Best Practices for Ensuring AI Compliance in European Businesses
Best Practices for Ensuring AI Compliance in European Businesses
A staggering €35 million or 7% of a company’s worldwide annual turnover – that’s the maximum fine for violating AI rules under the EU AI Act.
This law, signed on August 1st, 2024, will change how European businesses handle AI.
Companies have until 2026 to make sure their AI practices meet these new standards.
The EU AI Act sets up a detailed framework for AI rules.
It divides AI systems into four risk levels: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal.
This system is key to managing AI risks, making companies review their AI use and ensure they follow the rules.
For European businesses, like those in Romania, it’s vital to understand and follow these rules.
The Act affects any company whose AI systems touch EU residents.
This shows how important it is to have strong AI compliance measures, not just to avoid fines but to promote responsible innovation.
Key Takeaways
- EU AI Act enforces strict penalties for non-compliance, up to €35 million or 7% of annual turnover;
- Full implementation expected by 2026, requiring immediate action from businesses;
- AI systems categorized into four risk levels, with specific requirements for each;
- Global impact: regulations apply to all AI systems affecting EU residents;
- Emphasis on transparency, accountability, and ethical AI development.
Understanding the EU AI Act Framework and Scope
The EU AI Act is a big step in regulating AI in Europe.
It aims to make AI trustworthy and encourage innovation.
Let’s explore its main points and how it affects businesses.
Key Objectives and Principles
The AI Act focuses on making AI accountable and transparent.
It uses a risk-based approach, dividing AI systems into four levels.
This balance aims to protect safety and rights while allowing innovation.
- Unacceptable risk: 8 prohibited practices;
- High risk: Strict obligations for critical applications;
- Limited risk: Transparency requirements;
- Minimal risk: No specific rules.
Stakeholders Affected by the Regulation
The EU AI Act affects many in the AI field.
Providers, deployers, importers, and distributors must follow rules based on their role and AI’s risk level.
This ensures AI is used responsibly.
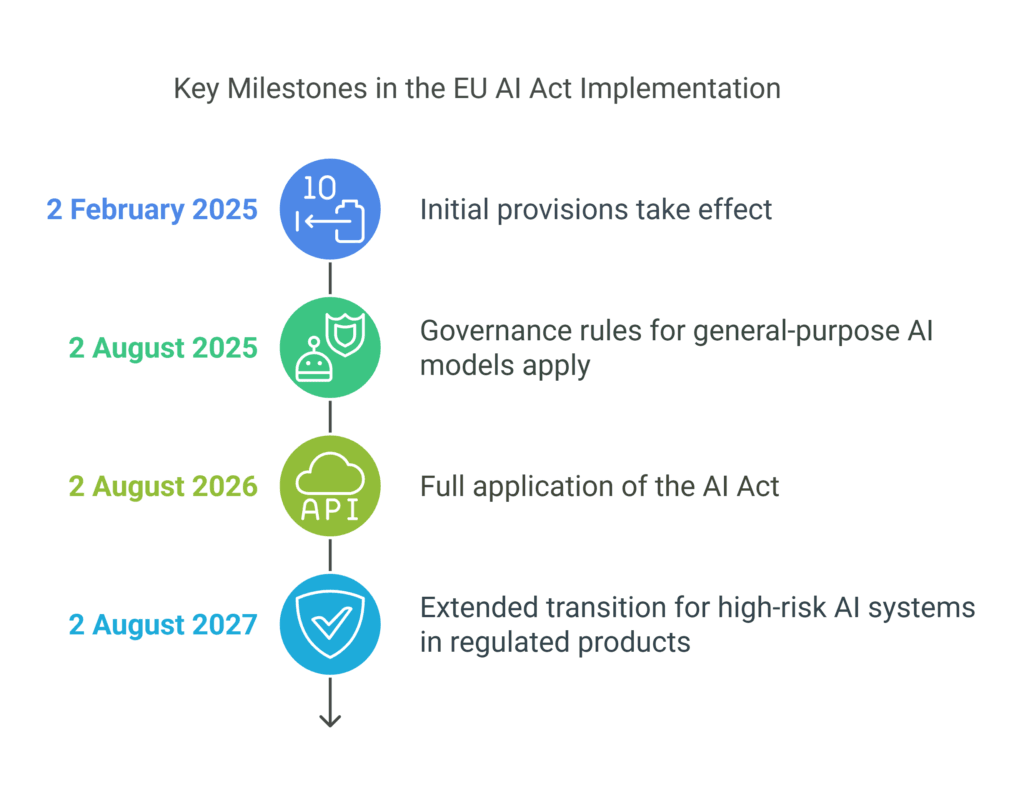
Timeline for Implementation
The EU AI Act will be implemented in phases:
- 2 February 2025: Initial provisions take effect;
- 2 August 2025: Governance rules for general-purpose AI models apply;
- 2 August 2026: Full application of the AI Act;
- 2 August 2027: Extended transition for high-risk AI systems in regulated products.
