Romania’s Administrative Fines: What You Need to Know Before You Pay
Romania’s Administrative Fines: What You Need to Know Before You Pay
Ever get a notice to pay for a rule you didn’t know about?
Dealing with fines can be tough, even more so if you don’t know the rules.
In Romania, fines follow rules set by Government Ordinance No. 2/2001.
This law outlines what fines are for and how much they cost.
It’s very important for both people and businesses in the country to understand this.
The way fines work in Romania has changed a lot.
Now, fines are the main way authorities make sure everyone follows the rules.
This is a big change from when fines were mostly for serious crimes.
If you get a fine, knowing your rights can help a lot.
The rules tell you how to figure out, pay, and even fight fines that seem unfair.
In this guide, you’ll learn all you need to know about fines in Romania.
This is true whether you live, work, or run a business here.
Key Takeaways
- Government Ordinance No. 2/2001 establishes the framework for contraventional offenses in Romania;
- Administrative penalties evolved from being part of the Criminal Code to administrative law;
- Understanding the regulatory framework is essential for both individuals and businesses;
- Legal sanctions serve as enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance with regulations;
- Specific procedures exist for calculation, payment, and contesting administrative fines;
- Knowing your rights regarding regulatory penalties can save time, money, and stress.
Understanding Romania’s Administrative Fines
Getting to know Romania’s fine system is key.
It’s based on laws and the groups that enforce them.
If you live or work in Romania, you might face Romanian administrative sanctions.
These fines are different from criminal penalties and help keep things in order.
Definition and Legal Basis
In Romania, fines for small mistakes are called contraventional sanctions.
They’re not as serious as crimes.
The rules for these fines come from Government Ordinance No. 2/2001.
This ordinance says a contravention is a small mistake done on purpose or by accident.
It must be listed as a contravention in the law. And it’s not as big of a deal as a crime.
These fines are meant to help people follow the rules, not to punish them.
They’re not like criminal fines.
Instead, they aim to fix the problem and make sure everyone follows the rules.
There are also laws for specific areas that add to the main rules.
These laws list what’s wrong and what the fines are for those mistakes.
Key Regulatory Authorities in Romania
Many government groups watch over the rules and give out Romanian corporate compliance fines when needed.
Each group looks after a certain area.
The National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) checks on the market and protects consumers.
They deal with unsafe products, false ads, and unfair business practices.
They focus on businesses that don’t follow the rules for consumers.
The National Environmental Guard and local agencies handle environmental issues.
They make sure companies follow the rules about pollution and waste.
Breaking these rules can lead to big fines.
The Labor Inspectorate (Inspecția Muncii) looks after work places.
They make sure employers follow the rules about safety, fair pay, and working hours.
If employers don’t follow these rules, they can face big fines.
Tax authorities, like the National Agency for Fiscal Administration (ANAF), deal with tax issues.
They handle things like not reporting income or keeping bad records.
This can lead to fines and extra taxes.
Local police and special teams enforce local rules and handle small public order issues.
They deal with things like noise, unauthorized building, and breaking local rules.
Knowing who to talk to when you get a fine in Romania is important.
Each group has its own way of doing things, but they all follow the main rules set by Government Ordinance No. 2/2001.
Common Types of Administrative Violations in Romania
Knowing the common administrative infractions in Romania can save you from big fines and legal trouble.
The country has rules for both businesses and individuals.
Knowing these rules helps you stay compliant and avoid penalties.
Corporate and Business Infractions
Businesses in Romania must follow strict rules to avoid Romanian corporate fines.
These fines help keep businesses in line and protect everyone involved.
Labor law violations are a big problem.
Issues like bad employment contracts, too many working hours, and safety problems are common.
The Romanian Labor Inspectorate checks these and fines can be from 1,500 to 20,000 RON.
Consumer protection infractions are also a big deal.
This includes false ads, unfair contracts, and not honoring warranties.
The National Authority for Consumer Protection is getting tougher on these issues.
Tax reporting mistakes are a top concern for Romanian authorities.
This includes late tax filings, wrong revenue reports, and VAT issues.
These mistakes can lead to fines and extra taxes with penalties.
| Business Infraction Type | Regulatory Authority | Typical Fine Range (RON) | Common Examples |
| Labor Law Violations | Labor Inspectorate | 1,500 – 20,000 | Undocumented workers, safety violations |
| Consumer Protection | ANPC | 2,000 – 50,000 | Misleading advertising, unfair terms |
| Tax Compliance | ANAF | 5,000 – 100,000 | Late filings, incorrect reporting |
| Environmental | Environmental Guard | 30,000 – 80,000 | Waste disposal violations, emissions |
Individual Administrative Offenses
People in Romania face their own set of rules that can lead to fines.
Knowing these can help you avoid trouble.
Traffic violations are a big issue.
This includes speeding, illegal parking, and not wearing seatbelts.
Fines can be from 290 to 2,900 RON, with serious cases leading to losing your license.
Public disturbance offenses are another common problem.
