Legal Aspects of Online Surveillance in Romania
Legal Aspects of Online Surveillance in Romania
Exploring online surveillance in Romania is complex.
The country’s history deeply affects its laws and how it handles intelligence.
After 1989, Romania’s Securitate was broken up.
This move marked the start of its modern surveillance and data privacy rules.

Now, Romania’s laws on online surveillance are guided by cybersecurity regulations and data privacy laws.
These rules try to keep the country safe while also protecting people’s privacy.
For more details on Romania’s online surveillance laws, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Key Takeaways
- Romania’s history influences its current surveillance laws.
- Cybersecurity regulations play a key role in online surveillance.
- Data privacy laws are vital for balancing security and privacy.
- Romania’s intelligence community was reformed after 1989.
- Understanding Romanian data privacy laws is key for following the rules.
The Current State of Online Surveillance in Romania
To understand online surveillance in Romania, we must look at its history and recent changes.
Romania’s surveillance has grown a lot, shaped by both national security and EU rules.
Historical Development of Surveillance Laws
The history of surveillance laws in Romania has seen big changes, mainly after communism fell.
Post-Communist Era Reforms
After communism ended, Romania made big legal changes.
These aimed to protect privacy while keeping the country safe.
Recent Legislative Changes
In recent years, Romania’s laws on surveillance have changed a lot.
Now, electronic surveillance needs court approval, which helps protect people’s rights.
For more details on Romania’s surveillance laws and their impact, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Key Government Agencies Involved in Surveillance
In Romania, three main agencies handle surveillance: the Romanian Intelligence Service (SRI), the Foreign Intelligence Service (SIE), and the Protection and Security Service (SPP).
Each agency does different things, working together to keep the country safe.
| Agency | Primary Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| SRI (Romanian Intelligence Service) | Domestic intelligence and security |
| SIE (Foreign Intelligence Service) | International intelligence gathering |
| SPP (Protection and Security Service) | Protection of high-ranking officials and security for critical infrastructure |

Knowing about these agencies helps us understand how surveillance works in Romania.
It’s important to know the laws and who does what to keep your online privacy safe.
Legal Framework Governing Online Surveillance in Romania
To understand online surveillance laws in Romania, we need to look at both local laws and EU rules.
The country’s laws on surveillance are based on its constitution, national security laws, and EU rules.
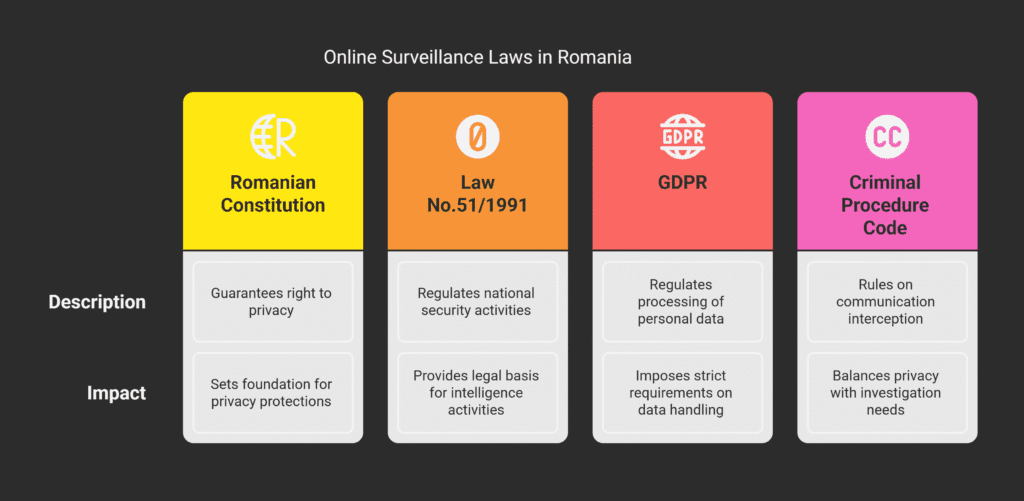
Romanian Constitution and Privacy Protections
The Romanian Constitution is key to understanding privacy rights.
Article 26 of the Constitution protects privacy.
This right is important for online surveillance laws.
National Security Laws
National security laws in Romania are important for online surveillance.
They balance national security with privacy rights.
Law No.51/1991 on National Security
Law No.51/1991 is a major law on national security. It sets rules for intelligence work, including online surveillance.
This law makes sure surveillance respects privacy rights.
Criminal Procedure Code Provisions
The Criminal Procedure Code has rules on communication interception.