This timeline helps businesses adjust and meet the new AI rules.
It supports the growth of reliable AI systems.
AI Compliance in European Businesses: Risk Classification System
The European AI strategy has a detailed risk classification system for AI.
It aims to ensure ai fairness and ethics.
It also promotes responsible ai deployment in different sectors.
Prohibited AI Practices
The EU AI Act bans some AI uses.
These include systems for controlling behavior, social scoring, and real-time biometric identification.
This rule helps protect fundamental rights, as part of the European AI strategy.
High-Risk AI Systems
High-risk AI systems have strict rules.
They are used in critical areas like infrastructure, education, and law enforcement.
These systems need thorough ai audits and must pass conformity assessments before they can be used.
Limited and Minimal Risk Categories
AI systems with lower risks have less strict rules.
They don’t have to follow specific laws but are encouraged to follow voluntary guidelines.
This balance allows for innovation while keeping ethics in mind.
| Risk Category | Examples | Regulatory Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Prohibited | Social scoring AI | Banned |
| High-Risk | AI in critical infrastructure | Strict regulations |
| Limited Risk | Chatbots | Transparency requirements |
| Minimal Risk | AI-enhanced video games | Voluntary guidelines |
Essential Requirements for AI System Providers and Deployers
The EU AI Act has strict rules for AI system providers and deployers.
These rules aim to make AI trustworthy and follow ethical practices.
Providers must prepare AI systems carefully before they hit the market.
Deployers focus on using these systems safely and legally.
AI providers must take strong steps to protect privacy and manage data well.
They also need to keep detailed records for 10 years after the system is introduced.
This helps follow AI regulation and improve data privacy.
Deployers are key to keeping AI trustworthy.
They must keep system logs for at least six months.
They also need to report serious incidents within 15 days.
For big disruptions, they have only two days to report.
| Requirement | Providers | Deployers |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation Retention | 10 years | 6 months (logs) |
| Incident Reporting | 15 days | 15 days |
| Critical Incident Reporting | 2 days | 2 days |
| CE Marking | Required | Not applicable |
Providers must put CE markings on high-risk AI systems.
They also need to have an EU representative if they’re outside the union.
These steps help meet AI regulation standards in the European market.
Data Governance and Privacy Requirements
As AI Regulation in Europe evolves, businesses face complex data governance and privacy rules.
The EU AI Act, set to take effect in 2026, brings new challenges.
It works with GDPR to ensure strong AI ethics and governance.
GDPR Alignment with AI Systems
AI systems must follow GDPR principles like lawfulness, fairness, and transparency.
You must ensure your AI practices meet these standards, mainly for high-risk areas like finance and healthcare.
Do Data Protection Impact Assessments for high-risk activities to stay compliant.
Data Quality and Management Standards
High-quality data is vital for ai bias mitigation and following rules.
