Navigating Collective Labor Agreements in Romania
Navigating Collective Labor Agreements in Romania
In 2023, Romania’s labor laws changed a lot.
More than 67% of businesses were affected by new rules on collective bargaining.
These changes have made a big difference in how jobs are set up and managed.
To understand collective bargaining in Romania, you need to know about the latest laws.
These laws have made it clearer and more organized for workers to negotiate at work.
The Ministry of Labor and Social Solidarity made big changes with Order no. 798/2023.
This order sets up a clear way to group businesses and handle negotiations at the sector level.
It’s all about making sure everyone follows the same rules in different industries.
Key Takeaways
- New legislative framework implemented in 2023;
- Enhanced transparency in collective bargaining;
- Standardized classification of business units;
- Improved protection of employee rights;
- Sector-level negotiation opportunities expanded;
- Clear guidelines for employment contracts.
Understanding the Legal Framework of Romanian Labor Laws
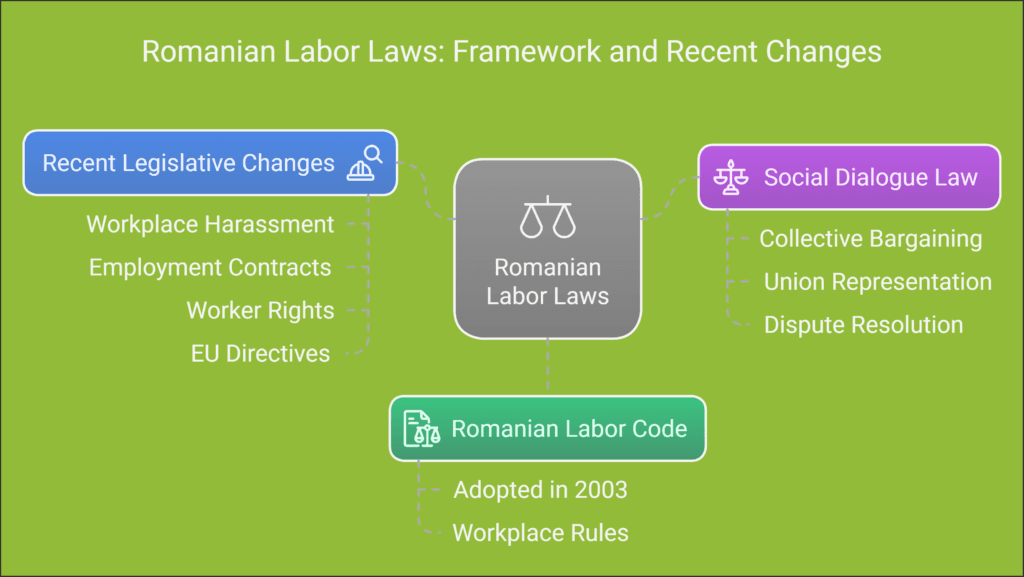
Understanding Romanian labor laws is complex.
The Romanian labor code is key, guiding employers and employees. It sets the rules for the workplace.
Recently, employment laws in Romania have changed a lot.
New rules aim to protect workers better and improve talks between employers and employees.
Key Legislation Governing Labor Relations
Romania’s labor laws are based on several important laws:
- The Romanian Labor Code (adopted in 2003);
- Social Dialogue Law (Law No. 367/2022);
- Constitutional provisions;
- European Union employment directives;
- International Labor Organization (ILO) standards.
Social Dialogue Law Overview
The Social Dialogue Law is a big step forward.
It makes sure employers and workers talk openly.
It helps solve problems and negotiate better.
| Legislative Aspect | Key Requirement |
|---|---|
| Collective Bargaining | Mandatory for companies with 10+ employees |
| Union Representation | Minimum 35% employee membership for company-level recognition |
| Dispute Resolution | Structured mediation processes established |
Recent Legislative Changes in 2023-2024
Romania’s labor laws keep changing. Recent updates focus on:
- Stopping workplace harassment better;
- Making employment contracts clearer;
- Protecting workers’ rights more;
- Following EU employment rules.
It’s vital for businesses in Romania to know these laws.
This ensures they follow the rules and have good relationships with workers.
Mandatory Collective Bargaining Requirements
It’s important for employers and employees in Romania to know about collective bargaining rules. New laws have changed how labor talks work. It’s key to keep up with these changes.
Now, companies with 10 or more workers must do collective bargaining.
This is a big change from the old rule of 21 workers.
The government wants to protect workers more and improve work agreements.