This is a form of online surveillance.
It needs court approval to balance privacy with investigation needs.
European Union Regulations Applicable in Romania
As an EU member, Romania follows EU rules on online surveillance.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a big rule for personal data handling.
The GDPR has strict rules for personal data, including online surveillance.
Companies in Romania must follow these rules.
They must handle personal data in a way that is open, safe, and respects individual rights.
| Regulation | Description | Impact on Online Surveillance |
|---|---|---|
| Romanian Constitution | Guarantees the right to privacy | Sets the foundation for privacy protections in online surveillance |
| Law No.51/1991 | Regulates national security activities | Provides the legal basis for intelligence activities, including online surveillance |
| GDPR | Regulates the processing of personal data | Imposes strict requirements on the handling of personal data in online surveillance |
For more information on online surveillance laws in Romania, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Data Protection and Privacy Legislation in Romania
Romania’s data protection laws come from both national rules and EU regulations.
This has led to a detailed framework to safeguard personal data.
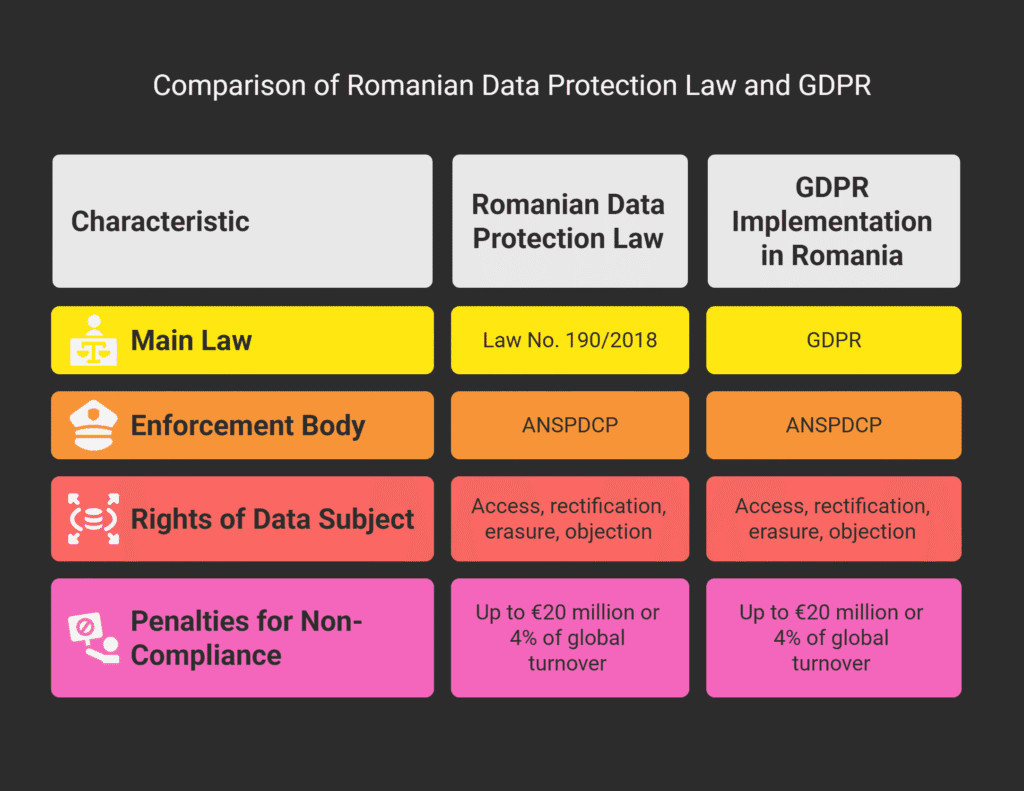
Romanian Data Protection Law
Romania has its own data protection law, working alongside the EU’s GDPR.
Law No. 190/2018 is the main law for data protection in Romania.
It makes sure Romanian laws match EU standards.
Key aspects of the Romanian Data Protection Law include:
- Establishing the National Supervisory Authority for the Processing of Personal Data (ANSPDCP);
- Defining the rights and obligations of data controllers and processors;
- Regulating the processing of personal data.
GDPR Implementation in Romania
Romania, as an EU member, has fully adopted the GDPR.
The GDPR sets a common data protection level across the EU.
Romania’s adoption ensures it meets these standards.
Local Enforcement Mechanisms
The ANSPDCP enforces data protection laws in Romania.
It looks into complaints, does audits, and can impose penalties for breaking the rules.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Companies that don’t follow data protection rules in Romania face big penalties.
