Recognition of Paternity in Romania: Insights into Romanian Civil Law
Recognition of Paternity in Romania: Insights into Romanian Civil Law
Ever wondered how paternity recognition works in Romania?
Romanian laws on paternity are important for families.
They affect child support and who gets what in the future.
Figuring out paternity in Romania might seem hard, but it’s important for kids and parents.
Paternity tests in Romania are very accurate.
They help solve family mysteries.
Romanian laws on child support aim to help kids while considering both parents’ roles.
Key Takeaways
- Romanian paternity laws blend modern practices with cultural traditions;
- Establishing paternity is key for child support and inheritance rights;
- Paternity testing in Romania uses advanced methods for accuracy;
- Legal services are available for international paternity cases;
- Understanding the process is essential for both mothers and fathers.
Legal experts in Romania can help with paternity cases, even those involving other countries.
They make sure your rights are looked after.
For cases with foreign divorce decisions or marriages with Romanian citizens, they know how to handle it.
Understanding Romanian Paternity Laws and Legal Framework
Romanian family law has clear rules for recognizing paternity.
The new Romanian Civil Code (287/2009) explains how to establish and challenge paternity.
This code impacts the rights of unmarried fathers and the process of acknowledging paternity voluntarily.
Overview of Current Legislation
The Civil Code says the legal conception period is 180 to 300 days before birth.
It allows using DNA tests to challenge paternity.
The law sets time limits for proving or disputing paternity.
International Treaties and Agreements
Romania follows international agreements that affect paternity cases with foreign citizens.
These agreements help apply paternity laws consistently across borders.
They influence how to challenge paternity in Romania.
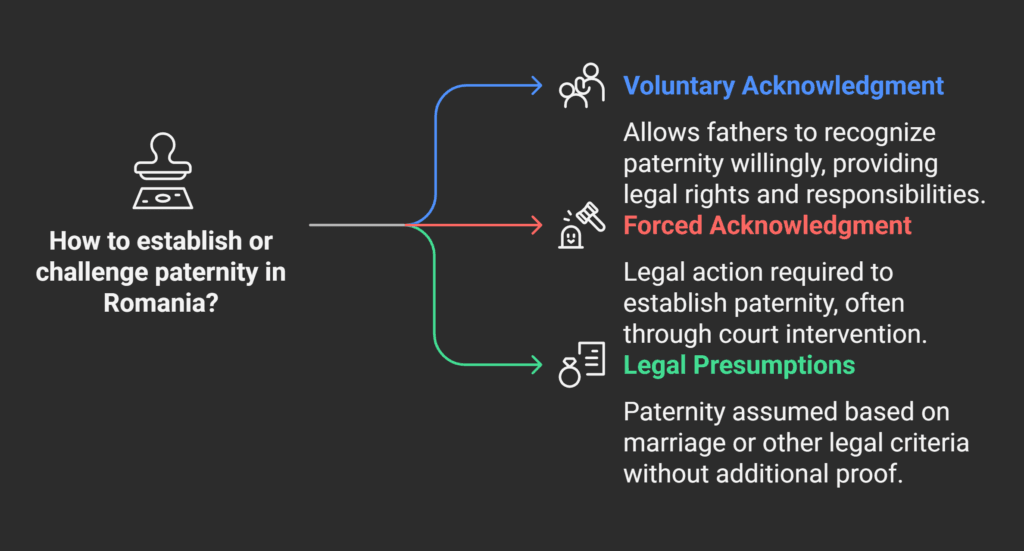
Legal Definition of Paternity in Romania
Romanian law has three ways to prove paternity: voluntary, forced, and legal presumptions.
Children born in marriage are presumed to have a father.
Those born out of wedlock need a recognition statement or court order.
The Civil Code also gives rights to children born through assisted reproduction, just like naturally conceived ones.
Paternity Recognition in Romania: Basic Procedures
In Romania, establishing paternity follows certain legal steps.
The 2011 Romanian Civil Code sets out the rules for both married and unmarried couples.
If a child is born within 180 to 300 days of marriage, the husband is usually considered the father.
Unmarried fathers in Romania can also claim their rights.
They can sign a voluntary acknowledgment of paternity with the mother’s consent.
If there’s a dispute, the court may get involved.
DNA testing is key in disputed cases.
Romanian Courts often order these tests to confirm paternity.
Two labs perform the tests to ensure they’re accurate.
