Data Protection Meets AI: GDPR Compliance When Using AI in Romania
The digital transformation in Romania brings new challenges for companies using artificial intelligence.
The country’s data protection laws create a complex regulatory landscape.
This demands careful navigation from organizations.
The National Authority for Personal Data Processing and Supervision (ANSPDCP) oversees these critical requirements.
The 2024-2027 National AI Strategy, approved by the Romanian Government, sets new priorities for technology governance.

Companies must balance innovation with strict regulatory adherence.
Romania’s artificial intelligence legal framework continues to evolve, influenced by EU directives.
Professional guidance is essential for businesses seeking sustainable solutions.
For expert consultation, organizations can contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
A qualified Romanian lawyer can offer tailored strategies for successful implementation. Our team ensures full regulatory adherence.
Key Takeaways
- Romania relies on EU frameworks while developing specific AI legislation through its 2024-2027 National Strategy,
- ANSPDCP compliance requirements govern data protection obligations for AI implementation,
- The EU AI Act provides legal definitions that will be applied within Romanian jurisdiction,
- Organizations need professional legal guidance to navigate complex regulatory requirements,
- Current data protection laws must be carefully balanced with emerging AI regulations,
- Romanian law firms offer specialized expertise for technology compliance matters.
Romania’s Data Protection Legal Landscape for AI Technologies
The legal framework for AI in Romania blends European standards with national rules.
This setup outlines clear duties for companies using AI to process personal data.
Romanian businesses must grasp how these laws shape their AI strategies.
Three main pillars form this framework.
They include GDPR implementation, national oversight, and EU AI Act integration.
Each pillar adds vital elements to the compliance structure.

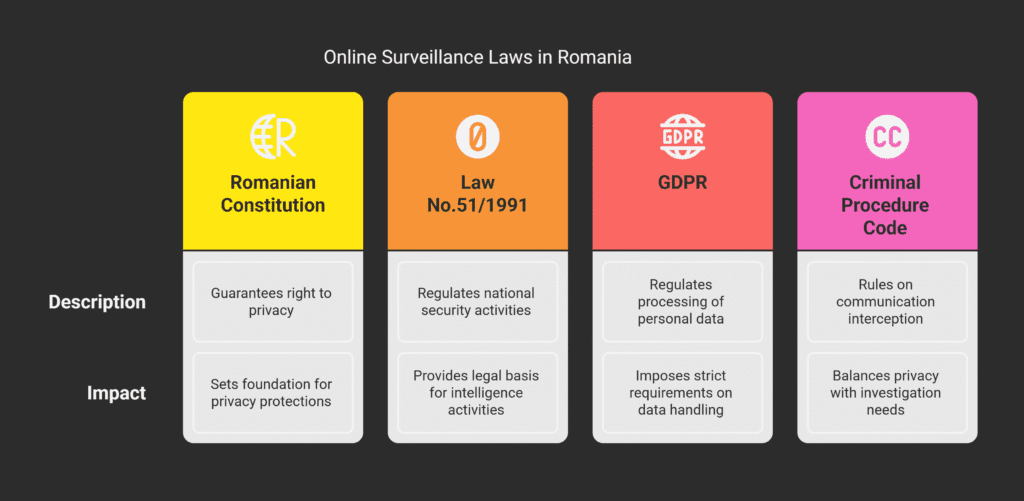
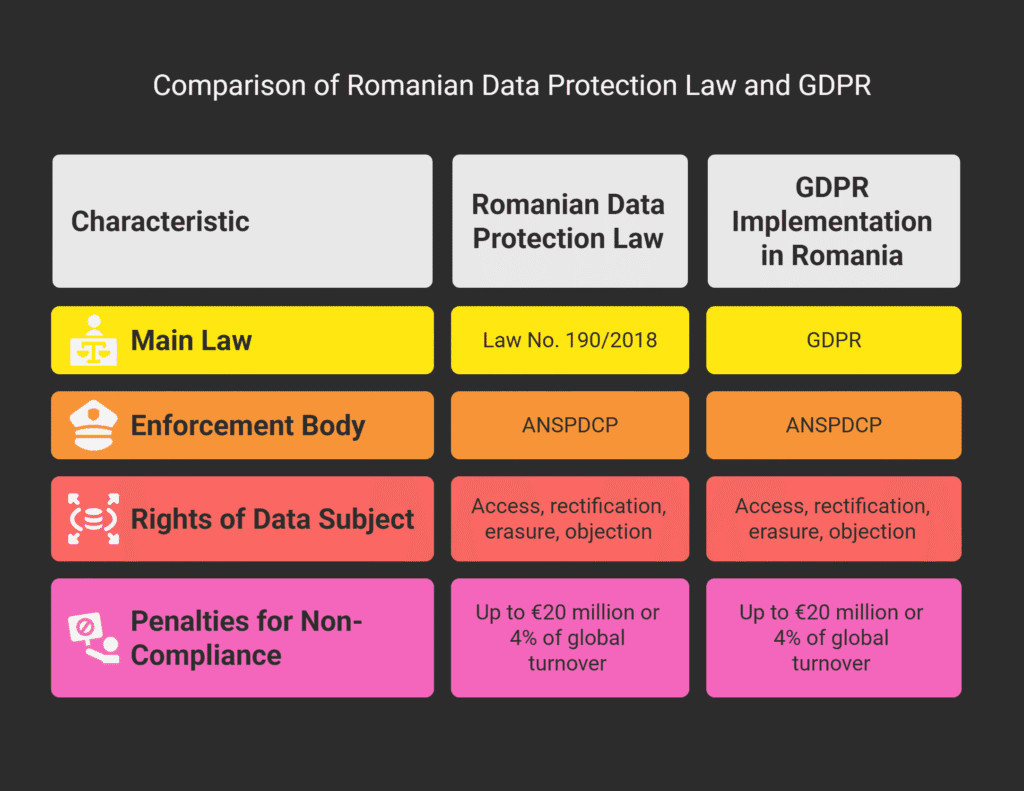
GDPR Implementation Through Romanian Law 190/2018
Romanian Law 190/2018 is key in applying GDPR within the country.