The EU AI Act stresses strict data management, mainly for high-risk AI systems.
You need to have strong data governance to avoid penalties and keep client trust.
This includes managing various data sources well and ensuring data minimization.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Keeping detailed records is essential to show you’re following the rules.
Keep records of AI training data, biases, and system performance.
For high-risk AI systems, log activity and do regular checks.
Also, remember, importers must keep EU declarations of conformity and technical documentation for ten years after market placement.
By focusing on these data governance and privacy needs, you’ll be ready for the changing AI regulation in Europe.
This will help you develop ethical and responsible AI.
Transparency and Explainability Obligations
The EU AI Act makes it clear how AI systems must be transparent and explainable.
These rules help make sure AI is fair and protects privacy.
Companies need to tell users when they’re dealing with AI, unless it’s very obvious or used for legal reasons like catching criminals.
For AI systems that are very high-risk, providers must give ‘instructions for use’.
These instructions should include details on how the system works, its accuracy, and its security.
The Act also requires detailed technical documents for audits and ongoing checks.
AI-generated content, like deepfakes, must be labeled as artificial.
This helps stop fake information and protects people.
The Act also creates a database for high-risk AI systems.
This makes it easier for the public to learn about these technologies.
- High-risk AI systems need to be transparent so users understand how they work;
- AI companies must tell users when they’re not talking to a human;
- Providers must make sure their AI solutions are effective, work well together, are strong, and reliable.
These rules help follow ethical AI guidelines and support AI governance.
By being open and clear, businesses can gain trust and follow the EU AI Act.
This could lead to more people using AI and feeling confident about it.
Risk Management and Compliance Monitoring
European businesses need strong risk management and compliance monitoring to follow the EU AI Act.
These steps help make sure AI is trustworthy and keeps data safe.
Risk Assessment Frameworks
Businesses must create detailed risk assessment frameworks for AI accountability.
These frameworks spot risks, check their impact, and plan how to fix them.
Regular checks help companies stay on top of new challenges and follow rules.
Continuous Monitoring Systems
It’s key to have systems that watch AI all the time.
These systems check how AI is doing, find odd things, and make sure it follows rules.
By always watching AI, companies can catch and fix problems early.
Incident Response Protocols
Having clear plans for AI problems is very important.
These plans should say how to find, report, and fix issues.
Quick action helps reduce harm and shows a company’s commitment to AI safety.
| Component | Purpose | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Assessment | Identify and evaluate AI risks | Proactive risk mitigation |
| Continuous Monitoring | Track AI system performance | Early issue detection |
| Incident Response | Address AI-related issues | Minimize possible damages |
By using these risk management and compliance monitoring steps, European businesses can make sure their AI systems follow rules.
This keeps trust with everyone involved.
Penalties and Enforcement Measures
The EU AI Act has strict penalties for not following the rules.
It focuses on making sure AI is transparent and private.
Businesses need to know these rules to avoid fines and stay in line with GDPR and AI laws.
Financial Penalties Structure
The Act has a system of fines based on how serious the violation is:
- Up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover for prohibited AI practices;
- Up to €15 million or 3% for violations of specific provisions;
- Up to €7.5 million or 1% for providing misleading information.
Small businesses are capped at lower fines to help them stay afloat while keeping the rules strict.
Compliance Violations Categories
Violations are split into levels based on their impact on AI safety and ethics.
Serious violations include banned AI practices.
Less serious ones might be not monitoring AI well or not keeping proper records.
Enforcement Mechanisms
Here’s how the AI Act will be enforced:
- Member States report to the European Commission every year;
- The new AI Office will watch over General-Purpose AI Models;
- Authorities can investigate and take documents.
These steps help keep AI safe and transparent across the EU.
| Violation Type | Maximum Fine | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|
| Prohibited AI Practices | €35M or 7% of turnover | August 2, 2025 |
| Other Obligations | €15M or 3% of turnover | August 2, 2025 |
| Misleading Information | €7.5M or 1% of turnover | August 2, 2025 |
Implementation Strategies for Business Compliance
The EU AI Act will start in August 2026. Businesses need to act fast to follow the rules.
