Understanding Judicial Control Romania – Legal Insights
Exploring Judicial Control in Romania: What You Need to Know
How did a nation change its legal system from an authoritarian regime to a modern European one in just 30 years?
This journey shows how checks and balances evolved in Romania’s government from 1989.
The fall of communism was a key moment for Romania’s legal system.
The country adopted democratic values, and its courts changed to meet European standards.
The push for EU integration sped up these changes.
The system now balances executive power and judicial freedom.
The Constitutional Court is key in keeping this balance.
It makes sure laws respect basic rights and principles.
Key Takeaways
- Romania’s legal system changed a lot after the 1989 fall of communism;
- EU integration was a big push for judicial reform;
- The Constitutional Court checks if laws follow basic principles;
- Judges faced challenges applying always changing laws during the transition;
- An independent judiciary is key for democratic checks and balances;
- The separation of powers is the base of Romania’s legal system.
The Romanian Judicial System: An Overview
The Romanian judicial system is unique and has a rich history.
It follows a civil law system, influenced by France and Italy.
After joining the European Union in 2007, the Romanian judiciary system has seen major changes.
These changes aim to meet European standards while keeping its own identity.
The judiciary is a key part of Romania’s democracy, along with the legislative and executive branches.
Its main job is to ensure justice by applying laws fairly.
It also protects citizens’ rights and solves disputes according to the constitution.
Structure of Courts in Romania
The Romanian judicial system has a four-tier structure.
At the base are local courts, dealing with simple cases.
These courts are found in cities and towns, making justice accessible to all.
Next are tribunals, handling more complex cases and appeals from local courts.
Each county has one tribunal, usually in the county capital.
The third level is the courts of appeal, reviewing tribunal decisions and some first-instance cases.
Romania has 15 courts of appeal, covering many counties.
At the top is the High Court of Cassation and Justice.
It ensures laws are applied uniformly across the country.
This court deals with appeals and cases involving high officials.
| Court Level | Jurisdiction | Territorial Coverage | Primary Function |
| Local Courts | Minor civil and criminal cases | Cities and towns | First instance for common disputes |
| Tribunals | Complex cases, appeals from local courts | County level | First instance for major cases, appeals |
| Courts of Appeal | Appeals from tribunals, specific first instance cases | Multiple counties | Regional appellate review |
| High Court of Cassation and Justice | Final appeals, cases involving high officials | National | Ensuring uniform law interpretation |
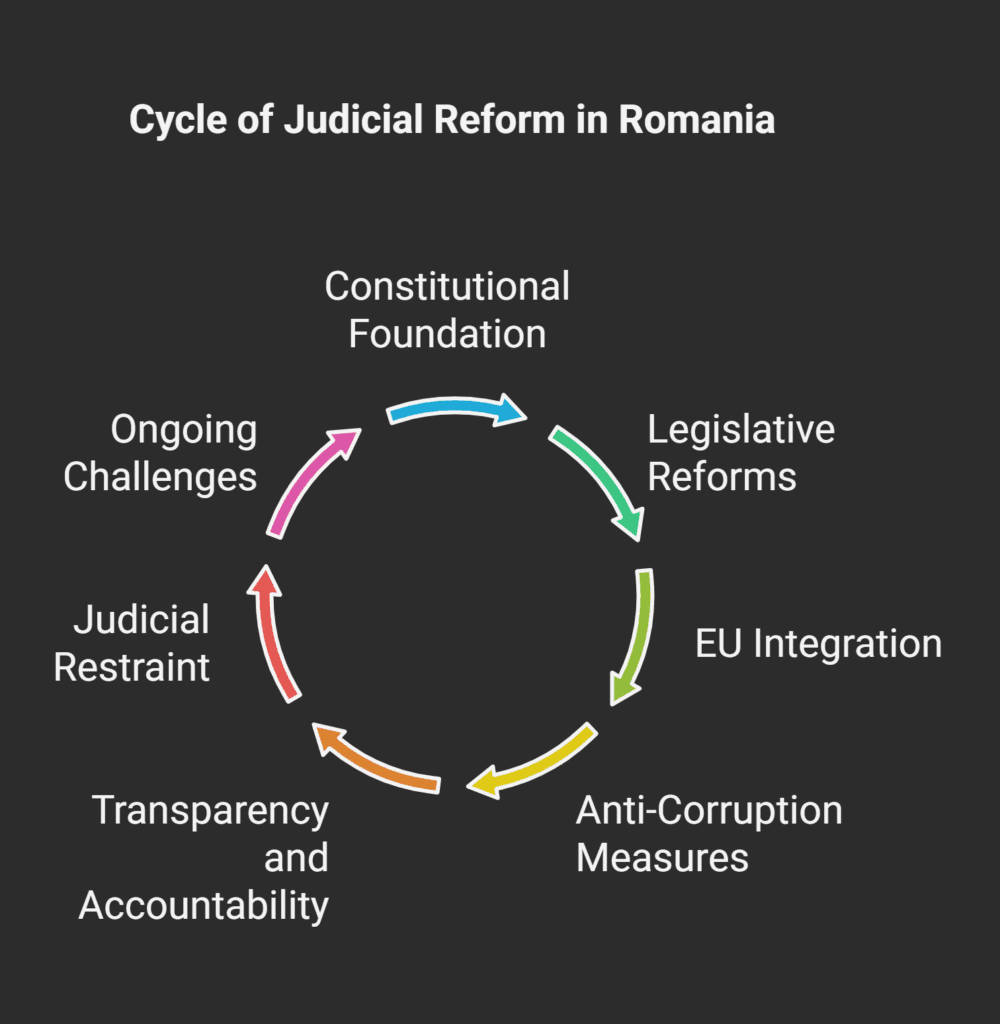
Evolution of the Romanian Legal Framework
After communism fell in 1989, Romania’s legal system changed a lot.
It moved from a totalitarian regime to a democratic state.
This change needed big reforms to make the judiciary independent and meet European standards.
The 1991 Constitution, updated in 2003, laid the groundwork for a democratic judiciary.