This includes loud noise, bad waste disposal, and acting out in public.
Local police can fine you from 100 to 500 RON for these.
Age matters when it comes to fines in Romania.
Kids under 14 can’t be fined.
Those 14 to 18 face smaller fines than adults, showing Romania’s approach to responsibility.
GDPR and Data Protection Violations
With the GDPR in place, data protection is a big deal in Romania.
Both businesses and public bodies must follow strict rules to avoid fines.
Processing data without permission is a serious mistake.
This includes collecting data without consent, using it for the wrong reasons, or keeping it too long.
The National Supervisory Authority for Personal Data Processing can fine up to 20 million euros or 4% of global turnover for the worst cases.
Not telling people about data breaches fast enough is another big no-no.
Companies must tell the authority and those affected within 72 hours if data is at risk.
Not protecting data well enough is also a big problem.
Companies must have good security measures to keep data safe, based on the risk involved.
Not respecting people’s data rights is another common issue.
This includes not giving access to data, not fixing wrong data, erasing data, and not letting people take their data with them.
Companies must respond to these requests within a month, with some exceptions.
Knowing about these common violations helps with business risk management and personal compliance in Romania.
By spotting problems before they happen, you can avoid fines and protect your business’s reputation.
The Romanian Regulatory Framework
Romania has a detailed legal system for handling administrative offenses.
It combines general rules with specific ones for different areas.
Knowing these rules is key for businesses and residents, as they cover everything from traffic rules to corporate rules.
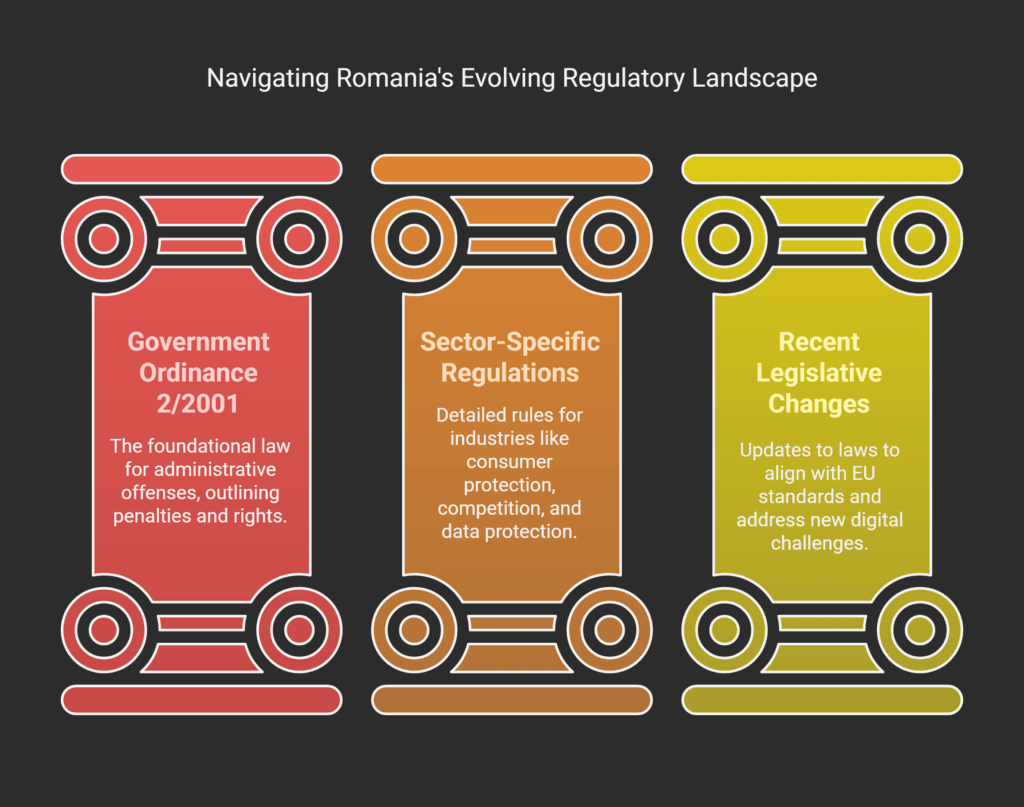
Government Ordinance No. 2/2001
At the heart of Romania’s administrative offenses legislation is Government Ordinance No. 2/2001.
It’s the main law for handling contraventions.
This ordinance is as important as laws passed by parliament, but it comes from the government.
GO 2/2001 sets up three main types of punishments for contraventions:
- Warnings (verbal or written cautions);
- Contraventional fines (monetary penalties);
- Community service (remedial work for the public benefit).
This ordinance makes contraventions a separate category from crimes.
It outlines how fines are given, sets rules for penalties, and protects the rights of those facing charges.
Sector-Specific Regulations
While GO 2/2001 is the base, many specific rules add complexity to the Romanian regulatory framework.
These rules cover different industries and activities.
Traffic laws, for example, have detailed rules on driving and vehicle requirements.