It sets out specific rules for AI systems handling personal data in Romania.
The law details how to develop, deploy, and maintain AI applications.
The law covers critical aspects of AI compliance, such as data processing rules and individual rights.
Romanian companies must align their AI with these laws and EU standards.
They need to focus on both GDPR and national specifics.
Law 190/2018 goes beyond GDPR in automated processing systems.
It requires more transparency, human oversight, and accountability in algorithms.
Companies must document their compliance and show they meet the law’s technical and organizational standards.
ANSPDCP Authority and AI Oversight Responsibilities
The National Authority for Personal Data Processing and Supervision (ANSPDCP) oversees AI in Romania.
It has the expertise to check AI systems for compliance.
The authority offers guidance, investigates, and enforces rules across sectors.
ANSPDCP reviews data protection impact assessments and offers consultation for high-risk AI projects.
It has guidelines for AI challenges.
These help companies understand their duties and implement necessary safeguards.
The authority works with other EU data protection bodies.
This ensures consistent application of EU data privacy rules.
Romanian companies benefit from this cooperation, getting clear regulatory expectations and compliance paths.
Integration with EU AI Act Requirements
Romania is making preparations to incorporate the regulations outlined in the EU AI Act into its legal framework.
This process aligns existing data protection rules with new AI-specific ones.
It ensures smooth compliance for AI systems processing personal data.
The EU AI Act introduces risk-based classifications for AI systems, building on GDPR.
Romanian regulations will address how these classifications fit with current AI rules.
Companies must prepare for more documentation, risk assessments, and governance.
Legal advice is vital for navigating this changing landscape.
The integration requires analyzing how new AI Act provisions affect existing rules.
Early preparation and strategic planning are key for Romanian businesses as these rules come into effect.
| Regulatory Component | Primary Function | Key Requirements | Enforcement Authority |
|---|
| Romanian Law 190/2018 | GDPR domestic implementation | Data processing principles, individual rights, accountability measures | ANSPDCP |
| ANSPDCP Oversight | National supervision and guidance | DPIA review, prior consultation, investigation procedures | National DPA |
| EU AI Act Integration | AI-specific regulatory framework | Risk classification, governance systems, documentation requirements | Coordinated EU enforcement |
| GDPR Article 22 | Automated decision-making rules | Human involvement, transparency, individual rights protection | ANSPDCP coordination |
Core Principles of GDPR and AI Compliance in Romania
The intersection of artificial intelligence and data protection regulations in Romania brings specific compliance obligations under GDPR’s core principles.
These foundational requirements establish the regulatory framework that Romanian organizations must follow when implementing AI systems that process personal data.
Romanian GDPR implementation requires businesses to embed these principles into their AI development lifecycle from the initial design phase.
Organizations cannot treat compliance as an afterthought but must integrate data protection considerations into every aspect of their artificial intelligence operations.

The GDPR establishes nine core principles that apply comprehensively to AI systems processing personal data within Romanian jurisdiction.
These principles create binding obligations that extend far beyond traditional data processing scenarios to encompass the unique challenges posed by automated systems and algorithmic decision-making processes.
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency in Automated Systems
Lawfulness requires Romanian organizations to establish valid legal bases before implementing AI systems that process personal data.
Organizations must identify appropriate legal grounds such as consent, legitimate interests, contractual necessity, or compliance with legal obligations before initiating any AI-driven data processing activities.
Fairness extends beyond mere legal compliance to address ethical considerations in AI system design and operation.
Romanian businesses must ensure their artificial intelligence compliance EU standards prevent discriminatory outcomes and biased algorithmic decisions that could unfairly impact individuals or specific demographic groups.
Transparency obligations demand clear communication about AI system operations and decision-making processes.
Organizations must provide individuals with understandable information about:
- The logic involved in automated decision-making,
- The significance and consequences of such processing,
- The categories of personal data being processed,
- The purposes for which data is collected and used.
Purpose Limitation and Data Minimization for AI Applications
Purpose limitation requires Romanian organizations to collect and process personal data only for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
AI systems cannot repurpose data collected for one objective to serve entirely different functions without establishing new legal bases and obtaining appropriate permissions.
Data minimization mandates that organizations limit data collection to what is directly relevant and necessary for their stated AI purposes.
This principle challenges traditional machine learning approaches that often rely on extensive data collection, requiring Romanian businesses to adopt more targeted data acquisition strategies.
Romanian GDPR implementation emphasizes that organizations must regularly review their AI systems to ensure continued compliance with purpose limitation requirements.
Any expansion of AI system functionality must undergo thorough assessment to verify alignment with original data collection purposes.
Accuracy and Storage Limitation in Machine Learning
Accuracy requirements mandate that personal data processed by AI systems remains correct and current.
Romanian organizations must implement technical and organizational measures to identify and rectify inaccurate data that could lead to erroneous automated decisions or unfair individual treatment.
Machine learning compliance standards require organizations to establish data quality management processes that include:
- Regular data validation and verification procedures,
- Automated error detection and correction mechanisms,
- Clear protocols for handling data accuracy complaints,
- Systematic review of training data quality.
Storage limitation principles impose temporal boundaries on data retention within AI systems.
Romanian businesses must establish clear data retention schedules that specify how long personal data will be maintained for AI training, operation, and improvement purposes.
Organizations must implement automated deletion processes that remove personal data when retention periods expire or when the data is no longer necessary for the original AI system purposes.
This requirement presents particular challenges for machine learning systems that rely on historical data patterns for ongoing algorithmic improvement.
The integration of these core principles into AI system architecture requires thorough planning and ongoing monitoring.
Romanian organizations must adopt privacy-by-design approaches that embed compliance considerations into every stage of AI development, deployment, and maintenance to ensure sustained adherence to data protection regulations in Romania.
Automated Decision-Making and Profiling Regulations
Article 22 of the GDPR sets strict limits on automated decision-making, impacting AI in Romania.
It outlines a detailed framework for using artificial intelligence in decision-making processes affecting individuals.
The framework emphasizes the importance of individual rights and procedural safeguards.
In Romania, automated decision-making means any process where technology makes decisions without human input.
This includes AI systems used for credit scoring, employment screening, insurance assessments, and content moderation.