It ensured the separation of powers and judicial independence.
Laws passed later organized courts and set up new judicial bodies.
Between 2000 and 2007, Romania’s EU membership pushed for more judicial reforms.
The country made many legal changes to match EU rules.
These changes improved judicial oversight and set up bodies to fight corruption.
European integration has helped Romania uphold judicial independence.
Rule of Law Principles in Romania
The Romanian judiciary is based on key rule of law principles.
Judicial independence is the most important, protected by the constitution and other measures.
This independence lets judges make decisions without outside influence, like from politicians.
Transparency is also key in the Romanian judicial system.
Court proceedings are open, and decisions must be explained and published.
This openness builds trust and allows judicial oversight by the public and civil groups.
The principle of judicial restraint means courts should only decide on legal questions.
They should not get involved in policy matters.
This helps keep the balance of power in Romania’s democracy.
To fight corruption, Romania has special bodies.
The Romanian Anti-corruption Directorate investigates high-level corruption.
The General Anti-corruption Directorate deals with corruption in the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
The Directorate for the Fight against Fraud works on fraud affecting EU money, and the National Integrity Agency checks assets and interests of public officials.
Despite progress, challenges remain.
Political interference, lack of resources, and uneven law application test Romania’s rule of law commitment.
But, ongoing reforms and EU monitoring help the judiciary stay strong in upholding these principles.
Understanding Judicial Control Romania: Fundamental Concepts
It’s key to know the basics of judicial control in Romania to see how it protects people’s rights.
This control uses legal tools to make sure justice follows the law.
It’s a big part of keeping the rule of law and protecting freedom in Romania.
Definition and Purpose of Judicial Control
In Romania, judicial control means courts watch over legal actions.
They check if laws are followed in court cases, government decisions, and laws passed by the government.
The main goal is to stop abuse of power and make sure the government acts legally.
This control does a few important things in Romania’s legal system:
- It makes sure laws are followed;
- It protects human rights from being broken;
- It keeps the separation of powers between government branches;
- It gives legal help to people whose rights are not respected.
In criminal cases, judicial control helps by watching suspects while they are presumed innocent.
It balances the need to solve crimes with protecting people’s rights.
Legal Basis for Judicial Control in Romanian Law
The basis of judicial control in Romania comes from several laws.
The Romanian Constitution sets the rules for judicial independence and fair trials.
These are the basics of good judicial control.
The Romanian Criminal Procedure Code (RCPC) is very important.
It sets the rules for all crimes, including corruption, unless there are special laws.
It tells how judicial control works in investigations and trials.
Law no. 78/2000 also plays a big role. It adds specific rules for corruption crimes.