The ANSPDCP can fine up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s global turnover, whichever is higher.
The following table summarizes the penalties for non-compliance with GDPR in Romania:
| Violation | Maximum Fine |
|---|---|
| Failure to implement adequate security measures | €10 million or 2% of global turnover |
| Non-compliance with data subject rights | €20 million or 4% of global turnover |
| Failure to report data breaches | €10 million or 2% of global turnover |
Rights of Data Subjects Under Romanian Law
Data subjects in Romania have several rights under the GDPR and national law, including:
- The right to access their personal data;
- The right to rectify or erase their personal data;
- The right to restrict or object to processing;
- The right to data portability.
For more information on data protection and privacy legislation in Romania, you can contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Legal Aspects of Online Surveillance in Romania: Permitted Practices
Romania has clear rules for online surveillance.
It’s important for people and businesses to know these rules.
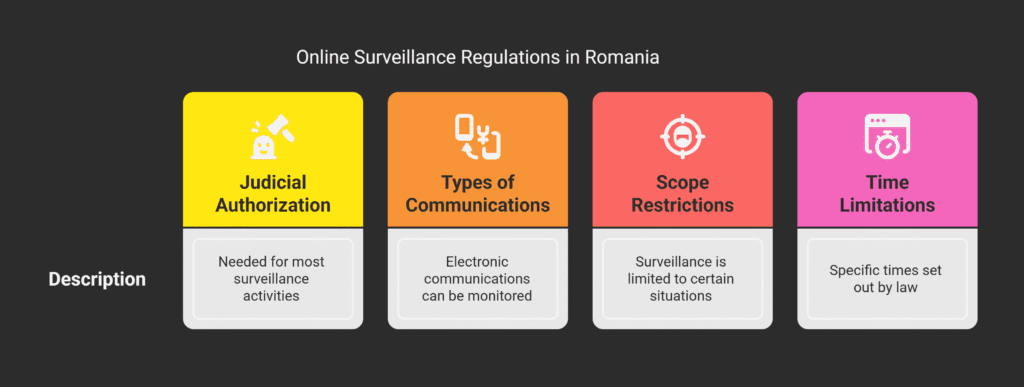
Lawful Interception Requirements
Lawful interception in Romania has strict rules.
To do surveillance, you must meet certain conditions.
Necessary Conditions for Surveillance
To start surveillance, you need judicial authorization.
This makes sure surveillance is legal and watched over.
- Judicial authorization is needed for most surveillance;
- The process checks the surveillance request carefully.
Types of Communications Subject to Monitoring
Many communications can be monitored, like electronic ones.
The law says which ones can be tapped.
Key aspects of lawful interception include:
- Electronic communications can be monitored;
- You need specific judicial authorization.
Judicial Authorization Process
The judicial authorization process is key in Romania’s surveillance laws.
It makes sure surveillance is legal and watched.
For more details on the judicial authorization process, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Judicial Authorization | Needed for most surveillance activities |
| Types of Communications | Electronic communications can be monitored |
| Scope Restrictions | Surveillance is limited to certain situations |
Time Limitations and Scope Restrictions
Surveillance in Romania has time limits and scope rules.
These rules make sure surveillance is fair and needed.
Knowing these rules is key for following the law.
The law sets out specific times and areas for surveillance.
Cybersecurity Regulations and Their Impact on Surveillance
The cybersecurity scene in Romania is changing fast.
New rules are shaping how we watch and record things.
Romania has set up a detailed plan to tackle cyber threats.