Article 22 GDPR Requirements for AI Systems
The GDPR bans automated decision-making that has legal effects or significant impacts on individuals, unless certain conditions are met.
Organizations using AI systems must comply with these restrictions under Romanian data privacy laws.
This ban applies to AI applications across various sectors.
There are three exceptions to this ban.
First, organizations can use automated decision-making with explicit consent from the data subject.
Second, it’s allowed when necessary for contract performance between the organization and individual.
Third, applicable law may permit automated decision-making with appropriate safeguards.
Organizations must implement robust protection measures and maintain transparency about their systems.
The GDPR enforcement for AI systems requires strict adherence to these exceptions.

Organizations must document which legal basis applies to their automated decision-making processes.
This documentation is critical during regulatory audits and individual rights requests.
The European Data Protection Authority stresses the importance of identifying the legal basis correctly.
Meaningful Human Involvement Standards
Meaningful human involvement requires genuine oversight, not just superficial reviews.
Human reviewers must have the authority and capability to assess automated decisions and override them when necessary.
This involvement cannot be superficial or ceremonial.
Organizations must train human reviewers to understand the automated system’s logic and biases.
Reviewers need access to relevant information to evaluate system outputs.
The AI governance framework in Romania emphasizes substantive human participation.
Technical implementation of meaningful human involvement includes providing reviewers with decision explanations and relevant data inputs.
Organizations should establish clear protocols for when human intervention is mandatory.
These standards ensure that automated systems remain accountable to human oversight.
Documentation requirements extend to recording human involvement instances and decision modifications.
Organizations must maintain records showing that human reviewers actively participated in the decision-making process.
Individual Rights Against Automated Processing
Individuals have specific rights when subject to automated decision-making processes under Romanian data privacy laws.
These rights include obtaining human intervention in automated decisions, expressing personal viewpoints about the decision, and contesting automated outcomes that affect their interests significantly.
The right to human intervention requires organizations to provide accessible channels for individuals to request human review of automated decisions.
Organizations must respond to these requests promptly and provide meaningful human evaluation of the contested decision.
This right extends beyond simple complaint mechanisms.
Individuals can express their viewpoints about automated decisions, requiring organizations to consider these perspectives during human review processes.
This right ensures that automated systems account for individual circumstances that algorithms might not properly evaluate.
The GDPR enforcement for AI systems mandates genuine consideration of individual input.
Organizations must establish robust procedures for handling individual rights requests related to automated processing.
These procedures should include clear timelines, communication protocols, and decision modification processes.
The AI ethics legal framework requires transparent and accessible rights enforcement mechanisms that protect individuals from inappropriate automated decision-making.
Legal Bases for AI Data Processing in Romania
Choosing the right legal bases for AI applications is a critical step in Romania’s data protection law.
Organizations must find valid legal grounds before processing personal data through AI systems.
This choice affects individual rights, data retention, and transfer mechanisms throughout the AI lifecycle.
Romanian personal data processing regulations require identifying one of six legal bases under GDPR Article 6.
Each basis has specific requirements and limitations that impact AI system design and operation.
Professional legal analysis is essential for determining the most suitable legal foundation for specific AI processing activities.

The six legal bases include consent, contract performance, legal obligation compliance, vital interests protection, public task execution, and legitimate interests pursuit.
Organizations must carefully evaluate which basis aligns with their AI processing purposes and operational requirements.
This decision influences data subject rights, processing limitations, and overall compliance obligations.
Consent Mechanisms for AI Training Data
Consent is one of the most transparent legal bases for AI data processing activities.
Obtaining valid consent for AI training data presents unique challenges under Romanian GDPR standards.
Organizations must ensure that consent meets four key criteria: freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous.
AI training datasets often contain vast amounts of personal information collected from multiple sources.
This complexity makes it difficult to provide specific information about processing purposes.
Organizations must clearly explain how personal data will be used in machine learning algorithms and model training processes.
The following requirements apply to consent mechanisms for AI applications:
- Clear explanation of AI processing purposes and methodologies,
- Specific information about data usage in training and inference stages,
- Easy withdrawal mechanisms without negative consequences,
- Regular consent renewal for ongoing processing activities,
- Documentation of consent collection and management processes.
Individuals must understand the implications of their consent decision.
This includes information about automated decision-making capabilities and profiling activities.
Organizations should provide simple, accessible language that explains complex AI processes in understandable terms.
Consent withdrawal mechanisms must be as easy as the original consent process.
Organizations cannot make service access conditional on consent for AI processing unless absolutely necessary for service provision.
This requirement often complicates business models that rely heavily on data-driven personalization.
Legitimate Interest Assessments
Legitimate interest provides an alternative legal basis that offers greater flexibility for AI implementations.
This basis requires a three-part assessment that balances organizational interests against individual privacy rights.
Romanian organizations must conduct thorough legitimate interest assessments before relying on this legal foundation.
The three-part test examines purpose necessity, processing effectiveness, and proportionality of privacy impact.
Organizations must demonstrate that their AI processing serves genuine business interests that cannot be achieved through less intrusive means.
This analysis requires detailed documentation and regular review processes.
Key considerations for legitimate interest assessments include:
- Business necessity evaluation for AI processing activities,
- Assessment of alternative processing methods and their effectiveness,
- Analysis of individual privacy expectations and possible harm,
- Evaluation of existing safeguards and mitigation measures,
- Documentation of balancing test results and decision rationale.
Organizations must consider reasonable expectations of data subjects when conducting these assessments.
Individuals should not be surprised by AI processing activities based on the context of data collection.
Transparent privacy notices help establish appropriate expectations and support legitimate interest claims.
The proportionality analysis requires careful consideration of possible adverse effects from AI processing.
This includes risks from automated decision-making, profiling activities, and possible discrimination or bias.
Organizations should implement appropriate safeguards to minimize these risks and protect individual rights.
GDPR implementation for machine learning often relies on legitimate interest assessments for research and development activities.
Organizations must ensure that processing remains within the scope of their assessed legitimate interests and does not expand beyond documented purposes.
Public Task and Vital Interest Applications
Public task and vital interest legal bases serve specific governmental and essential service applications in AI implementations.