This law helps control judicial actions in corruption cases, which are a big focus for Romania’s justice system.
Other laws also shape judicial control in Romania:
- Law no. 304/2004 on judicial organization;
- Law no. 303/2004 on the status of judges and prosecutors;
- Law no. 317/2004 on the Superior Council of Magistracy.
Distinction Between Judicial Control and Judicial Review
Judicial control and judicial review are not the same in Romania’s legal system.
Knowing the difference is important for understanding how the system works.
Judicial control is about courts watching over legal actions, mainly in criminal cases.
It makes sure rules are followed and everyone’s rights are respected during legal processes.
| Aspect | Judicial Control | Judicial Review |
| Primary Focus | Procedural compliance in specific cases | Constitutionality of laws and regulations |
| Exercised By | Regular courts within their court jurisdiction | Constitutional Court mainly |
| Timing | Often preventive or concurrent | Usually after laws are made |
| Legal Effect | Case-specific remedies | Potential invalidation of laws with wide effect |
Judicial review, on the other hand, is about checking if laws follow the Constitution.
It’s a special kind of control that looks at if laws are okay, not just how cases are handled.
Both control and review help keep the law strong and protect people’s rights.
They work together to make sure the law is followed and everyone is treated fairly in Romania.
The Constitutional Framework of Judicial Control
The Romanian Constitution sets up rules to protect democracy and citizens’ rights.
It outlines how the government works and keeps everyone in check.
Knowing these rules helps understand how the courts watch over the government.
It made Romania’s laws stronger, focusing on an independent judiciary.
Constitutional Provisions for Judicial Oversight
Romania’s Constitution has specific articles for judicial oversight.
These articles let courts check laws and government actions.
They make sure everything follows the Constitution.
The Constitution talks about the court system’s structure and what it can do.
It’s all about keeping the law in order.
The key points for judicial oversight are:
- Article 124 says justice is based on law and judges are independent.
- Article 126 explains the court system’s setup and what it can do.
- Article 142 makes the Constitutional Court the top authority on the Constitution.
These rules help courts keep the government in line.
They protect your rights through the legal system.
Separation of Powers in the Romanian Constitution
The Romanian Constitution divides power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
This creates a system of checks and balances.
It stops any one branch from getting too much power.
Article 1(4) says the State is organized with these powers.
It makes sure each branch can watch over the others.
The judiciary plays a big role in this.
The judicial branch’s main jobs are:
- Interpreting laws;
- Checking if executive actions are legal;
- Resolving disputes between government bodies;
- Protecting individual rights.
These jobs help keep the government in balance.
The separation of powers has been made stronger through legal reforms.
Constitutional Safeguards for the Judiciary
The Romanian Constitution protects the judiciary’s independence. This lets judges make decisions based on law, not politics.
Important safeguards include:
- Judicial tenure security (Article 125);
- Prohibition against transferring judges without their consent;
- Financial independence of the judiciary;
- The Superior Council of Magistracy’s role in protecting judicial independence.
Article 133 makes the Superior Council of Magistracy the guardian of judicial independence.
It oversees judicial appointments and promotions.
This is key for transparency in the judiciary.
Recent judicial reforms have aimed to strengthen these safeguards.
But finding the right balance between independence and accountability is a challenge.
| Constitutional Safeguard | Constitutional Article | Purpose | Implementation Challenges |
| Judicial Independence | Article 124 | Ensures judges are subject only to the law | Political pressure and media influence |
| Judicial Tenure | Article 125 | Protects judges from arbitrary removal | Balancing security with accountability |
| Superior Council of Magistracy | Article 133-134 | Guarantees judicial independence | Ensuring representative composition |
| Constitutional Court | Articles 142-147 | Ensures constitutional compliance | Maintaining political neutrality |
The framework for judicial control in Romania is always changing.
It’s shaped by laws and court decisions.
As Romania gets closer to European legal standards, these rules are key for legal reform.
Knowing these rules helps you see how administrative law in Romania works.
They protect your rights against government overreach.
The safeguards show Romania’s commitment to a balanced democracy.
Key Institutions in Romania’s Judicial Control System
It’s important to know the key institutions in Romania’s judicial control system.
They work together to ensure justice is served and human rights are protected.
Each institution plays a unique role in keeping the legal system in check.
The Role of the High Court of Cassation and Justice
The High Court of Cassation and Justice is at the top of Romania’s judicial system.