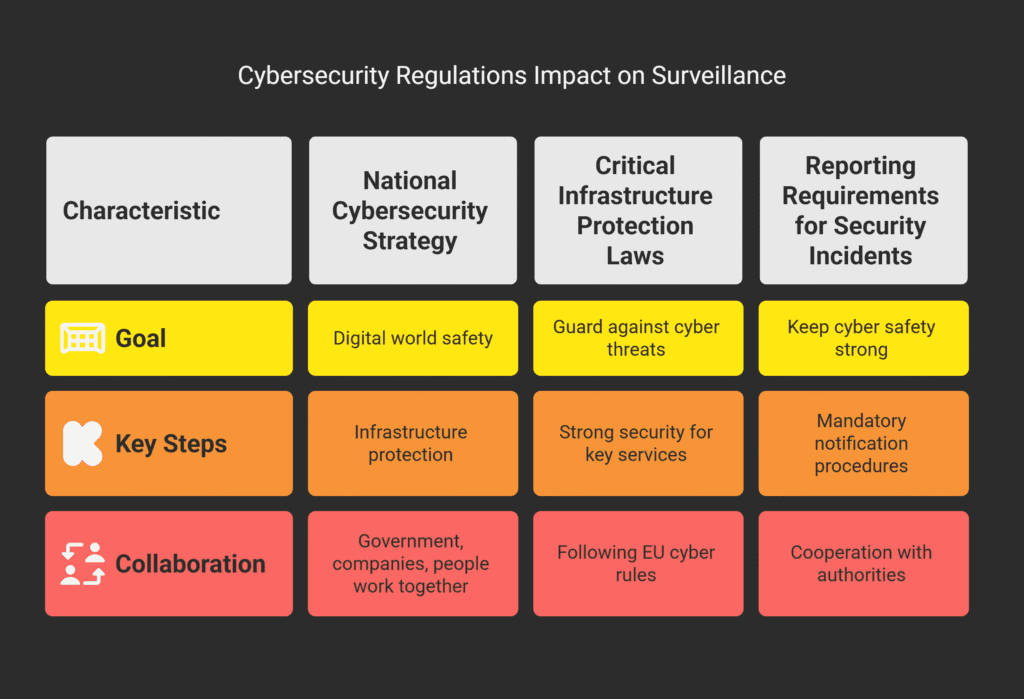
National Cybersecurity Strategy
Romania’s National Cybersecurity Strategy aims to keep its digital world safe.
It involves the government, private companies, and people working together.
Key parts of the strategy are:
- Protecting key infrastructure;
- Getting better at handling cyber attacks;
- Teaching everyone about staying safe online.
Critical Infrastructure Protection Laws
Keeping critical infrastructure safe is a big part of Romania’s cyber plan.
Laws are in place to guard against cyber threats.
Some key steps are:
- Using strong security for key services;
- Doing regular checks for risks;
- Following EU cyber rules..
Reporting Requirements for Security Incidents
Romania has rules for reporting cyber attacks quickly.
This helps keep the country’s cyber safety strong.
Mandatory Notification Procedures
Companies must tell the right people fast if they spot a cyber attack.
This quick action helps fix problems fast.
Cooperation with Authorities
Working well with authorities is key to handling cyber attacks.
It helps share info and learn from each other.
For more on cybersecurity laws in Romania and how they affect watching and recording, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Electronic Communications Monitoring: Legal Boundaries
In Romania, there are clear legal rules for monitoring electronic communications.
ISPs and users must follow these rules to stay legal.
Internet Service Provider Obligations
ISPs in Romania must work with law enforcement under certain rules.
They need to have the right setup to intercept communications legally when asked.
For more details on ISP duties and their impact, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Data Retention Requirements
Data retention is key in monitoring electronic communications.
ISPs must keep certain data for a set time.
Types of Data Subject to Retention
The data ISPs must keep includes:
- Subscriber information;
- Traffic data;
- Location data.
Storage Duration and Security Standards
Data is kept for 6 months to 2 years, depending on the type.
ISPs must follow strict security rules to keep data safe.
Encryption and Anonymity Regulations
Romania has rules on encryption and anonymity in online communications.
Encryption is usually okay, but there are times when decryption is needed by law.
Users have the right to stay anonymous, but this right can be limited.
This is true in cases like criminal investigations.
For advice on how these rules affect you, talk to legal experts in Romanian telecom law.
Practical Implications for Businesses and Individuals
It’s important for foreign companies to know about Romania’s online surveillance rules.
This knowledge helps them stay in line and avoid risks.
If you’re a business in Romania, you need to understand the country’s data protection and online surveillance laws.