They must set up strong ai governance frameworks.
These should cover risk assessment, quality management, and cybersecurity to protect data and avoid risks.
Companies should keep a list of their AI use cases and systems.
This list helps them know where they need to focus on compliance.
They also need to do regular checks and audits to make sure AI systems are fair and transparent.
Building trustworthy AI is key to following the rules.
This means adding privacy and ethics into AI development from the start.
Companies should also have clear rules with AI vendors and check AI systems often for fairness and accuracy.
Training programs are important for AI risks.
Employees working with critical systems, like those making credit decisions, need more training.
This is different from those doing less sensitive tasks.
If you need help with these strategies, contact our lawyers in Romania at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Our Romanian law office can offer great advice on AI compliance for European businesses.
Challenges and Considerations for Global Companies
Global companies face unique challenges in implementing responsible AI deployment strategies that comply with the EU AI Act.
They must harmonize international AI regulations with robust ai risk mitigation strategies.
Companies need to navigate diverse regulatory landscapes while keeping up with EU standards.
A key challenge is conducting thorough ai bias and fairness audits across different cultural contexts.
They need to develop culturally sensitive evaluation methods.
This ensures AI systems remain unbiased and fair in various global markets.
Implementing AI transparency and accountability measures on a global scale is another hurdle.
Companies must create standardized processes for explaining AI decisions to stakeholders from diverse backgrounds.
This may involve developing multilingual explainability tools and adapting communication strategies to local norms.
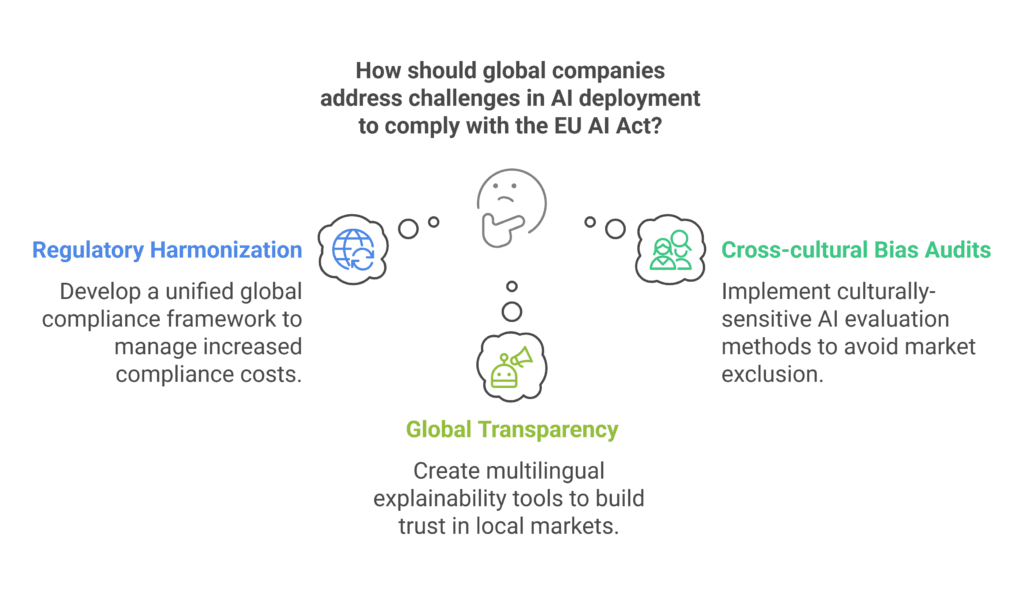
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Harmonization | Increased compliance costs | Develop unified global compliance framework |
| Cross-cultural Bias Audits | Potential market exclusion | Culturally-sensitive AI evaluation methods |
| Global Transparency | Trust issues in local markets | Multilingual explainability tools |
While challenging, early compliance with the EU AI Act can provide a strategic advantage.