The results are very important in making legal decisions.
In cases where the father has passed away, courts look at all the evidence.
This might include DNA from relatives or other biological samples.
The Civil Code allows for changes in civil status based on new evidence.
It’s important to understand paternity rights in Romania.
The process can be complex, even more so in international cases.
Getting legal advice is a good idea to make sure parental rights are recognized correctly.
Voluntary Acknowledgment of Paternity Process
In Romania, making a father legally recognized is easy.
This way, dads can officially acknowledge their kids without going to court.
It’s key for the child’s birth record and for figuring out child support.
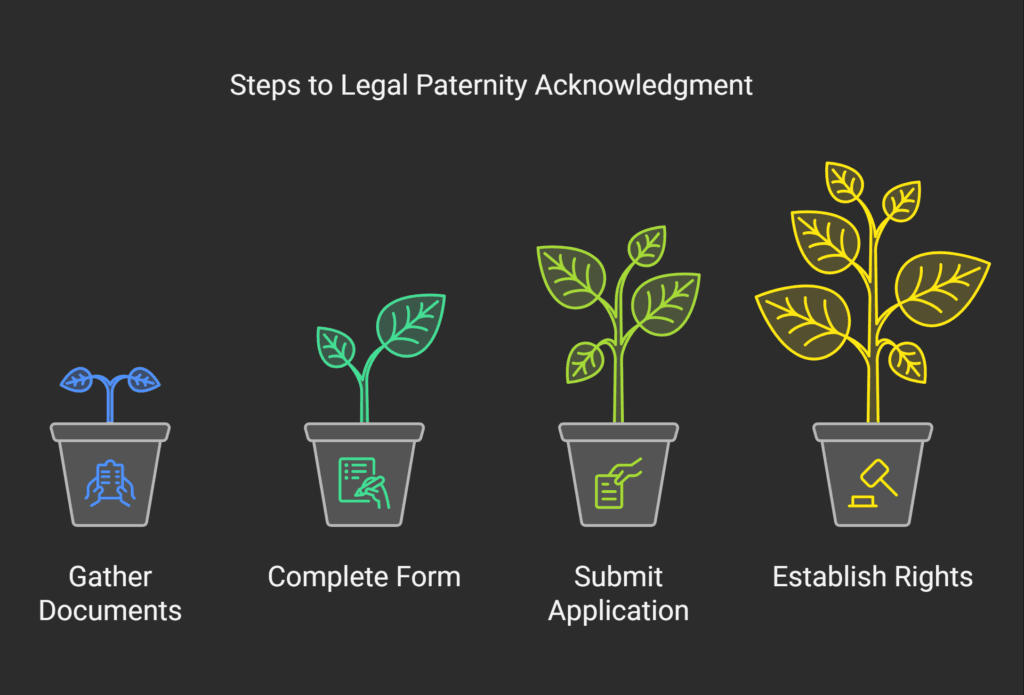
Required Documentation
To begin, you need certain papers.
These are:
- Valid identification papers for both parents;
- Child’s birth certificate;
- Declaration of paternity form.
The form must have the father, mother, and child’s details.
Both parents must sign it.
Filing Procedures
Take your application to the civil status registration authority (RACS).
During martial law, you can even send it remotely.
This makes things easier for parents who are far apart or live abroad.
Timeline and Costs
The time it takes to acknowledge paternity is short.
The costs are low, mostly for administrative fees.
After it’s done, the father’s legal rights are established.
This is important for the child’s birth record and for child support in Romania.
If problems come up later, parents can try mediation or get legal help.
The Brussels IIb Regulation helps with cases across the EU.
It makes sure decisions are followed everywhere.
DNA Testing for Paternity Establishment
DNA testing in Romania is key for proving family ties.
It’s used when someone doubts a parent’s identity or when a court needs to decide.
The European Court of Human Rights sees DNA tests as vital in these cases.
Want to prove who a child’s father is in Romania?
DNA tests can help.
They can be asked for by parents or ordered by judges.
Samples from the child, mother, and alleged father are taken and checked in labs.
For unmarried dads, DNA tests are very important.
A positive test can help prove you’re the father.
This might lead to changes on the child’s birth certificate and legal rights.
The Romanian courts look at DNA tests as strong evidence.
But they also think about what’s best for the child.
If you’re in a dispute, getting legal advice is smart.
It helps understand DNA testing’s role in your rights and duties.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities of Fathers in Romania
Paternity establishment in Romania gives fathers big rights and duties.