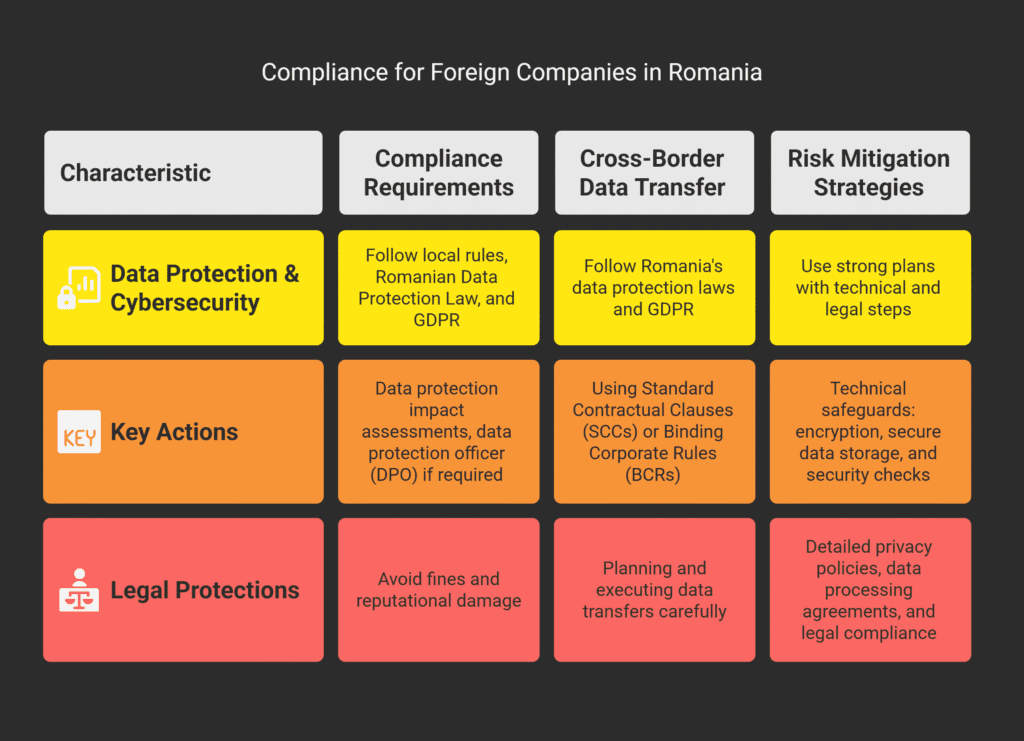
Compliance Requirements for foreign Companies Operating in Romania
Foreign companies in Romania must follow local data protection and cybersecurity rules.
This means they must stick to the Romanian Data Protection Law and the GDPR in Romania.
Following these rules is key to avoid big fines and harm to your reputation.
To meet these requirements, you should:
- Do regular data protection impact assessments;
- Use the right technical and organizational steps to keep data safe;
- Have a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if the law says you must.
Cross-Border Data Transfer Considerations
When moving data across borders, foreign companies must follow Romania’s data protection laws and the GDPR.
This might mean using Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) to protect data transfers.
Planning and executing cross-border data transfers carefully is essential for compliance.
You need to pick the best data transfer method for your business.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
To lower risks from online surveillance and data protection, foreign businesses in Romania should use strong risk mitigation plans.
These plans should include both technical and legal steps.
Technical Safeguards
Technical safeguards are key to protecting your business from data breaches and cyber threats.
Using encryption, secure data storage, and regular security checks can greatly reduce risks.
Legal Protections
Legal protections are also essential.
This includes having detailed privacy policies, data processing agreements, and making sure your business follows all relevant laws and regulations.
For more details on compliance and risk mitigation, reach out to a legal expert at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Your Rights and Protections Against Unlawful Surveillance
In Romania, you have rights that protect you from unwanted spying.
Knowing these rights is key to keeping your privacy safe.
Constitutional Safeguards
The Romanian Constitution has strong protections against spying.
Article 30 guards your freedom of speech.
Article 26 protects your right to privacy.
These laws are the foundation of Romania’s rules on surveillance.
Legal Remedies for Privacy Violations
If you think your privacy has been broken, you have legal options. You can go to court for help with privacy issues.
| Legal Remedy | Description |
|---|---|
| Judicial Recourse | Seeking legal action through the courts for privacy violations. |
| Complaint to National Data Protection Authority | Filing a complaint with the National Data Protection Authority for violations of data protection laws. |
How to File Complaints with Romanian Authorities
If you think your privacy has been broken, you can report it to the right Romanian authorities.
National Data Protection Authority Process
The National Data Protection Authority watches over data protection laws in Romania.
To report a problem, write or use their online portal.
Judicial Recourse Options
You can also go to court for help.
A judge will look at your case and decide.
For more on your rights against spying in Romania, email a Romanian lawyer at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Conclusion
You now know a lot about the laws that govern online surveillance in Romania.
The country’s laws on online surveillance, data protection, and cybersecurity are very important.
They shape how we use the internet.
Online surveillance laws in Romania are shaped by both national and European Union rules.
The data protection laws in Romania follow the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This means people’s personal data is well-protected.
Cybersecurity laws in Romania focus on keeping critical infrastructure safe and ensuring secure online communication.
If you’re doing business or living in Romania, it’s key to understand these laws.
This helps you stay in line with regulations and protect your rights.
For more details or help with these laws, you can reach out to the Romanian lawyers at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