Consumer protection laws set rules for businesses on product safety and advertising.
| Sector | Primary Legislation | Key Regulatory Authority | Common Violations |
| Consumer Protection | Law No. 296/2004 | National Authority for Consumer Protection | Misleading advertising, unfair contract terms |
| Competition | Law No. 21/1996 | Competition Council | Cartel formation, abuse of dominant position |
| Data Protection | Law No. 190/2018 | National Supervisory Authority | GDPR violations, data breaches |
| Environmental | GEO No. 195/2005 | Environmental Guard | Pollution, waste management failures |
Environmental laws are strict about pollution and waste.
The GDPR compliance fines in Romania can be up to 4% of global turnover for big violations.
Financial laws, overseen by the National Bank of Romania and the Financial Supervisory Authority, have their own penalties.
These rules work with GO 2/2001 for matters not covered in specific laws.
Recent Legislative Changes
Romania’s fine system has changed a lot in recent years.
Fine amounts have gone up in many areas, showing a focus on stopping violations.
In 2021, changes to GO 2/2001 gave more rights to those accused of offenses.
New EU rules have also led to updates in areas like unfair competition and consumer protection.
The rise of digital services has brought new violations, like in ecommerce and online marketing.
Romania has updated laws to handle these new challenges.
Romania’s laws are getting closer to EU standards, making it easier for businesses in Europe.
This means new rules but also a more stable environment for international companies.
It’s important to keep up with these changes to avoid fines.
Romania’s laws are always evolving, so staying informed is key for everyone.
How Administrative Fines Are Calculated and Imposed
Knowing how Romanian authorities set and apply fines is key for individuals and businesses.
The Romanian legal system has a clear method to make sure fines match the violation’s severity.
This helps you understand and avoid risks, and prepare for compliance.
Penalty Assessment Criteria
Romanian agencies look at several factors to decide on fines.
These penalty assessment criteria make sure fines are fair based on the violation’s impact.
The main things considered are:
- The seriousness of the violation and its impact;
- If the violation was intentional or by mistake;
- The offender’s history of following rules;
- The economic gain from the violation;
- The harm caused to others or public interests.
Fines are set based on the violation’s seriousness.
For example, a small paperwork mistake gets a lower fine than a serious violation.
Also, extra sanctions might be added based on the violation’s severity.
It’s important to know that for one offense, there’s one main penalty and one or more extra sanctions if needed.
Fine Calculation Methods

The fine calculation methods in Romania follow strict rules.
The system sets both a minimum and a maximum for fines, guiding how fines are applied.
The smallest fine for any violation is 25 lei (about 6 Euros).
But, the maximum fine varies based on who set the rule:
| Authority Level | Maximum Fine (Lei) | Maximum Fine (Euros) | Typical Application | Legal Basis |
| Law or Government Ordinance | 100,000 | 25,000 | Serious national violations | Primary legislation |
| Government Decision | 50,000 | 12,500 | Significant regulatory breaches | Secondary legislation |
| County Authorities | 5,000 | 1,250 | Regional administrative violations | County regulations |
| Municipal/Communal Authorities | 2,500 | 600 | Local ordinance violations | Local council decisions |
For repeat offenders, fines get higher with each offense.
Young offenders (ages 14-18) usually get lower fines than adults for the same violations.
Notification Process
After finding a violation and calculating the fine, Romanian authorities send a formal notice.
This step is key in administrative proceedings and must follow legal rules.
The notice, called a “Proces-Verbal de Contravenție” (contravention report), must include important details:
- The date, time, and place of the violation;
- A detailed description of the violation;
- The laws broken;
- The fine amount and how to pay;
- Info on appealing and deadlines;
- Details of the offender and the authority.
This document is usually given in person at the time of the violation.
If not possible, it’s sent by registered mail with proof of delivery.
You have the right to receive this notice within 30 days of the violation being found.
The notice will tell you when to pay the fine, usually 15 days after getting it.
You can either pay the fine or contest it legally during this time.
Ignoring this can lead to more penalties and actions.
Knowing about assessment criteria, calculation methods, and the notification process helps you understand Romania’s fine system.
This knowledge helps you avoid penalties and follow Romanian laws correctly.
The Payment Process for Romanian Administrative Fines
When you get an administrative fine in Romania, knowing how to pay it is key.
It saves you money and avoids legal trouble.
Romania has clear steps for paying fines, important for both individuals and businesses.
The Romanian system has standard payment ways and chances for lower payments.
But, these benefits need you to follow the rules on time.
Let’s look at how to handle administrative sanctions in Romania.