- Collective bargaining is now compulsory for companies employing 10+ workers;
- Written agreements must be registered with the Territorial Labor Inspectorate;
- Negotiation period cannot exceed 60 days without mutual agreement.
Employers must follow certain steps when starting labor talks.
They need to start talks at least 45 days before the current contract ends.
If they don’t, workers or unions can ask for talks in writing within 10 days.
Important things about union talks in Romania include:
- Collective agreements must be written and registered officially;
- Agreement duration ranges from 12 to 24 months;
- One-time extension of 12 months is permitted;
- Parties must document each negotiation meeting with signed minutes.
Trade unions are very important in these talks.
A union can start at a company with 15 members and get recognized with 35% of the workers.
This helps workers have a say in their rights and work conditions.
Role of Trade Unions and Employee Representatives
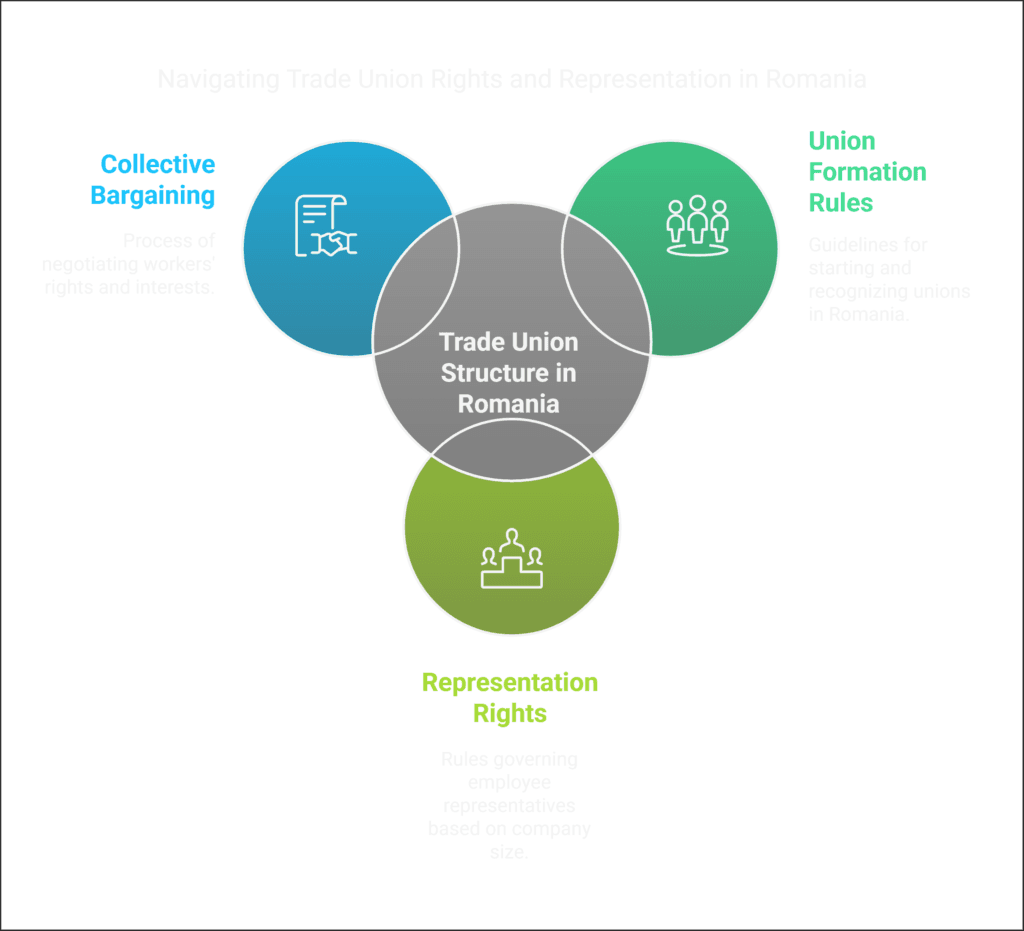
It’s important to know how workers are represented in Romania.
Trade unions play a big role in protecting workers’ rights.
They help with negotiations in many industries.
Labor unions in Romania have rules for starting and representing workers.
Here are the main steps to form workers’ associations:
- At least 10 employees in the same company can start a union.
- 20 employees from different companies in the same sector can also start a union.
- A union must have at least 35% of company employees to be recognized.
Union Formation and Representation Rights
The rules for union representation in Romania are clear.
Companies have specific rules for choosing representatives based on their size:
| Company Size | Maximum Representatives |
|---|---|
| Less than 100 employees | 2 representatives |
| 101-500 employees | 3 representatives |
| 501-1000 employees | 4 representatives |
| 1001-2000 employees | 5 representatives |
| Over 2000 employees | 6 representatives |
Collective Bargaining Priority
Workers’ voices are important in negotiations in Romania.