These bases support critical infrastructure systems, emergency response mechanisms, and public safety applications.
Romanian AI ethics standards recognize the importance of these applications while maintaining strict compliance requirements.
Public task applications must be based on legal obligations or official authority vested in the data controller.
This includes government agencies implementing AI systems for administrative efficiency or public service delivery.
Organizations must demonstrate clear legal mandates for their AI processing activities under this basis.
Vital interest applications address life-threatening situations where AI systems provide critical support.
Healthcare emergency response systems and disaster management applications often rely on this legal basis.
Organizations cannot use vital interests as a general justification for AI processing without demonstrating genuine emergency circumstances.
The Romanian data protection authority provides guidance on appropriate applications of these legal bases.
Organizations should consult official guidance and seek legal advice when determining whether their AI systems qualify for public task or vital interest justifications.
Documentation requirements for these legal bases include:
- Legal mandates or official authority supporting public task claims,
- Emergency circumstances justifying vital interest processing,
- Scope limitations ensuring processing remains proportionate,
- Regular review processes for continued necessity,
- Safeguards protecting individual rights and freedoms.
Organizations must ensure that AI processing under these bases remains strictly necessary for the stated purposes.
Scope creep beyond original justifications can invalidate the legal basis and create compliance violations.
Regular legal review helps maintain appropriate boundaries and compliance standards.
Special Category Data and AI Applications
In Romania, processing sensitive personal information through AI applications demands enhanced legal safeguards.
Special category personal data under GDPR includes racial or ethnic origin, political opinions, religious beliefs, genetic data, biometric identifiers, health information, and data about sexual orientation.
These data types require additional protection measures beyond standard personal data processing requirements.
Organizations implementing AI systems must establish specific legal justifications for processing special category data.
The heightened protection requirements reflect the increased risks to individual privacy and fundamental rights.
Romanian privacy laws mandate that companies demonstrate both necessity and proportionality when processing sensitive information through automated systems.

Biometric Data Processing Requirements
Biometric data processing in AI systems faces strict regulatory controls under EU GDPR implementation Romania.
Facial recognition, fingerprint analysis, voice identification, and behavioral biometrics all qualify as special category data requiring enhanced protection.
Organizations must establish explicit legal bases before implementing biometric AI technologies.
Technical safeguards for biometric processing include encryption during transmission and storage.
Access controls must limit biometric data availability to authorized personnel only.
Regular security assessments help maintain protection standards throughout the data lifecycle.
Biometric template storage presents particular challenges for Anspdcp compliance.
Organizations should implement irreversible hashing techniques where possible.
Data retention periods must align with processing purposes, with automatic deletion mechanisms ensuring compliance with storage limitation principles.
Health Data in AI Healthcare Solutions
Healthcare AI systems processing patient information must navigate complex regulatory requirements.
Medical data enjoys special protection status, requiring careful balance between innovation benefits and privacy protection.
Healthcare providers implementing AI diagnostic tools must ensure patient consent mechanisms meet enhanced standards.
AI-powered medical research applications often qualify for public interest derogations.
Organizations must implement appropriate safeguards protecting patient rights.
Pseudonymization techniques help reduce privacy risks while enabling beneficial medical research outcomes.
- Patient consent documentation requirements,
- Medical professional oversight obligations,
- Research ethics committee approvals,
- Data sharing agreements with research partners.
Cross-border health data transfers require additional scrutiny under ai ethics framework Romania.
International medical AI collaborations must establish adequate protection levels for Romanian patient information.
Explicit Consent and Derogations
Explicit consent for special category data processing requires clear, specific agreement from data subjects.
Consent mechanisms must explain AI processing purposes, data types involved, and possible risks.
Pre-ticked boxes or implied consent do not satisfy explicit consent requirements for sensitive data categories.
Consent withdrawal procedures must remain accessible throughout the processing lifecycle.
Organizations should implement user-friendly mechanisms allowing individuals to revoke consent easily.
Withdrawal must not affect processing legality before consent removal.
| Derogation Type | Application Scope | Additional Safeguards Required |
|---|
| Substantial Public Interest | Law enforcement AI, fraud detection | Proportionality assessment, impact evaluation |
| Medical Diagnosis | Healthcare AI diagnostics | Medical professional oversight, patient information |
| Preventive Medicine | Public health monitoring AI | Anonymization techniques, limited access controls |
Derogations from explicit consent requirements exist for specific circumstances under Romanian privacy laws.
Public interest applications, medical treatment purposes, and preventive healthcare activities may qualify for alternative legal bases.
Organizations must carefully evaluate whether their AI processing activities meet derogation criteria and implement appropriate additional safeguards.
Regular compliance reviews help ensure ongoing adherence to special category data requirements.
Legal counsel should evaluate AI system changes affecting sensitive data processing.
Documentation requirements extend beyond standard processing records to include derogation justifications and safeguard implementations.
Data Controller and Processor Obligations
In Romania, the roles of data controllers and processors are key to AI compliance.
Companies must set up clear legal frameworks.
These frameworks define roles, ensure accountability, and uphold data protection laws in AI development.
AI projects often involve many stakeholders with different data control levels.
This complexity demands precise legal documents and clear contracts.
Such agreements are essential for meeting privacy laws for AI systems in Romania.
Joint Controllership in AI Ecosystems
When multiple organizations work together on AI data processing, joint controllership arises.
They need detailed agreements outlining each party’s GDPR responsibilities in Romania.
Joint controllers must have clear procedures for handling data subject rights.
They must decide who will handle individual requests and how information will be shared.
Liability in AI joint controllership is complex.
Partners must agree on who is responsible for data breaches, violations, and penalties.
They need to address technical failures, biases, and security incidents in their agreements.
Processor Agreements for AI Service Providers
AI service providers must have thorough agreements that cover AI’s technical aspects.
These contracts should detail security measures, audit rights, and breach notification procedures specific to AI.
Agreements with processors should include sub-processor authorization clauses.
They must outline data retention, deletion, and return procedures upon contract end.
Cross-border data transfer clauses are critical in AI processor agreements.
Providers must show they comply with adequacy decisions or use standard contractual clauses for data outside the European Economic Area.