Payment Deadlines and Options
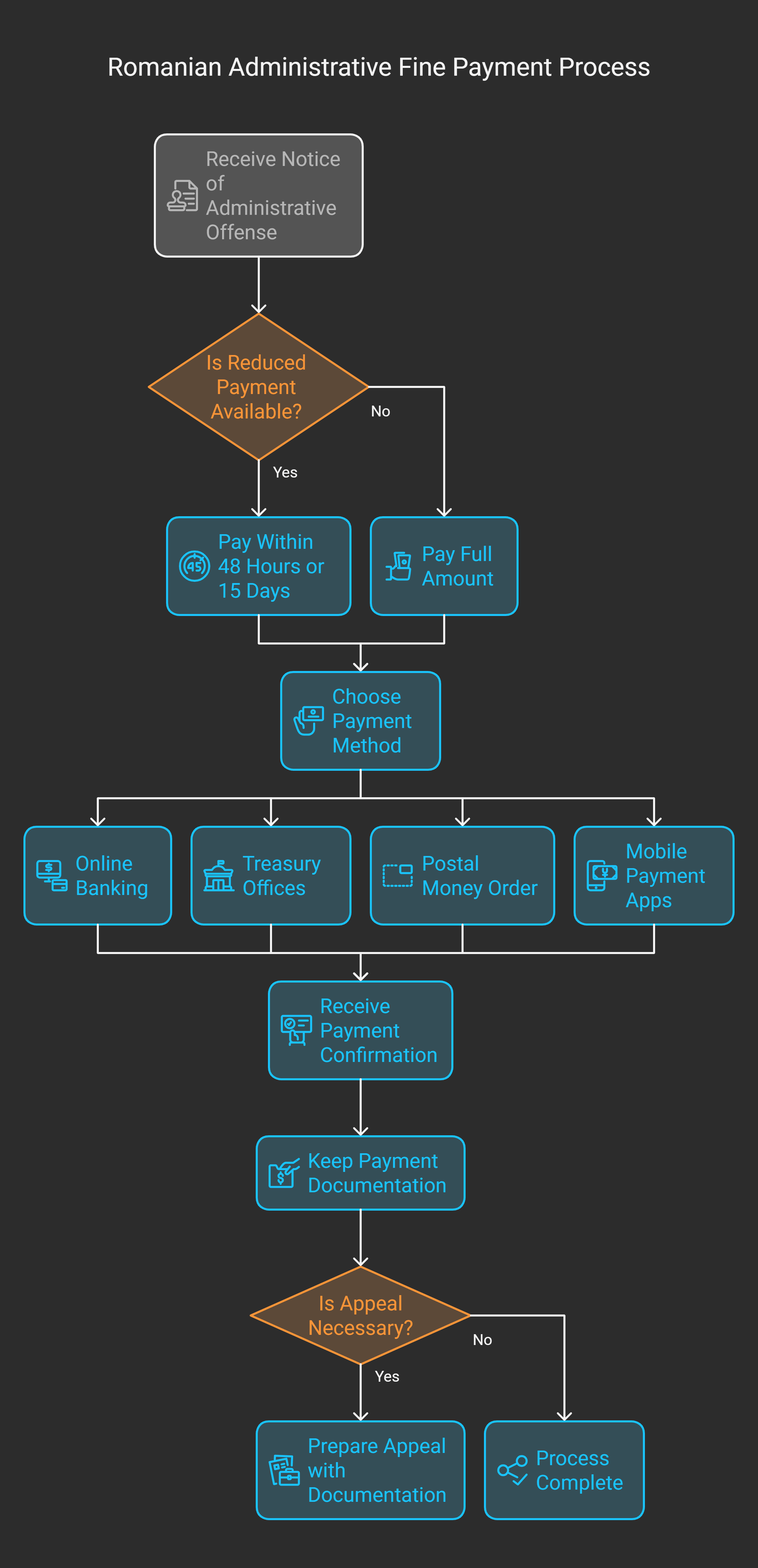
When you get a notice of an administrative offense, you have 15 to 30 days to pay.
The exact time depends on the violation and who issued it.
Always check the deadline on your notice to avoid trouble.
Romania has many ways to pay penalty fees.
You can use online banking, visit a bank, send a postal money order, or use mobile apps.
Each method has its own time, which might affect your deadline.
If you miss the payment deadline, the authorities can take action.
They might take your money directly from your accounts.
This can add extra fees and interest, making the fine even higher.
| Payment Method | Processing Time | Advantages | Documentation Provided |
| Online Banking | 1-2 business days | Convenient, accessible 24/7 | Electronic receipt, transaction ID |
| Treasury Offices | Immediate | Official confirmation, guidance available | Official stamped receipt |
| Postal Money Order | 3-5 business days | No bank account needed | Postal receipt with tracking number |
| Mobile Payment Apps | 1-3 business days | Convenience, digital record | Digital receipt, confirmation code |
Reduced Payment Opportunities
Romanian law gives big savings for quick payment of fines.
For many fines, you can pay half the amount if you pay within 48 hours or 15 days.
This depends on the type of violation.
Not all fines offer this chance.
Minor and some moderate infractions qualify, but serious ones don’t.
Your notice will say if you can pay less.
To get the reduced payment, follow the steps in your notice carefully.
Use the right payment details and pay on time.
Any mistake or delay means you can’t get the reduced payment.
Documentation Requirements
Keeping the right documents is key when dealing with fines in Romania.
Always save the original notice.
It has important details about the fine, payment, and deadlines.