Representatives need at least 50% + 1 vote from employees.
They can only represent workers for two years.
Non-representative unions can also join negotiations if they have at least 7% of sector employees.
Collective Labor Agreement Romania: Essential Components
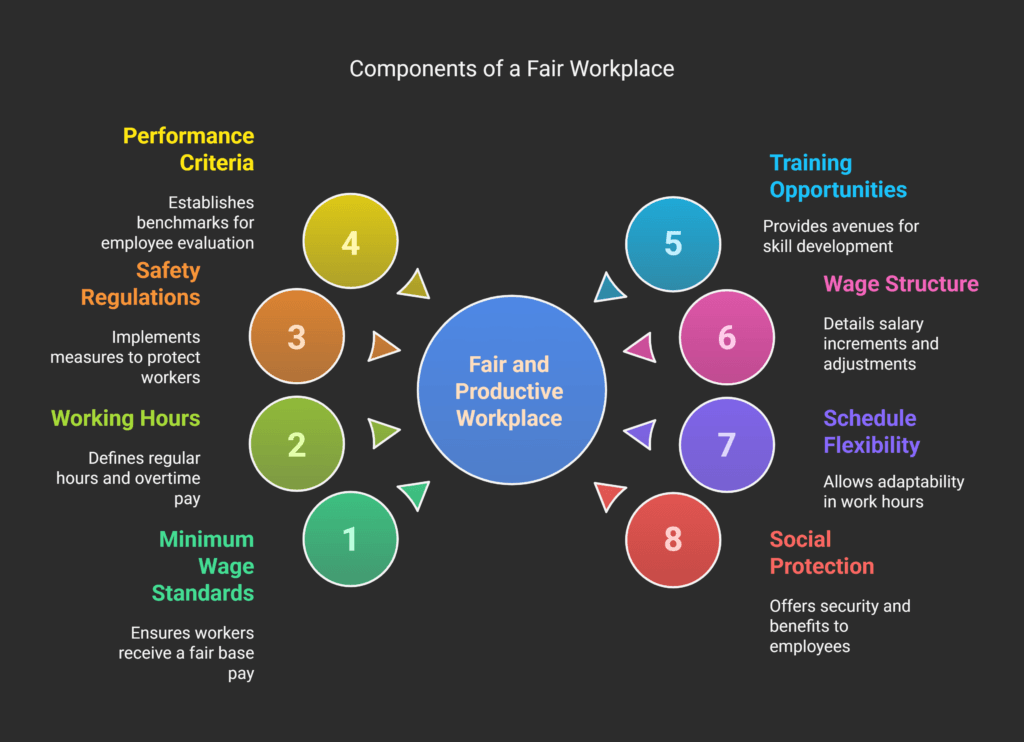
Understanding the key parts of collective labor agreements in Romania is vital for protecting workers’ rights.
These agreements are detailed plans that cover important aspects of work and employee safety.
The main parts of these agreements focus on several key areas.
They affect how workers are treated and what benefits they get:
- Minimum wage standards for different job categories;
- Detailed working hours and overtime compensation;
- Workplace safety regulations;
- Performance evaluation criteria;
- Employee training and development opportunities.
Romanian labor laws have specific rules for these agreements.
Since 2011, changes have made it easier for workers to talk about their jobs.
Now, only 10 employees are needed to start collective negotiations.
Important parts of these agreements include:
- Wage structure and salary increments;
- Work schedule flexibility;
- Social protection mechanisms;
- Dispute resolution procedures;
- Professional development pathways.
Employers need to see these agreements as more than just paperwork.
They are essential for keeping workplaces fair and productive.
By negotiating and implementing strong agreements, companies can build better relationships with their employees.
They also make sure they follow Romania’s changing labor laws.
Negotiation Process and Procedures
Negotiating collective bargaining in Romania needs a smart plan.
It’s about structured talks between employers and unions.
This ensures rules in the workplace are followed well.
Knowing the legal rules for labor talks is key.
Romanian laws set out clear steps for both sides to follow.
Initiating Collective Bargaining
Starting collective bargaining involves several important steps:
- Employers with over 10 workers must start talks;
- They must tell employees 15 days before talks begin;
- Talks should start 60 days before the current deal ends.