As other regions look to the EU as a model for AI regulations, companies that adapt now may find themselves better positioned in the global market.
Future Trends and Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The AI regulatory scene is changing fast. By 2026, the EU AI Act will fully come into play.
It will bring a new risk-based system for AI apps.
This means companies will need to update their privacy and security measures.
Recent stats show AI governance is becoming more critical:
- 56% of organizations plan to use Generative AI in the next year;
- 72% of companies already use AI, seeing improvements in many areas;
- Only 18% of organizations have a council for responsible AI governance.
As rules get stricter, companies could face big fines.
The EU AI Act might fine violators up to €35 million or 7% of their global income.
To keep up, companies need to train their AI teams and follow strict ethics guidelines.
The future of AI rules will include more audits and risk checks.
Healthcare and finance will need special plans to use AI ethically and follow the law.
Conclusion: Embracing Ethical AI for Sustainable Growth
The EU AI Act is a big change in artificial intelligence.
It got 523 votes in favor, setting a new AI governance standard.
Your business needs to follow these rules to avoid fines up to 7% of global turnover.
It’s important to have a good ai risk assessment strategy.
The Act covers all AI systems in the EU market, no matter where they are.
High-risk AI systems must go through checks and be registered in an EU database.
This ensures AI systems are safe and trustworthy.
It also makes sure they respect basic rights.
Ai fairness testing is now a must for following the rules.
The European AI Office will make sure everyone follows the Act.
There’s also an AI Sandbox for testing within ethical limits.
These rules start on August 1, 2024, with most parts taking effect on August 2, 2026.
Understanding the EU AI regulation can be tough.
For help with compliance, contact our lawyers in Romania at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
By using ethical AI, your business can grow sustainably in this new AI world.
FAQ
What is the EU AI Act and why is it important for European businesses?
The EU AI Act is a new rule for AI in the European Union.
It helps businesses by setting rules for ethical AI use.
It also makes sure AI is governed well and meets certain standards.
How does the EU AI Act classify AI systems based on risk?
The Act sorts AI systems into four risk levels.
There are banned practices, high-risk systems, systems with limited risk, and those with minimal risk.
Each level has its own rules. Knowing this helps businesses understand their duties.
What are the essential requirements for AI system providers and deployers under the EU AI Act?
Providers and deployers must focus on data quality and system reliability.
They also need to ensure human oversight and transparency.
These steps are key from start to finish to follow the Act’s rules.
How does the EU AI Act intersect with existing data protection regulations like GDPR?
The Act works with the GDPR to protect data.
Businesses must follow GDPR rules for AI use.
Keeping data safe and well-documented is essential for following both laws.
What are the transparency and explainability requirements under the EU AI Act?
The Act requires clear information about AI systems.
Businesses must make AI decisions clear and explainable.
This builds trust and follows the regulation.
What risk management and compliance monitoring measures are required by the EU AI Act?
The Act demands good risk management and constant checks.
Businesses need to have plans for risks and keep an eye on their AI systems.
This keeps them in line with the Act.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the EU AI Act?
Breaking the Act can cost up to €30 million or 6% of global sales.
The fine depends on the violation’s impact.
This shows how serious following the Act is.
How can businesses implement AI compliance measures in line with the EU AI Act?
Businesses can start by making AI inventories and doing impact assessments.
They should also think about privacy and ethics in AI.
Keeping AI systems up to date is key.
For complex issues, getting legal advice is a good idea.
What challenges do global companies face in complying with the EU AI Act?
Global companies must align with many AI rules worldwide.
They need a global plan for AI compliance.
This means adjusting their current systems to fit EU rules.
What future trends are expected in AI regulation?
We might see more AI offices and independent bodies.
The rules will likely change, so businesses need to stay updated.
Being ethical and flexible in AI compliance is important for growth.