After paying, keep all payment receipts safe.
Include the date, amount, payment reference, and confirmation from the authority.
For online payments, save electronic receipts and bank statements.
For in-person payments, ask for a stamped receipt.
Documentation is vital if you need to appeal a fine or if there’s a payment mistake.
Romanian authorities might not always record payments correctly.
Having all your documents ready helps solve problems fast and avoids legal trouble.
If you’re a business, organize all fine-related documents well.
This includes letters from authorities, payment records, and any supporting evidence.
Good organization helps with penalty appeals and shows you’re following the law.
Contesting Administrative Fines in Romania
If you get an administrative fine in Romania, you can fight it under certain conditions.
The legal system in Romania uses civil procedure for these challenges.
But, some fines might need criminal law if they seem too harsh.
Knowing your rights and the right steps can really help your appeal.

Legal Grounds for Appeals
There are several good reasons to appeal an administrative fine in Romania.
It’s important to know which one fits your situation best.
Procedural errors are a common reason.
This includes wrong notices, wrong info, or not following due process when the fine was given.
Also, if the fine report got the facts wrong, you can appeal.
If you have evidence that shows the report was wrong, you can use it to challenge the fine.
Another reason is if the fine is too big for the crime.
Romanian laws say fines should match the crime.
If your fine seems too high, you can appeal based on this.
The European Court of Human Rights has set important rules for fines in Romania.
They’ve said Romania can’t ignore the idea that you’re innocent until proven guilty.
These rules help if you’re appealing because of rights issues.
The Appeals Process Timeline
Time is key when you’re appealing a fine in Romania.
You have 15 days from when you get the fine notice to appeal.
If you miss this, you can’t appeal anymore.
The appeal process has a clear schedule:
1. Within 15 days of getting the notice: Send your appeal in writing to the fine issuer or the court.
2. Within 5 days after you send it: The court will register your appeal and give it a number.
3. 20-30 days later: You’ll have your first court hearing (estimated).
4. 1-3 months: The first court decision will take this long, depending on the case (estimated).
5. Within 30 days of the first decision: You can appeal to a higher court if you need to (estimated).
For simple cases, the whole process can take 3-6 months.
But, if it’s more complicated, it might take longer.
Required Documentation for Appeals
Having the right documents is key for a good appeal.
Get everything ready before you start.
This will help your case and avoid delays.
Here’s what you need for an appeal in Romania:
| Document Type | Purpose | Required Copies | Special Requirements |
| Original Fine Notification | Shows why you’re appealing | 1 original + 2 copies | Must include all pages and attachments |
| Written Appeal Statement | Explains why you’re appealing | 3 copies | Must say what you want to happen |
| Supporting Evidence | Backs up your appeal | 3 copies of each document | Translated if not in Romanian |
| Power of Attorney | Allows someone to represent you | 1 original + 2 copies | Notarized if represented by attorney |
| Proof of Payment (court fees) | Shows you’ve paid to appeal | 1 original + 2 copies | Fee amount varies by fine value |
Your appeal statement should clearly say why you’re appealing.
Include any witness statements that support your side, if you’re questioning the facts of the violation.
Reports from experts can be very helpful, too.
They’re good for fines in areas like construction or environmental rules.
These reports give a third view that courts often find convincing.
When you appeal, you can send it to the fine issuer or the court.
For most fines, you should appeal to the local court (Judecătoria) where the fine was given or where you live.
Remember, all documents must be in Romanian or have a certified translation if they’re not.
Consequences of Non-Payment
Not paying Romanian administrative fines can lead to bigger problems.
You could face more penalties, legal actions, and even disruptions to your business.
It’s important to manage risks in Romania well, whether you’re an individual or a company.
The Romanian legal system is strict about fines.
They have rules to make sure everyone follows the law.