Documentation Requirements
Keeping detailed records is vital in Romanian labor talks. The negotiation process needs accurate and formal documents.
| Document | Purpose | Copies Required |
|---|---|---|
| Collective Labor Agreement | Formal negotiation outcome | 3 copies (company, employees, Labor Inspectorate) |
| Negotiation Minutes | Record of discussions | 2 copies (each party) |
| Representative Voting Records | Validate employee representation | 1 copy (company) |
Timeline and Deadlines
Romanian rules set strict times for bargaining:
- Maximum negotiation time: 45 days;
- Extension possible: Up to 12 months with agreement;
- Deal length: 12-24 months.
Ignoring these rules can lead to big fines.
Fines can be between 5,000 to 20,000 RON.
Sector-Level Collective Bargaining
Sector-level collective bargaining is now key in Romania’s industrial relations.
New laws have changed how employers and workers make agreements in different sectors.
Key features of sector-level collective bargaining include:
- Mandatory bargaining for employers with at least 10 employees;
- Recognition of unions representing 35% of workers at sector level;
- Potential extension of agreements to entire sectors under specific conditions.
The new rules change how workplace disputes are solved.
They make it clear what employer groups in Romania must do.
Companies now have to follow more detailed rules for bargaining, focusing on workers’ voices.
Notable developments in sector-level collective bargaining include:
- Reduced union establishment thresholds;
- Simplified negotiation timelines;
- Enhanced protections for employee representatives.
Romania is leading the EU in changing collective labor agreements.
The goal is to get workers more involved and make industrial relations clearer in various sectors.
Employers must now get ready for detailed negotiations at the sector level.
These agreements will influence industry standards for jobs, pay, and work conditions.
Implementation and Compliance Measures
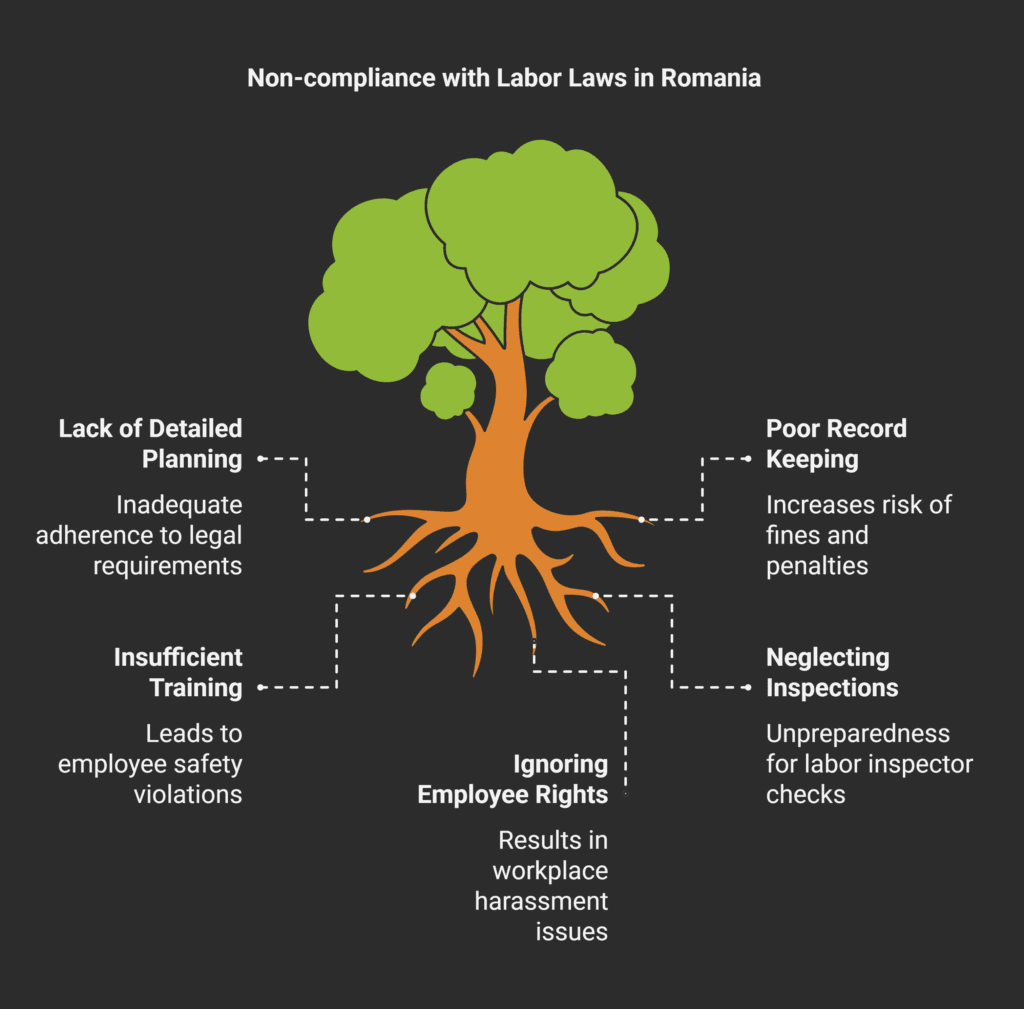
To follow labor laws in Romania, employers need a detailed plan.