Accountability Documentation Requirements
Organizations must keep detailed records showing GDPR compliance in AI systems.
This includes records of AI processing activities and their data protection implications.
Data protection impact assessments are required for high-risk AI activities.
Companies must document risk assessments, mitigation steps, and ongoing monitoring to meet AI ethics standards in Romania.
Record-keeping includes privacy policies, consent records, and evidence of security measures.
These records must reflect AI’s unique characteristics and provide audit trails for inspections.
| Responsibility Area | Data Controller Obligations | Data Processor Obligations | Joint Controller Requirements |
|---|
| Purpose Determination | Define AI processing purposes and legal basis | Process only according to controller instructions | Jointly determine purposes through formal agreement |
| Data Subject Rights | Respond to all individual rights requests | Assist controller with rights fulfillment | Designate point of contact and response procedures |
| Security Measures | Implement appropriate technical safeguards | Maintain security throughout processing lifecycle | Coordinate security standards across organizations |
| Breach Notification | Notify authorities within 72 hours | Alert controller without undue delay | Establish notification protocols and responsibilities |
Compliance records must show ongoing adherence to data minimization in AI training and deployment.
Companies should document how they limit data collection and implement retention policies suitable for AI.
Cross-Border Data Transfers and AI Systems
Organizations deploying AI systems internationally face complex data protection requirements.
The intersection of artificial intelligence and international data flows creates unique compliance challenges.
These challenges require specialized legal analysis under Romanian privacy legislation.
Cross-border AI implementations involve multiple layers of regulatory oversight.
These systems process vast amounts of personal data across different countries with varying protection standards.
Romanian organizations must ensure their data protection laws extend seamlessly to international AI operations.
The complexity increases when AI systems operate in real-time across multiple jurisdictions.
Data flows continuously between servers, processing centers, and analytical platforms located in different countries.
Each transfer point represents a compliance risk that organizations must address through appropriate safeguards.
Third Country AI Service Provider Compliance
Third country AI service providers present distinct compliance challenges for Romanian organizations.
These providers often operate under different legal frameworks that may not provide equivalent protection to GDPR standards.
Companies must conduct thorough due diligence assessments before engaging international AI vendors.
The evaluation process involves analyzing the provider’s data protection practices, security measures, and legal obligations in their home jurisdiction.
Romanian ai governance requires organizations to verify that third country providers implement adequate technical and organizational measures.
This assessment must consider government access to data and surveillance programs that could compromise personal data protection.
“The adequacy of protection must be assessed in light of all the circumstances surrounding a data transfer operation or set of data transfer operations.”
Organizations must also evaluate the provider’s ability to comply with individual rights requests.
AI service providers must demonstrate capacity to facilitate access, rectification, and erasure rights across their international operations.
This capability becomes complex when AI systems process data through multiple interconnected platforms.
Standard Contractual Clauses Implementation
Standard Contractual Clauses serve as the primary mechanism for legitimizing AI data transfers to third countries.
These clauses must be carefully adapted to address the specific characteristics of artificial intelligence processing activities.
The implementation requires detailed consideration of AI system architectures and data processing flows.
Organizations must ensure that Standard Contractual Clauses accurately reflect their AI processing activities.
The clauses should specify data categories, processing purposes, and retention periods relevant to machine learning operations.
Technical measures for protecting transferred data must align with AI system requirements and capabilities.
The Romania artificial intelligence regulations framework requires organizations to supplement Standard Contractual Clauses with additional safeguards when necessary.
These supplementary measures may include encryption, pseudonymization, or access controls designed for AI environments.
Regular monitoring and review processes ensure ongoing compliance with contractual obligations.
Adequacy Decisions and Transfer Impact Assessments
European Commission adequacy decisions provide the foundation for unrestricted data transfers to approved countries.
Most AI service providers operate in countries without adequacy decisions, requiring alternative transfer mechanisms.
Organizations must stay informed about evolving adequacy determinations that may affect their AI operations.
Transfer Impact Assessments represent a critical compliance tool for AI data transfers.
These assessments evaluate specific risks associated with transferring personal data for AI processing purposes.
The data protection impact assessment Romania methodology must consider unique factors affecting artificial intelligence systems.
The assessment process examines government surveillance capabilities, data localization requirements, and available technical protections in the destination country.
Organizations must evaluate whether proposed safeguards provide effective protection for AI-processed data.
This analysis includes reviewing the enforceability of data protection rights and the independence of supervisory authorities.
Romanian privacy legislation requires organizations to document their transfer impact assessments and update them regularly.
Changes in political conditions, legal frameworks, or technical capabilities may necessitate reassessment of transfer arrangements.
Organizations must maintain evidence demonstrating ongoing compliance with transfer requirements throughout their AI system lifecycle.
Data Protection Impact Assessment for AI Projects
The use of artificial intelligence systems in Romania triggers the need for Data Protection Impact Assessments.
These assessments are critical for compliance, going beyond traditional privacy evaluations.
AI systems require a detailed risk analysis, addressing both established privacy concerns and new challenges.
Seeking professional legal advice is essential for thorough data protection impact assessments.
Romanian organizations must integrate DPIA processes into their AI development lifecycle.
This ensures compliance with GDPR standards and demonstrates a commitment to privacy protection.
Mandatory DPIA Triggers for AI Systems
GDPR Article 35 outlines clear triggers for Data Protection Impact Assessments.
These triggers include processing activities that pose high risks to individual rights and freedoms.
Organizations must evaluate their AI implementations against these triggers to determine if a DPIA is required.
Automated decision-making with legal or significant effects is a primary trigger.
This includes credit scoring, employment screening, and healthcare diagnostic applications.
The GDPR requires DPIAs for AI systems that make decisions affecting individual rights or legal status.
AI-powered surveillance systems also require DPIAs.
This includes video analytics, facial recognition, and behavioral monitoring technologies.
Large-scale processing of special category personal data through AI applications also necessitates DPIA completion before deployment.
Risk Assessment Methodologies and Mitigation
Risk assessment methodologies for AI systems must address traditional privacy risks and new challenges from machine learning.