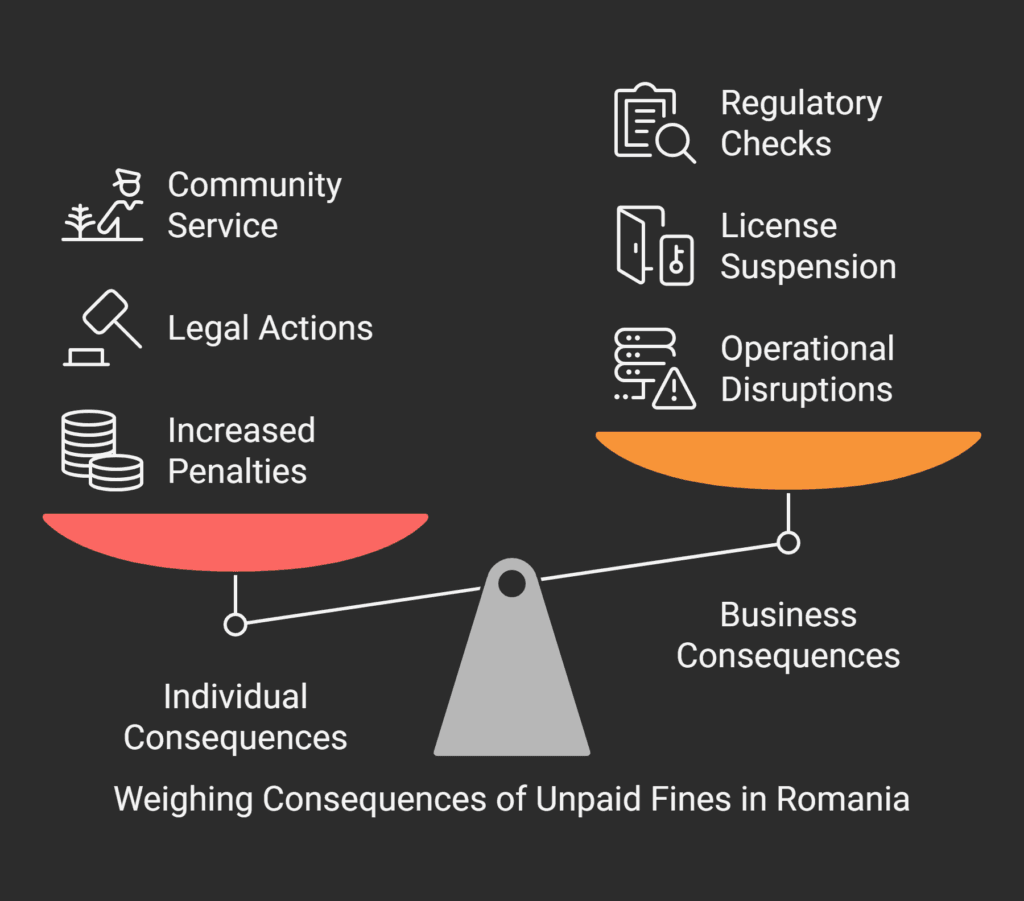
Legal Enforcement Actions
If you don’t pay your fine in 30 days, Romanian regulatory authorities will start legal actions.
They will send you a writ of execution.
This is the first step in enforcing the fine.
Authorities have several ways to enforce fines:
- They can seize your property, both movable and immovable.
- They can take money directly from your wages.
- They can freeze your bank accounts and take money from them.
- They can make you do community service instead of paying the fine.
If you can’t pay the fine and don’t have property, you can ask the court for community service.
You can also ask for more time to pay the fine at your first court appearance.
Doing community service can mean up to 300 hours of work.
Before, you had to agree to this.
But now, the court can decide it’s necessary to enforce the law.
Additional Penalties and Interest
Not paying your fine adds more costs.
You’ll have to pay interest every day.
The rate depends on the type of fine.
These extra costs can add up:
- Penalties for late payment get higher over time.
- There are costs for the enforcement officers.
- You’ll have to pay court fees for the enforcement process.
- Legal fees if you fight the enforcement in court.
For example, a 5,000 RON fine can grow to over 7,500 RON in six months.
This is a 50% increase. Paying on time is usually the best option.
Impact on Business Operations
Unpaid fines can hurt businesses a lot.
They can disrupt operations and affect your reputation.
Romania’s corporate governance requires following the law, including paying fines on time.
Businesses that ignore fines might face:
- Their licenses or permits could be suspended or taken away.
- They might not be able to get government contracts.
- They could face more checks from regulators.
- They might be listed as non-compliant in public records.
- They could lose clients and partners because of bad publicity.
Financial institutions are hit hard too.
Unpaid fines for anti-money laundering or other financial rules can lead to more checks.
This includes more audits, programs to fix problems, and more reports.
Companies should have plans for dealing with fines.
This can stop small problems from becoming big issues.
It’s part of following Romanian business regulations.
Ignoring fines can hurt your business’s credit score, relationships with suppliers, and even employee morale.
For companies outside Romania, ignoring fines can make dealing with Romanian authorities harder in the future.
Compliance Strategies to Avoid Romanian Administrative Fines
Businesses in Romania need to be proactive about following the rules.
The rules are getting more complex, and companies must find ways to avoid fines.
It’s cheaper and better for your reputation to prevent problems than to fix them after they happen.