Knowing these can help you play your role well.
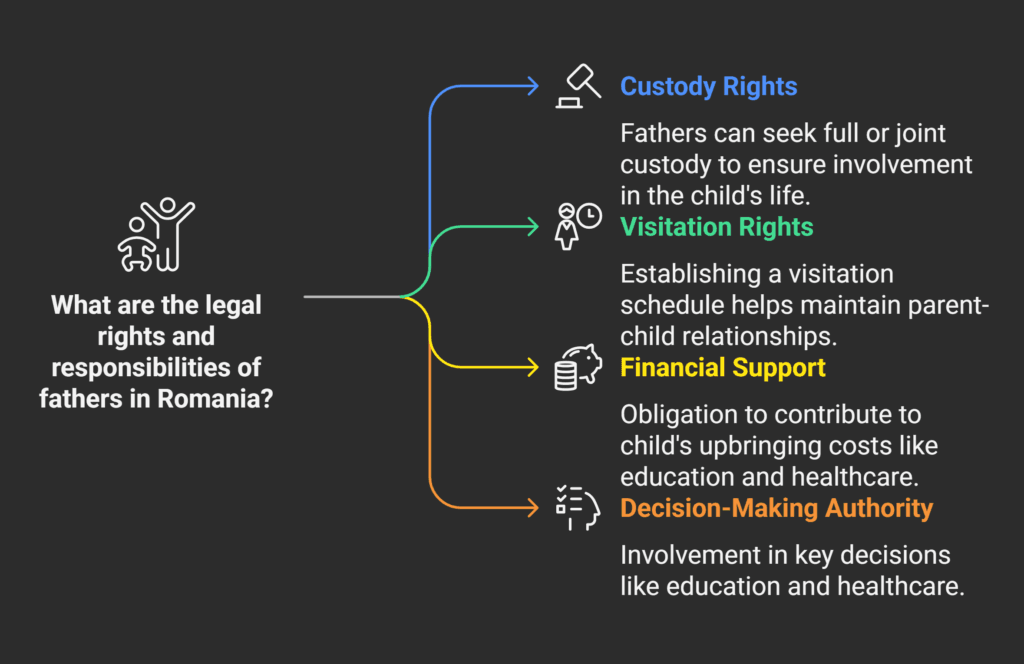
Custody and Visitation Rights
In Romania, courts decide on custody and visits based on what’s best for the child.
They try to keep both parents involved.
If you’re not together, you can ask for custody or visitation rights.
Financial Obligations
By acknowledging paternity in Romania, you must help with your child’s costs.
This includes education, healthcare, and everyday expenses.
Courts will decide how much you should pay based on your income and the child’s needs.
Decision-Making Authority
As a father with established paternity, you get to make big decisions for your child.
This includes education, healthcare, and religious choices.
If you have joint custody, you and the other parent must agree on these decisions.
| Aspect | Father’s Rights/Responsibilities |
| Custody | Right to seek full or joint custody |
| Visitation | Right to establish visitation schedule |
| Financial Support | Obligation to contribute to child’s upbringing |
| Decision Making | Authority in education, healthcare, and religious choices |
Remember, DNA paternity testing in Romania is key if there’s doubt.
Once paternity is confirmed, you’ll need to update the birth certificate.
This makes sure your rights and duties are legally recognized.
Challenging Paternity in Romanian Courts
In Romania, the legal process for challenging paternity is complex.
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) has made rulings on child support cases.
They stress the importance of fairness between family stability and individual rights.
Grounds for Contesting Paternity
Fathers can challenge paternity by filing a court case.
This usually involves DNA tests to confirm biological ties.
The rules for these challenges are found in Romania’s Civil and Family Codes.
Legal Time Limits
Romania’s new Civil Code says paternity suits can be reopened during the child’s lifetime.
This means cases can be reopened even years after the initial decision.
Court Procedures
The court procedures for challenging paternity are detailed.
They may require affidavits of paternity, DNA test results, and other evidence.
For unmarried parents, the rights can be complex.
It’s wise to get a Romanian lawyer to help with the process.
Remember, challenging paternity can change child support and the rights of the legal father in Romania.
The ECHR has given damages in cases where paternity proceedings were unfairly denied.
This shows the need for fair process in these matters.
International Aspects of Paternity Recognition
Figuring out paternity in Romania gets tricky when there are international ties.