Organizations implementing automated decision-making solutions must evaluate algorithmic bias, data accuracy, security vulnerabilities, and function creep.
These assessments require expertise from legal, technical, and ethical fields.
Comprehensive risk profiles must identify specific privacy threats associated with AI system operations.
Data quality risks arise from training datasets with inaccurate or biased information.
Security risks include unauthorized access, data poisoning attacks, and inference attacks revealing sensitive information about training data subjects.
Mitigation strategies must address identified risks through technical and organizational measures.
Technical safeguards include differential privacy, federated learning, and robust access controls.
Organizational measures include staff training, algorithm audits, and governance frameworks.
The AI compliance framework in Romania requires documenting these measures and monitoring their effectiveness.
Risk mitigation must also consider AI ethics in Romania.
Organizations should implement fairness testing, transparency mechanisms, and accountability measures.
These ethical considerations strengthen risk management and demonstrate responsible AI development.
Prior Consultation with ANSPDCP Procedures
Prior consultation with ANSPDCP is necessary when DPIAs identify high residual risks.
This consultation process requires detailed documentation of processing activities, risk assessment findings, proposed mitigation measures, and justifications for proceeding with high-risk AI implementations.
Organizations must prepare thorough consultation packages.
These packages should demonstrate consideration of privacy implications and commitment to implementing recommended safeguards.
The documentation should include technical specifications, data flow diagrams, risk assessment matrices, and proposed monitoring mechanisms.
ANSPDCP evaluates these submissions to determine if additional safeguards are necessary or if processing can proceed as planned.
The consultation timeline is typically eight weeks from submission of complete documentation.
Organizations cannot deploy AI systems requiring prior consultation until receiving ANSPDCP approval or recommendations.
This ensures that high-risk AI implementations receive appropriate regulatory oversight and incorporate necessary privacy protections.
Privacy by Design and Security Measures
Creating robust privacy safeguards in AI systems demands a holistic approach.
Organizations must embed protection mechanisms from the outset to the deployment phase.
This proactive stance ensures they meet Romanian data protection laws and establish strong security bases.
GDPR Article 25 mandates privacy by design and default.
These mandates go beyond mere compliance, influencing system architecture.
Romanian firms must show that data protection guides AI development and deployment fully.
“Data protection by design and by default requires that appropriate technical and organizational measures are implemented in such a manner that processing will meet the requirements of this Regulation and protect the rights of data subjects.”
Technical Safeguards in AI Development
Technical safeguards are the core of compliant AI systems.
Data minimization limits personal data to what’s necessary for processing.
This prevents excessive data that could breach Romanian data security rules.
Pseudonymization and anonymization lower identification risks in machine learning.
Advanced encryption safeguards data during training and use.
Access controls limit data to authorized personnel and processes.
Secure data storage meets AI-specific needs.
Version control tracks data and model changes.
Audit trails document data access and processing for compliance checks.
Organizational Measures and Data Governance
Organizational measures are key to privacy in AI.
Clear roles and responsibilities are essential for data handling in AI projects.
Staff training on Romanian AI regulations is also vital.
Data governance frameworks set policies and procedures.
Compliance audits ensure ongoing adherence to laws.
Incident response plans handle privacy breaches and vulnerabilities.
Documentation is critical for accountability.
Organizations must keep detailed records of AI system design and privacy measures.
These records help with regulatory inspections and internal checks.
- Staff training on data privacy Romania requirements,
- Incident response protocols for AI systems,
- Regular compliance monitoring and assessment,
- Clear data handling procedures and responsibilities.
Security by Default Implementation
Security by default ensures AI systems apply maximum privacy settings automatically.
This approach eliminates the need for user configuration or technical expertise.
Default settings must protect data without hindering system performance.
GDPR Article 25 mandates default privacy settings that prioritize data subject rights.
Organizations cannot rely on users or administrators for privacy settings.
Automated privacy controls reduce human error in deploying protection mechanisms.
System updates must enhance privacy safeguards.
Configuration management prevents unauthorized security setting changes.
| Protection Layer | Implementation Method | Compliance Benefit |
|---|
| Data Encryption | End-to-end encryption protocols | Confidentiality protection |
| Access Controls | Role-based authentication systems | Unauthorized access prevention |
| Data Minimization | Automated filtering mechanisms | Purpose limitation compliance |
| Audit Logging | Comprehensive activity tracking | Accountability demonstration |
Privacy by design and security measures need continuous improvement.
Organizations must regularly evaluate protection effectiveness and adapt to new threats.
This ongoing effort ensures compliance with Romanian data protection laws and emerging regulations.
Individual Rights in AI-Driven Environments
Romanian GDPR enforcement mandates that AI systems uphold fundamental data protection rights.
Organizations must deploy artificial intelligence with frameworks that safeguard data subject autonomy.
The legal framework for machine learning outlines clear obligations for protecting individual rights in automated environments.
Data subjects retain all GDPR rights when their personal information is processed by AI, regardless of system complexity.
These rights necessitate technical solutions that can locate, modify, or remove personal data from AI systems.
Organizations must strike a balance between algorithmic efficiency and individual privacy through carefully designed mechanisms.
Right to Explanation and Algorithmic Transparency
The right to explanation is a significant challenge in AI compliance under Romanian data protection law.
Individuals have the right to obtain meaningful information about automated decision-making logic that affects their interests.
This requirement goes beyond simple system descriptions, demanding specific explanations for individual automated decisions.
Organizations must provide clear, understandable explanations that enable data subjects to comprehend AI system operations.
These explanations should detail how personal data influences automated decisions without revealing proprietary algorithms.
Transparency measures must balance individual understanding with trade secret protection.
The explanation requirement encompasses both general AI system information and specific decision rationales.
Organizations must develop documentation that explains algorithmic logic in accessible language.
Technical complexity cannot excuse inadequate transparency when individual rights are at stake.
Access, Rectification, and Erasure Rights
Access rights in AI environments require organizations to provide detailed information about personal data processing activities.
Data subjects can request details about AI training datasets, processing purposes, and automated decision outcomes.
Organizations must implement systems that can locate personal data across distributed AI architectures and training datasets.
Rectification rights present significant technical challenges within machine learning systems where personal data may be embedded in trained models.