As the supreme court of Romania, it makes final decisions on most legal issues.
It ensures laws are applied equally across the country.
This court has different sections for civil, criminal, commercial, and administrative cases.
Its decisions are final for lower courts.
This helps keep legal practices consistent in Romania.
The High Court also protects fundamental rights.
It reviews cases where legal mistakes might have caused injustice.
Its decisions help develop legal doctrine and protect constitutional values.
The Superior Council of Magistracy
The Superior Council of Magistracy (SCM) protects judicial independence in Romania.
It manages judges’ and prosecutors’ careers, keeping them free from outside influence.
The SCM has judges, prosecutors, and appointed members.
It handles appointments, promotions, and disciplinary actions.
Its structure ensures fair representation from all court levels and prosecutorial offices.
The SCM’s independence is key to preventing political interference in courts.
It ensures judges are impartial and operate within professional standards.
The Prosecutor’s Office and Anti-Corruption Directorate
The Prosecutor’s Office represents the state in criminal cases and protects public interests.
It has specialized units for different crimes.
The Romanian Anti-corruption Directorate (DNA) focuses on fighting corruption.
It deals with significant corruption cases and those involving high-ranking officials.
It’s a key part of anti-corruption efforts in Romania.
Several authorities work together to fight corruption in Romania:
- The Romanian Anti-corruption Directorate (DNA) – specializes in corruption cases;
- The General Anti-corruption Directorate (DGA) – focuses on corruption in the Ministry of Internal Affairs;
- The Directorate for the Fight against Fraud (DLAF) – protects EU financial interests;
- The National Integrity Agency (ANI) – checks asset declarations and conflicts of interest.
The DNA is part of the Prosecutor’s Office but operates independently.
It investigates corruption, gathers evidence, and brings cases to court.
It’s key in Romania’s transitional justice efforts, tackling corruption from the communist era.
Administrative Courts in Romania
Administrative courts handle disputes between citizens and public authorities.
They review the legality of government actions.
This gives you a way to challenge government actions you think are unlawful.
These courts have specialized sections within tribunals and courts of appeal.
The High Court’s Administrative and Fiscal Section is the highest authority.
They use specific procedures to balance individual rights and administrative efficiency.
Administrative courts are vital for protecting your rights against government overreach.
They enforce constitutional constraints on government power.
| Institution | Primary Function | Jurisdiction | Contribution to Judicial Control |
| High Court of Cassation and Justice | Final court of appeal | National | Ensures uniform interpretation of laws |
| Superior Council of Magistracy | Judicial governance | Oversight of all magistrates | Guarantees judicial independence |
| Anti-Corruption Directorate | Prosecution of corruption | High and medium-level corruption | Enforces accountability of officials |
| Administrative Courts | Review of administrative acts | Public authority disputes | Checks executive power |
These institutions form a system of checks and balances in Romania.
Their success depends on their legal powers, independence, and resources.
Knowing how they work helps you understand Romania’s legal system and the protections for your rights.
The Constitutional Court of Romania: Powers and Functions
The Constitutional Court of Romania is key in keeping the country’s laws in line with its constitution.
It was set up after communism fell.
This court helps ensure that the government follows the rules and protects people’s rights.
Jurisdiction and Authority
The Constitutional Court of Romania has a big role in the country’s legal system.
It was founded in 1992. This court can check if the government’s actions are legal, without being part of the government.
The Court has nine judges, each serving nine years.
Three are chosen by the Chamber of Deputies, three by the Senate, and three by the President.
This way, no one branch of government can control the Court.
The Constitutional Court’s main jobs include:
- Checking if laws are okay before and after they are made official;
- Fixing disputes between government bodies;
- Looking at if treaties and international deals are okay;
- Checking if presidential elections and referendums are fair;
- Seeing if rules made by Parliament are legal;
- Looking at if political parties are following the rules.
This Court doesn’t deal with individual cases.
It only looks at big questions about the constitution.
It’s the only one who can explain what the constitution means in Romania.