The Romanian Civil Code helps guide these cases.
For married couples, the law of their marriage at the child’s birth decides paternity.
If they were divorced before the child was born, the divorce law applies.
For unmarried parents, the child’s birth country’s law decides paternity.
Romania looks at the child’s citizenship to decide which law is best.
This way, genetic testing and parental rights are fair for everyone.
The laws cover important areas like the child’s name and who pays for their needs.
These rules help with paternity tests, even when countries are involved.
It makes sure everything is clear and fair.
Romanian laws on child custody also think about international cases.
The mother’s country’s law decides who pays for pregnancy and birth costs.
This helps make sure paternity is recognized fairly, even in complicated cases.
Birth Registration and Certificate Amendments
In Romania, registering a birth is key to establishing paternity and securing a child’s legal identity.
The process involves several steps and documents.
If changes are needed, there are specific procedures for amendments.
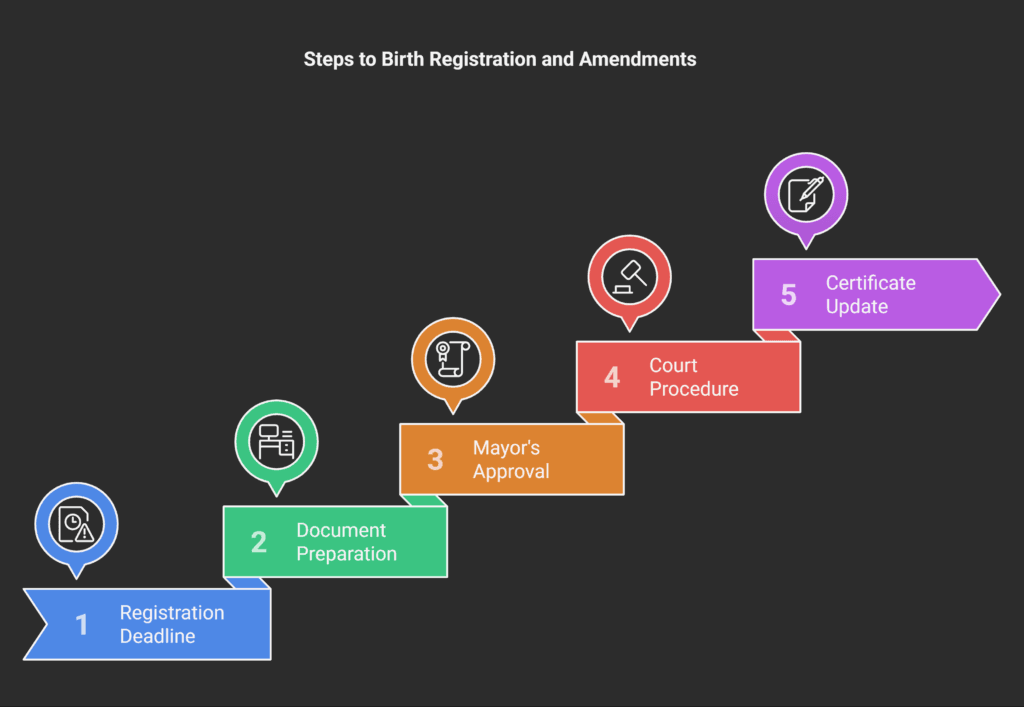
Registration Process
You must register your child’s birth within 15 days in Romania.
If you miss this deadline, you’ll need approval from the local mayor.
Delays beyond a year require a court procedure and a medico-legal assessment, which comes with a fee.
This process is part of family law Romania and affects father’s rights Romania.
Required Documents
To register a birth, you’ll need:
- Parents’ identity documents;
- Medical certificate of birth;
- Marriage certificate (if applicable);
- Declaration of name choice.
Amendment Procedures
If you need to amend a birth certificate, perhaps due to contested paternity Romania or DNA testing paternity Romania, you can request corrections.
The process involves submitting evidence to support the change.
For unmarried fathers rights Romania, establishing paternity after initial registration may require additional steps.
| Certificate Type | Description | Usage |
| Birth Certificate | Older version | Valid for official purposes |
| Birth Certificate Extract | New version | Current standard for new registrations |
Remember, Romania doesn’t distinguish between legitimate and illegitimate births.
All children are born legitimate, regardless of their parents’ marital status.
This approach simplifies many aspects of family law Romania.
