuit for contract termination or damages | Can take several months to years |
Remember, EU law makes unfair contract terms invalid.
This means you keep your rights, even when faced with unfair contracts.
European Union Influence on Romanian Consumer Protection
The European Union has greatly influenced Romania’s consumer protection laws.
This has led to better protection against unfair contract terms and predatory business practices.
EU Directives Implementation
Romania has adopted key EU directives to boost consumer rights.
Law no. 193/2000, for example, makes sure consumer contracts are fair.
It aims to protect consumers from unfair business tactics.
Cross-border Consumer Protection
EU rules also protect Romanian consumers when they deal with businesses from other EU countries.
This safeguard helps prevent unfair treatment in international deals.
Harmonization with EU Standards
The Romanian legal system works closely with the European Court of Justice.
This ensures EU consumer protection laws are applied correctly.
The court’s decisions have been key in clarifying what makes a contract unfair.
| EU Directive | Romanian Implementation | Key Provisions |
|---|---|---|
| Directive 2011/83/EC (Consumer Rights) | Government Emergency Ordinance no. 34/2014 | 14-day withdrawal period for distance contracts |
| Directive 93/13/EEC (Unfair Terms) | Law no. 193/2000 | Protection against significant contractual imbalances |
| Directive 2005/29/EC (Unfair Commercial Practices) | Law no. 363/2007 | Regulation of misleading and aggressive practices |
These EU laws have made consumer protection in Romania stronger.
They address unfair contract terms and business practices.
The ongoing effort to align with EU standards ensures Romanian consumers get the best legal protection.
Steps to Challenge Abusive Contractual Terms
Dealing with unfair contract terms?
You have rights as a consumer in Romania.
Here’s how to fight back:
- Check your contract for any unfair changes, unclear language, or high fees.
- Collect all important documents, like emails or letters from the company.
- Report the issue to the National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) within 15 days.
- If ANPC doesn’t help, you can take legal action in court.
- Get advice from a Romanian lawyer who specializes in consumer rights to guide you.
Remember, bank loans often have strict rules.
Watch out for high interest rates, hidden costs, and sudden payment changes.
Knowing your rights under the Romanian Civil Procedure Code is key.
When fighting foreclosure, act fast.
You must defend yourself within 15 days at the local court.
Winning can cancel the foreclosure and refund your costs.
But losing means you’ll have to pay more and court fees.
By acting quickly and getting legal advice, you can defend against unfair contracts.
This way, you make sure your consumer rights are respected.
Conclusion
As Romania gets closer to EU standards, protecting consumers gets even better.
Laws like the one on abusive clauses are being updated.
Keep an eye out, know your rights, and help make sure contracts are fair in Romania.
It’s important to know the laws in Romania about protecting consumers.
You might ask, what are abusive clauses?
These are terms that make it unfair for you and favor the trader too much.
Examples include changes made without your agreement, harsh penalties, and hidden fees.
If you think your contract has unfair terms, get legal help fast.
The Consumer Protection Law No. 21/1992 helps keep you safe from unfair practices.
Also, remember, traders can’t make you agree to terms you don’t understand.
Breaking these rules can lead to big fines.
Companies might have to pay up to 5% of their income.
The ANPC can also fine them and even close their business if they keep breaking the rules.
For expert advice, you can reach out to Atrium Romanian Lawyers.
Our team of lawyers in Romania is known for their business law expertise in Romania.
Romania’s consumer protection laws follow EU standards.
You have 15 days to ask for fixes or new products if something is wrong.
If you need help with unfair liability clauses, there are many legal resources to help protect your rights.
FAQ
What constitutes an abusive clause under Romanian law?
In Romania, an abusive clause is a term in a contract that wasn’t negotiated individually.
It creates a big imbalance in the rights and duties of the parties, hurting the consumer.
These clauses are often in standard contracts and go against the principle of good faith.
How can I identify potentially abusive clauses in my contracts?
Look for terms that limit your rights or impose harsh penalties.
Also, watch out for clauses that let one side change the contract without your consent.
If a term seems unfair or unclear, it might be abusive.
What should I do if I suspect a contract I’ve signed contains abusive clauses?
First, carefully review the contract and find the clauses you think are abusive.
Then, you can file a complaint with the National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) or get legal advice.
You might also challenge the clause in court or through alternative dispute resolution.
Can I negotiate or modify standard form contracts?
Yes, you can ask for changes in standard contracts. Some businesses might agree to modify certain terms.
If they say no and you think the terms are unfair, you can get help from consumer protection agencies or lawyers.
What are the most common types of abusive clauses in Romanian consumer contracts?
Common abusive clauses include terms that let one side change the contract without your consent.
They also include harsh penalties for breaking the contract, limits on the business’s liability, and unfair dispute resolution mechanisms.
Variable interest rates and hidden fees are also often problematic.
How long do I have to challenge an abusive clause after signing a contract?
There’s no time limit in Romania to challenge abusive clauses.
It’s best to act quickly when you find out about the issue.
The time limit for contractual claims is usually three years, but it can vary based on your case.
What are the possible consequences for businesses that use abusive clauses?
Businesses using abusive clauses might face fines from the ANPC.
Courts can also declare these clauses invalid, affecting the whole contract.
Repeated offenses can lead to harsher penalties and harm the company’s reputation.
In some cases, the business might have to pay affected consumers.
How does Romanian consumer protection law compare to EU standards?
Romanian consumer protection laws are mostly in line with EU standards.
Romania has adopted key EU directives, like Directive 93/13/EEC on unfair terms in consumer contracts.
The country keeps aligning its laws with EU regulations, ensuring Romanian consumers get similar protections as those in other EU countries.
Are there any specific industries or sectors where abusive clauses are more common?
Abusive clauses are often seen in banking and financial services, telecommunications, utility contracts, and rental agreements.
These sectors use standard contracts a lot, making them more likely to include unfair terms.
Where can I find legal assistance if I need help with an abusive clause issue?
You can get help from consumer protection associations, legal aid groups, or lawyers who specialize in consumer law.
The National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) also offers support.
Some universities and non-profit groups have free legal clinics for consumer rights issues.
What are abusive clauses in consumer contracts and how are they defined under Romanian law?
In Romania, abusive clauses (also known as unfair terms) in consumer contracts are defined by Law No. 193/2000 regarding unfair terms in consumer contracts.
An abusive clause is a contractual provision that has not been directly negotiated with the consumer and which, contrary to the requirement of good faith, creates a significant imbalance between the rights and obligations of the parties, to the detriment of the consumer.
The Romanian legislation is aligned with the European Union Directive 93/13/EEC. A clause is abusive when it creates this imbalance, giving the professional (seller or service provider) an unfair advantage over the consumer.
It’s important to note that abusive terms are not binding on consumers, even if they have signed the contract.
What is the comprehensive list of abusive clauses recognized under Romanian consumer law?
Romanian Law No. 193/2000 regarding consumer protection against unfair terms provides a non-exhaustive list of abusive provisions.
Some examples of abusive clauses in consumer contracts include:
1. Terms that exclude or limit the legal liability of the professional for damages caused to the consumer
2. Clauses that restrict the consumer’s right to terminate the contract
3. Terms that allow the professional to unilaterally modify the contract terms without a valid reason
4. Clauses that bind the consumer while making the professional’s obligations subject to conditions whose realization depends solely on their will
5. Terms imposing disproportionate penalties on consumers for breach of contractual obligations
6. Clauses allowing professionals to transfer the contract without the consumer’s consent when this might reduce guarantees.