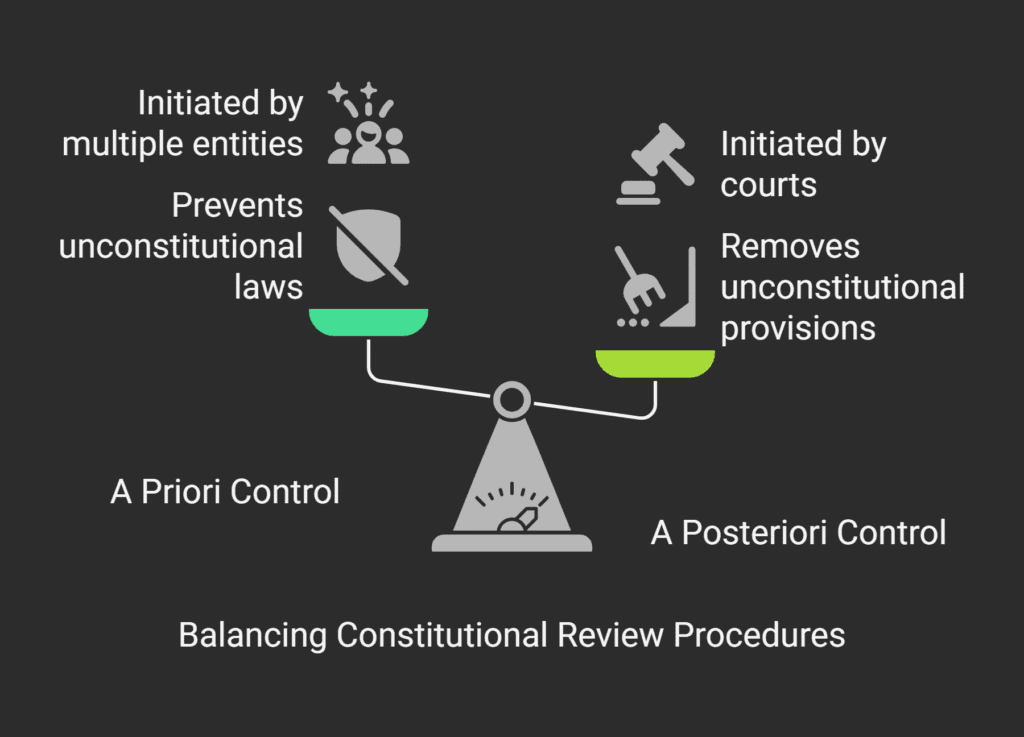
Constitutional Review Procedures
The Constitutional Court uses special ways to check laws and government actions.
These steps make sure everything is done right and follows the constitution.
This helps keep the legal system fair in Romania.
There are a few main ways the Court checks things.
These include looking at laws before they are made official and after they are.
Each method has its own purpose in making sure things are done right.
Before a law is made official, the Court can check it.
This can be started by the President, Parliament leaders, the government, or others.
It’s like a safety check before a law is put into action.
After a law is made official, the Court can also check it.
This happens when a court asks the Constitutional Court about a big question.
It’s like a second check to make sure everything is okay.
| Type of Review | Timing | Initiators | Scope | Effect |
| A Priori Control | Before promulgation | President, Parliament leaders, Government, High Court, Ombudsman, 50+ deputies or 25+ senators | Draft laws, treaties | Prevents unconstitutional laws from entering force |
| A Posteriori Control | After promulgation | Same as above | Laws in force | Removes unconstitutional provisions from legal system |
| Exception of Unconstitutionality | During litigation | Courts, parties in litigation | Specific provisions affecting a case | Suspends case until constitutional issue resolved |
| Abstract Review | Any time | Ombudsman | Any law or ordinance | Addresses systemic constitutional issues |
Impact of Constitutional Court Decisions
Decisions by the Constitutional Court are very important in Romania.
If the Court says a law is not okay, that law stops working after 45 days.
But, if the government changes it to fit the constitution, it can keep working.
These decisions are binding for everyone in government.
Parliament or the Government can’t just ignore what the Court says by making the same law again.
Some big decisions have changed Romania’s laws a lot:
- Decision 356/2007 set limits on emergency laws;
- Decision 1258/2009 changed the pension system for judges;
- Decision 766/2011 made judges more independent;
- Decision 80/2014 made it clearer how to change the constitution;
- Decision 405/2016 changed how abuse of power is seen in criminal law.
These decisions show how the Court keeps the government in check.
It helps make sure everyone follows the rules by explaining what the constitution means.
Relationship with European Courts
The Constitutional Court of Romania works with European courts too.
It’s important to balance Romania’s own laws with European rules. This can be tricky.
The Court talks to the European Court of Human Rights and the Court of Justice of the European Union.