They must carefully follow collective labor agreements and legal rules.
It’s important to handle work regulations in Romania with great care.
Here are some key steps for employers:
- Register all employment contracts in the electronic Revisal system;
- Do mandatory risk assessments for employee health and safety;
- Give the right protective gear and training;
- Keep accurate records of employee information;
- Set up systems for handling employee complaints.
Labor inspectors are key in checking if employee protection standards are met.
They do deep checks to make sure workers’ compensation rules are followed.
Your company should be ready for inspections by keeping detailed records and fixing any issues early.
Important compliance rules cover many areas of employee rights and duties.
This includes:
- Keeping all employment contracts on file;
- Updating payroll statements regularly;
- Telling labor authorities about service contracts;
- Having rules against workplace harassment;
- Ensuring fair chances in hiring and promotions.
Not following the rules can lead to big fines.
Fines can be between RON 5,000 and RON 100,000, based on the violation.
It’s crucial to manage well and do regular checks to avoid problems and keep the workplace legal.
Legal Support and Professional Assistance
Understanding collective labor agreements in Romania needs the help of a professional Romanian law office.
A skilled lawyer in Bucharest can guide you through the complex legal landscape of employment disputes in Romania.
We will make sure your organization follows strict labor regulations.
Legal consultants are key in managing collective bargaining processes and help prepare documents, understand Social Dialogue Law, and avoid legal risks.
With fines up to RON 20,000 for mistakes, having expert lawyers in Bucharest is vital for your business.
Role of Legal Consultants
Your Romanian lawyer will explain the rules for collective bargaining, especially for companies with 10 or more employees.
Our Law firm offers strategic advice on negotiations, documents, and ensuring your organization meets Romanian Labor Code standards.
Documentation Requirements
Getting professional legal help is important for employment documents.
Bucharest lawyers can create detailed collective labor agreements, handle employee representation, and keep up with Romanian labor laws.
For specialized legal help, contact us.
FAQ
What is a Collective Labor Agreement in Romania?
A Collective Labor Agreement is a legal document.
It’s made by employers and trade unions.
It sets rules for work, rights, and duties for employees in a company or sector.
It covers important things like pay, hours, benefits, and how to solve problems.
Who is required to participate in collective bargaining in Romania?
Companies with 10 or more employees must bargain collectively.
Employers and trade unions must both take part.
New laws have made it easier for smaller groups to bargain.
How do I form a trade union in Romania?
To start a trade union, you need 10 workers from the same field.
You must register with the court and show you’re independent from employers.
The union must also have a fair structure.
What are the key components of a Collective Labor Agreement?
A Collective Labor Agreement in Romania has many parts.
It includes the minimum wage, work conditions, and benefits.
It also covers hours, overtime, training, health, and how to solve problems.
These parts are talked about to protect both workers and employers.
What is sector-level collective bargaining?
Sector-level bargaining makes agreements for whole industries.
These agreements set rules for wages, work, and benefits for all in a sector.
It makes work rules the same for everyone in that field.
What happens if an employer does not comply with a Collective Labor Agreement?
If an employer breaks a Collective Labor Agreement, they could face fines or lawsuits.
They might have to fix the problem, pay for it, or get in trouble with labor authorities.
How long are Collective Labor Agreements valid in Romania?
Collective Labor Agreements last 12 to 24 months.
After that, the parties must talk about new terms.
The old agreement stays in place until a new one is made or until it’s decided to end it.
Can individual employment contracts deviate from the Collective Labor Agreement?
No, individual contracts can’t be worse than the Collective Labor Agreement.
Employers must make sure individual contracts are at least as good as the agreement.
What role do legal consultants play in collective bargaining?
Legal consultants help with labor laws and making agreements.
They check if rules are followed, help in talks, and solve disputes.
Their knowledge is key in understanding labor laws in Romania.
How are disputes resolved in Collective Labor Agreements?
Disputes are usually solved through talking, mediation, or arbitration.
If that doesn’t work, they can go to court.
The agreement usually says how to solve problems between employers and employees.