Child Support and Maintenance Obligations
In Romania, child support is key in legal parentage.
It’s based on income, number of kids, and custody.
Single mothers often start with parentage acknowledgment to get support.
DNA testing in Romania proves legal paternity when needed.
It’s very helpful in disputes. After confirming paternity, the court sets child support amounts.
Romania’s laws consider many factors for child support.
The State Allowance for kids is not taken from support. This means kids get both kinds of support.
| Aspect | Details |
| Legal Framework | Hague Convention 2007 |
| State Allowance | Not deducted from child support |
| International Cases | Diplomatic channels for non-convention countries |
| Free Legal Assistance | Available for child support cases |
For international cases, Romania uses the Hague Convention 2007.
This helps with child support across borders.
For non-convention countries, Romania gets help through diplomatic channels.
Legal Support and Professional Assistance
Understanding paternity in Romania can be tough.
Getting legal help is key to knowing your rights and duties.
Family lawyers in Romania can guide you on paternity, custody, and parental roles.
Finding Legal Representation
For legal aid on paternity in Romania, find lawyers with family law experience.
They can help from starting the affidavit of paternity to custody and child support.
They know about unwed father rights too.
Contact Information
For top legal help on paternity in Romania, reach out to Atrium Romanian Lawyers at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
They focus on international family law and can assist with the paternity process.
Conclusion
Understanding family law in Romania, like establishing paternity rights, can be tricky.
This article has covered the main points of paternity recognition.
It includes voluntary acknowledgment and the rights of unmarried fathers.
Knowing these details is key for parents and kids.
The Romanian Civil Code protects children born in and out of wedlock well.
It outlines clear rules for birth registration and paternity.
This ensures equal rights for all, no matter the birth circumstances.
DNA testing is now a key tool in proving biological paternity, accepted by Romanian courts.
Remember, getting professional help is very important.
Whether you’re acknowledging paternity or fighting it in court, legal advice is vital.
It helps protect your rights and ensures the best outcome for everyone.
Family law in Romania is changing, with new EU rules aiming to make recognizing parenthood easier across borders.
By knowing your rights and duties in paternity cases, you can make choices that are best for your child.
These legal rules aim to give children stability and protection.
They do this, no matter if the parents are married or not, or how the child was conceived.
FAQ
How is paternity legally established in Romania?
In Romania, paternity can be confirmed in a few ways.
The father can acknowledge it voluntarily, the court can order it, or DNA tests can prove it.
If a couple is married, the husband is usually considered the father of any children born during the marriage.
What documents are needed for voluntary paternity acknowledgment in Romania?
To acknowledge paternity voluntarily, you’ll need some documents.
These include ID for both parents, the child’s birth certificate, and a signed declaration of paternity.
The exact documents needed might change, so it’s wise to check with your local civil registry office.
How long does the voluntary paternity acknowledgment process take in Romania?
The time it takes to acknowledge paternity voluntarily in Romania varies.
It usually takes a few weeks after all documents are submitted.
In some cases, there might be a faster option.
Is DNA testing mandatory for establishing paternity in Romania?
DNA testing isn’t always needed but can be required by the court in disputes.
It’s also an option for fathers who want to confirm paternity on their own.
What rights does an unmarried father have in Romania?
Once paternity is confirmed, unmarried fathers in Romania have similar rights to married fathers.
These include custody and visitation rights.
But, they might need to take extra legal steps to claim these rights.
How is child support calculated in Romania?
Child support in Romania is based on the non-custodial parent’s income, the number of children, and the custody arrangement.
The court also considers other factors to ensure the child’s needs are met.
Can paternity be challenged after it has been established in Romania?
Yes, paternity can be challenged in Romanian courts.
There are legal limits and specific reasons for doing so, like fraud or mistaken identity.
How does Romanian law handle international paternity cases?
Furthermore, Romanian law deals with international paternity cases by considering both domestic laws and international treaties.
The process might involve recognizing foreign judgments or applying Romanian law, depending on the case.
Can a birth certificate be amended to add or change paternity information in Romania?
Yes, birth certificates in Romania can be updated to reflect changes in paternity.
You’ll need to submit a request to the civil registry office with the necessary documents.
Where can I find legal assistance for paternity issues in Romania?
For legal help with paternity issues in Romania, you can reach out to specialized family law attorneys.
Our Romanian Law Firm offer help for both Romanian citizens abroad and foreign citizens in Romania.