It often uses European court decisions when it makes its own.
This is true when it’s talking about basic rights.
The Court of Justice tries to respect both national laws and European rules.
This is a delicate balance that national courts have to handle.
When there are problems between Romanian laws and European rules, the Court tries to find a way to make them work together.
This is called harmonious interpretation.
It tries to keep Romania’s laws in line with European values.
But, the Court also says that Romania’s constitution is more important than European rules.
In Decision 668/2011, it said EU rules are more important than national laws, but not the constitution.
This shows Romania’s commitment to its own laws and European values.
This careful approach shows how the Court works in a system that respects both national and European laws.
It’s a way to balance different levels of law and keep things fair.
Types of Judicial Control in the Romanian Legal System
The Romanian legal system uses different judicial controls as key accountability tools.
These tools help keep all government branches in line and protect citizens’ rights.
Knowing about these controls helps you understand the Romanian legal system better and see how it keeps things transparent.
Preventive Judicial Control Measures
Preventive judicial control stops legal problems before they start. It keeps Romania’s judicial system strong and fair.
One important step is checking draft laws against the constitution. This makes sure laws are okay before they become law.
It helps avoid laws that go against the constitution.
Courts also give preliminary rulings on legal questions.
This helps clear up complex issues before they cause problems. It makes the legal process clearer.
Repressive Judicial Control
Repressive judicial control deals with legal problems after they happen.
It punishes wrongdoings and stops them from happening again. This strengthens judicial integrity.
Criminal sanctions are a big part of this control. Courts give penalties based on the Criminal Code.
These can be fines or jail time, depending on the crime.
Civil liability is another way to control wrongdoing.
Courts can order those who cause harm to pay for it.
Disciplinary actions for public officials also keep them in check.
Administrative Judicial Control
Administrative judicial control checks on government actions.
It’s key for keeping executive power in check and making sure government acts legally.
As a citizen, you can challenge government actions in administrative courts.
These courts check if government actions are legal and fair.
If government actions are wrong, courts can fix them.
They can cancel illegal acts, order payments for damages, or require specific actions.
This is a big part of keeping government accountable, affecting how citizens and government interact.
Judicial Control in Criminal Proceedings
The Romanian Criminal Procedure Code has special rules for criminal cases.
These rules make sure defendants are treated fairly and their rights are protected.
Prosecutors can use judicial control to keep an eye on defendants.
They can order reports to figure out damages caused by crimes.
This helps decide what actions to take and how to make things right.
Prosecutors can also freeze assets to protect victims’ interests.
This shows how judicial control helps with both fairness and justice.
Courts use different measures like bail, house arrest, or detention.
They consider the crime’s severity, the risk of flight, and the need to protect evidence.
These measures are reviewed often to make sure they’re fair and needed.
Through these controls, Romania’s legal system balances law enforcement and protecting rights.
The system keeps improving through judicial reform to make it more accountable and efficient.
Judicial Independence and Accountability in Romania
Romania’s judicial system is strong because it keeps its independence and follows democratic rules.
This balance is key to the rule of law in Romania.
Knowing how Romania balances judicial freedom with public oversight is important.
It shows how well the country’s democracy works and protects citizens’ rights.
Safeguards for Judicial Independence
Romania has set up many rules to protect the independence of judiciary in Romania.
These rules help judges make decisions based on law, without outside influence.
Key safeguards include:
- Constitutional rules that keep powers separate;
- Secure jobs for judges, so they can’t be removed easily;
- Enough money for judges, so they’re not influenced by it;
- The Superior Council of Magistracy acts as a shield against political interference;
- Judges have freedom in how they manage cases and make decisions.
These rules help judges do their jobs without fear.
The Romanian Constitution stops other branches of government from messing with the courts.
This sets clear limits for court jurisdiction in Romania.
But keeping judicial independence is hard. Politics, media, and public opinion can subtly affect judges.
The system must keep evolving to fight new threats while keeping its core protections.
Mechanisms for Judicial Accountability
Romania’s judicial system also has strong ways to check itself. These ways keep the judiciary oversight in Romania strong without hurting judicial freedom.
The main ways to check the judiciary include:
- The Superior Council of Magistracy can discipline judges and prosecutors
- Rules and standards for judges’ behavior
- Regular checks on judges’ performance
- Appeals that let higher courts review decisions
- The Constitutional Court can check laws that affect the judiciary
The disciplinary system is a key part of judicial accountability in Romania.