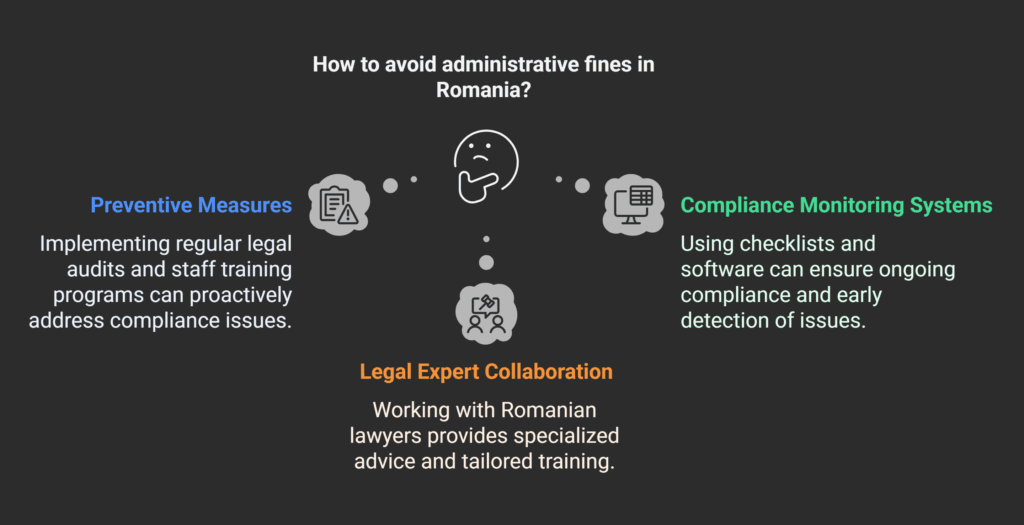
Preventive Measures for Businesses
Start by knowing what laws you must follow.
Regular legal audits help find and fix problems before they become big issues.
These audits check if your business is following the latest laws.
Make clear rules for your team based on Romanian laws.
These rules should cover specific areas and be updated when laws change.
Staff training programs are key to avoiding fines.
Make sure your team knows the basics and the specific rules for their jobs.
Training should happen often, like when laws change or new people join.
Keep up with new laws in Romania.
Sign up for updates from the government and industry groups.
This way, you’ll know about changes that might affect your business.
Compliance Monitoring Systems
Use strong systems to check if you’re following the rules.
Compliance checklists are a good way to make sure you’re doing things right.
They should be easy to use but cover all important points.
Do regular checks to find and fix problems early.
Look at both your documents and how things are done to make sure they match the laws.
Use software to help with monitoring.
It can check things automatically and alert you to any problems.
This is really helpful for keeping up with Romania’s changing rules.
Make it easy for employees to report any issues.
A culture that encourages openness helps find problems early, when they’re easier to fix.
Keep good records of your compliance efforts.
This is important if someone says you’re not following the rules.
Keep track of training, policy updates, and any fixes you’ve made.
Working with Legal Experts in Romania
Working with Romanian lawyers can really help.
They know the local laws well and can give advice that fits your business.
Legal experts can do special audits to find and fix problems before they cost you money.
They often spot things that regular checks miss.
They can also create training that’s just right for your business.
This kind of training is usually more effective than general courses.
Good legal advisors in Romania offer practical solutions that work for your business.
Work closely with your legal team all the time, not just when you have a problem.
Regular talks help keep your business in line with the rules as they change.
This is really important for dealing with Romania’s complex rules.
By following these strategies, your business can avoid fines and run smoothly in Romania.
Remember, staying on top of compliance is an ongoing job that needs constant attention and changes as the rules do.
International Context: Romania vs. EU Administrative Penalties
It’s important to know how Romania’s fines compare to other EU countries.
Romania’s EU membership has shaped its rules, but it also keeps its own way of handling fines.
This helps you understand Romania’s place in the EU’s rules better.
Comparative Severity of Romanian Fines
Looking at administrative sanctions in Romania shows some patterns.
In some areas, Romania’s fines are not as high as Western Europe’s.
But in others, they can be strict.
In data protection, Romania’s fines for GDPR breaches are lower than France or Germany’s.
But, Romania has been getting tougher, with more investigations.
For environmental rules, penalties in Romania are about average in the EU.
But how they enforce these rules can vary.
Romania’s fines for pollution are similar to Hungary and Bulgaria’s but less than Austria or Sweden’s.
| Regulatory Area | Romania (Average Fine) | Western EU (Average Fine) | Eastern EU (Average Fine) |
| Data Protection | 10,000-20,000 EUR | 50,000-200,000 EUR | 5,000-15,000 EUR |
| Consumer Protection | 2,000-10,000 EUR | 15,000-50,000 EUR | 1,000-8,000 EUR |
| Environmental | 5,000-50,000 EUR | 25,000-100,000 EUR | 3,000-30,000 EUR |
| Labor Law | 1,500-7,500 EUR | 10,000-40,000 EUR | 1,000-5,000 EUR |
One key thing about government fines in Romania is the process.
While fines might be lower, the rules can be stricter.
This includes shorter appeal times and more detailed paperwork.
EU Harmonization Efforts
The EU wants all countries to have similar rules for fines.
This helps businesses in different countries know what to expect.
Romania has followed EU rules in areas like consumer protection and financial services.
For example, it adopted a new law on unfair business practices in 2018.
But, how strictly these rules are enforced can vary.
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) has also played a big role.
It says some fines in Romania are like criminal penalties.
This means certain rights must be respected, even if the fine is called administrative.
This includes the right to a fair trial, being presumed innocent, having a lawyer, and seeing witnesses.
Romania’s Competition Council has started to follow these rules more closely.
This means better protection during investigations.
This process of making rules more similar is both a challenge and an opportunity.
It might make things more complicated for a while.