Organizations must develop mechanisms to correct inaccurate personal data without compromising system integrity.
The machine learning legal framework requires effective correction procedures that maintain AI system performance while ensuring data accuracy.
Erasure rights, commonly known as the “right to be forgotten,” require sophisticated technical implementations in AI contexts.
Personal data deletion must extend beyond primary datasets to include derived data and model parameters.
Organizations must implement data lineage systems that track personal information throughout AI processing pipelines.
- Complete data mapping across AI system components,
- Technical deletion mechanisms for embedded personal data,
- Verification procedures for successful data removal,
- Documentation of erasure implementation methods.
Data Portability in Machine Learning Contexts
Data portability rights enable individuals to receive their personal data in structured, commonly used formats.
In AI environments, determining portable data scope requires careful consideration of what constitutes personal data versus derived insights.
Organizations must distinguish between original personal data and AI-generated profiles or recommendations.
Cross-border data transfers complicate portability implementations when AI systems operate across multiple jurisdictions.
Organizations must ensure that portable data formats remain meaningful when transferred between different AI service providers.
Technical standards for data portability must preserve utility while protecting privacy interests.
Automated processing safeguards require that portable data includes relevant metadata about AI processing activities.
Data subjects should receive information about how their data contributed to automated decisions.
Biometric data protection considerations apply when AI systems process unique biological characteristics that require specialized portability measures.
| Right Category | AI Implementation Challenge | Technical Solution |
|---|
| Explanation | Complex algorithm transparency | Interpretable AI models and decision logs |
| Access | Distributed data location | Comprehensive data mapping systems |
| Rectification | Embedded model corrections | Model retraining and update procedures |
| Erasure | Complete data removal | Data lineage tracking and deletion verification |
| Portability | Meaningful data format transfer | Standardized export formats and metadata inclusion |
Organizations must establish clear procedures for rights fulfillment that account for AI system complexity while meeting legal obligations.
Regular testing and validation of rights implementation mechanisms ensure continued compliance as AI systems evolve.
The integration of individual rights protection into AI development lifecycles represents essential compliance architecture for Romanian organizations.
Sector-Specific Compliance Challenges
Industry-specific AI applications face unique regulatory hurdles, going beyond the standard GDPR rules.
Companies must navigate a complex legal landscape.
This landscape combines general data protection rules with specific sector regulations.
Understanding both Romanian data protection laws and industry-specific legal requirements is essential.
Different sectors encounter varying levels of regulatory complexity with AI.
Healthcare must comply with medical device and privacy laws.
Financial sectors deal with consumer protection laws that overlap with data privacy.
Employment sectors balance worker rights with automated decision-making.
Healthcare AI and Medical Data Processing
Healthcare AI systems are subject to strict regulations.
These regulations combine medical device compliance with data protection.
Companies developing healthcare AI must adhere to clinical evidence standards and protect sensitive health data.
They need robust consent mechanisms for both medical treatment and data processing.
Medical AI applications must have detailed audit trails for accountability.
Healthcare providers must ensure data accuracy for medical decisions while following patient safety standards.
The integration of AI legal requirements with healthcare regulations is complex, needing specialized legal knowledge.
Clinical trial data processing adds challenges for healthcare AI.
Companies must balance research goals with patient privacy rights.
This requires compliance with medical research regulations, going beyond GDPR.
Financial Services and Credit Decision AI
Financial institutions using AI for credit decisions face multiple regulations.
Consumer credit protection laws and data protection intersect, creating complex compliance.
These systems must ensure fair lending and prevent algorithmic bias.
Credit decision AI needs transparency to meet consumer rights and regulatory oversight.
Financial organizations must document automated decision-making processes and protect customer financial data.
Implementing Anspdcp compliance in finance requires attention to anti-discrimination principles.
Prudential regulations add complexity to financial AI.
Banks and financial institutions must ensure AI systems comply with risk management and operational resilience.
This requires governance frameworks addressing data protection and financial stability.
Employment AI Tools and Worker Rights
Employment AI systems face emerging compliance challenges.
These challenges intersect data protection law with labor regulations.
Organizations must respect worker dignity and provide transparency in automated employment decisions.
They must consider collective bargaining and employee monitoring regulations.
Worker privacy rights are critical for employment AI.
Companies must balance business interests with employee privacy expectations. Compliance with labor law is essential.
The deployment of machine learning GDPR in employment requires attention to non-discrimination and worker consultation.
Employee evaluation AI systems must ensure fairness and transparency.
Organizations must provide meaningful human involvement in automated decisions.
The integration of EU data privacy law with employment regulations requires ongoing legal assessment.
Recent Regulatory Developments
The regulatory landscape for AI compliance continues evolving rapidly.
The European Data Protection Board’s Opinion 28/2024 on AI model development addresses critical questions about data minimization in training datasets, individual rights in AI systems, and cross-border data transfers for AI purposes.
Recent CJEU clarifications on automated decision-making rights provide important guidance on balancing GDPR transparency requirements with legitimate trade secret protection.
These developments emphasize the importance of staying current with evolving guidance as Romanian organizations implement AI systems under GDPR requirements.
Conclusion
The blend of artificial intelligence and data protection brings forth complex compliance duties under Romanian law.
Companies must navigate through GDPR implementation Romania rules.
They also need to prepare for new regulatory frameworks on automated decision-making GDPR applications.
Personal data processing ai Romania necessitates thorough risk assessment strategies.
The European Data Protection Board Opinion 28/2024 highlights the need for proactive AI governance.
It calls for organizations to implement strong technical and organizational measures from design to deployment.
The Romanian AI governance framework is rapidly evolving.
Companies using AI technologies face increasing pressure from GDPR enforcement for technology companies Romania.
This makes professional legal advice critical for maintaining compliance programs.
Automated decision-making Romanian regulations demand a blend of legal and technical expertise.
Organizations must invest in frameworks that uphold privacy by design, protect individual rights, and monitor regulations continuously.
Non-compliance can lead to more than just financial penalties.
It can also cause reputational damage and disrupt operations.
Professional legal support ensures AI deployments meet their goals while adhering to all regulations and protecting privacy rights.