But in the long run, it should make things clearer for everyone.
Knowing about these international aspects is key to dealing with Romania’s fine system.
As Romania works to meet EU standards, staying up to date is important.
This helps you avoid fines and stay on the right side of the law.
Conclusion
Understanding Romania’s fine system is key for businesses and individuals.
Government Ordinance No. 2/2001 sets the rules for fines.
This knowledge helps you handle fines better.
Paying fines on time can lower the cost.
You can also appeal if a fine was wrongly given.
Keeping good records is your strongest defense.
Using smart compliance strategies can prevent fines.
By taking steps to avoid violations, businesses can save a lot.
This is cheaper than paying fines later.
For complex rules, get help from a Romanian administrative law expert.
A good law firm knows the system well.
They can guide you through it, even as Romania meets EU standards.
Whether you run a business or are an individual, a Bucharest lawyer is very helpful.
They know local laws and EU rules. Many law offices also do audits to find and fix problems before fines are issued.
Stay up to date with rules and get help when you need it.
This way, you can deal with Romania’s fine system well.
And you’ll reduce your chances of getting fined.
FAQ
What is an administrative fine in Romania?
An administrative fine in Romania is a fine for minor offenses.
It’s not as serious as a criminal act.
These fines are based on Government Ordinance No. 2/2001.
They are for breaking laws or decisions made by the government or local councils.
Which authorities can issue administrative fines in Romania?
Many bodies in Romania can give out fines.
This includes the National Authority for Consumer Protection (ANPC) and environmental agencies.
Also, labor inspectorates, tax authorities (ANAF), and local police can issue fines.
Each one deals with different types of violations.
What are the most common business violations that result in administrative fines?
Businesses often face fines for labor law issues and unfair practices.
They can also get fined for not following consumer protection laws or tax rules.
Environmental and GDPR breaches, as well as competition law issues, are also common.
Not having the right licenses can lead to fines too.
What are the typical administrative violations for individuals in Romania?
Individuals might get fined for traffic offenses or disturbing the peace.
Not reporting personal status changes is also a violation.
Minor property issues and littering can lead to fines.
Local ordinances are another area where fines can be given.
How are administrative fine amounts determined in Romania?
The amount of a fine depends on several things.
This includes how serious the offense is and if it was intentional.
The offender’s history and any benefits from the violation also play a part.
There are minimum and maximum fines based on who made the rule.
What is the deadline for paying an administrative fine in Romania?
You usually have 15 days to pay a fine. But this can change based on the rule broken.
If you don’t pay on time, the fine can be collected by the authorities.
This might cost you more money.
Can I pay a reduced amount for an administrative fine in Romania?
Yes, you can pay less for many fines.
You can pay half the minimum fine within 48 hours or 15 days.
This chance is available for many fines but not all.
You need to pay on time and keep proof of payment.
What payment methods are available for administrative fines in Romania?
There are several ways to pay fines in Romania.
You can use online platforms, bank transfers, postal money orders, or pay in person.
The details for payment will be on your fine notice.
Always save your payment receipt.
What are valid grounds for appealing an administrative fine in Romania?
You can appeal a fine for several reasons.
This includes mistakes in the fine notice or if the fine is too high.
You can also appeal if there’s no legal basis for the fine.
The European Court of Human Rights has also set rules for fair fines.
What is the process for contesting an administrative fine in Romania?
To appeal a fine, you need to file a complaint within 15 days.
You’ll need the fine notice and any evidence you have.
The court will hold a hearing.
You can represent yourself or get a lawyer.
You can appeal the court’s decision to a higher court within 30 days.
What happens if I don’t pay an administrative fine in Romania?
If you don’t pay, the authorities can take action.
They might seize your property or garnish your wages.
You could also be ordered to do community service.
Unpaid fines can also cost you more money.
Can administrative fines in Romania be converted to community service?
Yes, fines can be turned into community service.
The court can order up to 300 hours of service.
This is usually based on the minimum wage.
It’s a way to avoid paying the fine.
How can businesses prevent administrative fines in Romania?
Businesses can avoid fines by being proactive.
They should check their compliance regularly and train staff.
They should also have systems in place to monitor and report any issues.
Working with legal experts is also helpful.
Keeping records of compliance efforts is important.
How do Romania’s administrative fines compare to those in other EU countries?
Romania’s fines vary compared to other EU countries.
For GDPR, Romania’s fines are often lower.
But for consumer and environmental issues, fines can be higher.
Romania is trying to align its fines with EU standards.
The European Court of Human Rights has also influenced Romania’s approach to fines.
Are there special provisions for foreign individuals or companies facing administrative fines in Romania?
Foreigners face the same fine system as locals.
But they might find it harder due to language barriers.
Foreign companies should have a local representative.
Enforcement against foreign entities might involve extra steps.
What documentation should I keep related to an administrative fine in Romania?
Keep all documents related to a fine.
This includes the fine notice, any evidence, payment proof, and court documents.
Keep these for at least 5 years.
They might be needed to prove payment or to address any errors.