For detailed GDPR and AI compliance advice, companies should reach out to legal experts at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Our team of Romanian lawyers can offer customized legal solutions tailored to Romania’s specific regulations and the upcoming EU AI Act obligations.
FAQ
What is the primary legal framework governing AI data protection in Romania?
Romania’s AI data protection is governed by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This is implemented through Law 190/2018.
The National Authority for Personal Data Processing and Supervision (ANSPDCP) oversees compliance.
They ensure AI applications that process personal data meet the necessary standards.
How does ANSPDCP oversee AI compliance requirements in Romania?
ANSPDCP has specific responsibilities for AI systems processing personal data.
They evaluate data protection impact assessments and enforce automated decision-making regulations.
They also monitor compliance, investigate violations, and provide guidance on AI data protection matters.
What role does the EU AI Act play in Romania’s regulatory framework?
The EU AI Act is a significant development in Romania’s regulatory landscape.
It requires coordination between GDPR obligations and AI-specific requirements.
This creates a framework addressing traditional privacy concerns and new AI challenges.
What are the core GDPR principles that AI systems must comply with in Romania?
AI systems must follow lawfulness, fairness, and transparency.
They must operate under valid legal bases and avoid discriminatory outcomes.
Organizations must implement purpose limitation and data minimization principles.
How does Article 22 of GDPR affect automated decision-making in AI systems?
Article 22 prohibits solely automated decision-making with legal effects or significant impacts.
This applies to AI applications like credit scoring, employment screening, and content moderation.
What constitutes meaningful human involvement in automated decision-making?
Meaningful human involvement requires genuine oversight, not just a pro forma review.
It must be substantive, allowing human reviewers to assess and override automated decisions when necessary.
What legal bases can organizations use for AI data processing in Romania?
Organizations can use consent, legitimate interests, contract performance, or other recognized bases for AI data processing.
Consent for AI training data must meet GDPR standards.
Legitimate interest assessments must balance organizational interests against individual privacy rights.
How are biometric data processing requirements handled in AI systems?
Biometric data processing in AI systems requires enhanced protection measures and specific legal justifications.
Organizations must establish explicit legal bases and implement technical safeguards.
Biometric data must remain secure throughout its lifecycle.
What are the requirements for health data processing in AI healthcare solutions?
AI systems processing health information must comply with GDPR and sector-specific healthcare regulations.
They must navigate medical data protection requirements while enabling healthcare innovations.
Patient privacy must be protected throughout legitimate medical research and treatment.
How do joint controllership arrangements work in AI ecosystems?
Joint controllership emerges when multiple organizations collaborate in determining AI processing purposes and means.
Detailed agreements are necessary, specifying responsibilities, individual rights procedures, and liability allocation.
These arrangements address complex scenarios involving shared datasets and collaborative model training.
What must processor agreements for AI service providers include?
Processor agreements must address AI processing activities comprehensively.
They must include data security measures, sub-processor authorization procedures, data retention and deletion obligations, and assistance with data subject rights fulfillment.
These agreements require attention to cross-border data transfers and audit rights.
How do cross-border data transfers work with AI systems?
Cross-border AI data transfers require evaluating international data protection standards and transfer mechanisms.
Organizations must assess whether third country AI providers maintain adequate protection levels.
They must implement Standard Contractual Clauses adapted to specific AI processing activities and technical architectures.
When is a Data Protection Impact Assessment required for AI projects?
Mandatory DPIA triggers for AI systems include automated decision-making with legal or significant impacts, systematic monitoring of publicly accessible areas, and large-scale processing of special category personal data.
Many AI applications require DPIAs due to their inherent processing characteristics.
What risk assessment methodologies should AI systems use?
Risk assessment methodologies must address traditional privacy risks and novel challenges posed by machine learning technologies.
They must consider algorithmic bias, data accuracy issues, security vulnerabilities, and function creep.
These assessments require interdisciplinary expertise combining legal analysis, technical evaluation, and ethical considerations.
What technical safeguards must be implemented in AI development?
Technical safeguards must be embedded throughout the AI system lifecycle.
They include data minimization techniques, pseudonymization and anonymization methods, access controls, encryption protocols, secure data storage mechanisms, and robust authentication systems.
These safeguards protect personal data throughout AI processing activities.
How does privacy by design apply to AI systems?
Privacy by design requires embedding compliance considerations into AI system architecture from initial development phases.
Organizations must adopt approaches that incorporate data protection principles throughout system design.
This ensures privacy protection is built into AI systems, not added as an afterthought.
What is the right to explanation in AI systems?
The right to explanation requires organizations to provide meaningful information about automated decision-making logic.
This includes general information about AI system operations and specific explanations for individual automated decisions affecting personal interests.
It enables individuals to understand how AI systems process their data.
How do access, rectification, and erasure rights work with AI systems?
These rights require technical implementations that can locate, modify, or delete specific personal data within complex AI systems and training datasets.
Organizations must develop robust data lineage tracking systems and implement technical measures enabling effective rights fulfillment without compromising system integrity or performance.
What special considerations apply to healthcare AI compliance?
Healthcare AI must comply with GDPR requirements, medical data protection regulations, clinical trial standards, and healthcare quality assurance obligations.
These systems must implement robust consent mechanisms, ensure data accuracy for medical decision-making, and maintain detailed audit trails for clinical accountability purposes.
How do employment AI tools affect worker rights under Romanian law?
Employment AI tools present compliance challenges intersecting data protection law with employment regulations.
They require consideration of worker privacy rights, non-discrimination principles, and collective bargaining obligations.
Organizations must ensure employment AI systems respect worker dignity and maintain compliance with labor law requirements regarding employee monitoring.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with AI data protection requirements?
Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
The complexity of requirements necessitates a thorough compliance program addressing all aspects of AI data protection from initial system design through ongoing operations.
Why is professional legal guidance important for AI compliance in Romania?
Professional legal guidance is essential for navigating complex AI compliance requirements.
It combines legal knowledge, technical understanding, and practical implementation experience.
The regulatory landscape is rapidly evolving, with new guidance documents, enforcement actions, and legislative developments regularly updating compliance requirements for AI systems processing personal data.