When judges are accused of wrongdoings, the Superior Council investigates and can punish them.
This balance ensures accountability without unfair punishment.
These checks aim to address wrongdoings without interfering with judges’ work.
The system makes a clear difference between holding judges accountable for bad behavior and respecting their role in interpreting the law.
Transparency Initiatives in the Romanian Judiciary
Transparency is key to balancing judicial independence and accountability in Romania.
By making court actions open to the public, transparency strengthens both judicial freedom and public oversight.
Romania has started several transparency efforts:
- Allowing public to see court hearings and decisions;
- Online platforms for case info and schedules;
- Requiring judges and prosecutors to declare their assets;
- Annual reports from courts and prosecutors;
- Rules for media access to ensure fairness.
These steps have greatly improved court supervision in Romania.
When people can see court decisions and understand why they were made, it builds trust in the fairness and impartiality of the system.
The Romanian judiciary also works to better communicate with the public.
Through educational programs and media offices, they aim to make legal processes clearer and more accessible to everyone.
Despite progress, challenges in transparency remain.
Some people may face technical barriers to information, and complex legal language can make it hard to understand.
Efforts continue to make judicial transparency more meaningful through simpler language and better digital access.
As Romania works to strengthen its judicial system, the balance between independence, accountability, and transparency will be key.
Challenges and Reforms in Romania’s Judicial Control System
Romania has made good progress in building democratic institutions.
Yet, it faces ongoing challenges in its judicial control system.
These challenges call for continuous reforms.
The journey toward effective judicial reforms in Romania has seen both successes and setbacks.
This journey reflects the complex task of transforming a post-communist legal system into one that meets European standards.
Reforms touch on key governance issues, including checks and balances in Romania and ensuring judicial independence.
Anti-Corruption Efforts and Judicial Reform
Romania’s fight against corruption is a key part of its judicial reform agenda.
The country has a detailed plan to fight corruption, involving many institutions at local and national levels.
This plan uses self-assessments and risk evaluations by institutions.
The National Anti-corruption Directorate (DNA) plays a big role in these efforts.
It has tackled high-profile cases against politicians, judges, and business leaders.
This shows that anti-corruption efforts in Romania can lead to real results with the right support.
But, the anti-corruption strategy’s success has been measured mainly by its implementation level.
This level has dropped significantly after 2019.
The Government set clear goals in August 2016, but progress has been slow.
This slowdown shows the political challenges and resistance to anti-corruption efforts in Romania.
EU Cooperation and Verification Mechanism
When Romania joined the European Union in 2007, the EU set up the Cooperation and Verification Mechanism (CVM).
This tool monitored and guided judicial reforms.
It set specific goals for Romania in judicial independence, integrity, and anti-corruption.
The CVM has been a driving force and a measure for judicial reforms in Romania.
Recent Legislative Changes Affecting Judicial Control
The last decade has seen many changes to Romania’s justice laws and criminal codes.
These changes have sparked debates about their impact on judicial independence and constitutional oversight in Romania.
Between 2017 and 2019, several laws changed how the judiciary works.
Critics say these changes hurt judicial independence and weaken anti-corruption efforts.
The changes affected magistrates’ status, judicial inspection, and prosecutor appointments.
More recent laws aim to address these concerns.
But the legal framework is always changing.
Keeping it stable and coherent is key for effective checks and balances in Romania and public trust in the judiciary.
International Perspectives on Romanian Judicial Reforms
Romania’s judicial reforms have caught the world’s attention.
Many bodies have given their opinions and advice.
The European Commission, through the CVM, has closely watched Romania’s progress in constitutional oversight Romania.
The Venice Commission has also weighed in, stressing judicial independence and checks and balances in Romania.
Their opinions have highlighted both good steps and areas needing more work.
International groups like GRECO and UN bodies have also offered their views.
Their input has shaped the reform agenda and set benchmarks for judicial reforms in Romania.
While outside opinions can be controversial, they are essential for a strong reform process.
They bring independent expertise and keep focus on international standards.
This international view is vital for Romania’s judicial system to grow.
Practical Aspects: How Judicial Control Affects Your Rights in Romania
Judicial control in Romania affects everyone’s rights.
It offers important protections in civil and criminal cases.
Knowing how it works helps you deal with legal issues and keep your rights safe.
Whether you’re in a legal fight, questioning a government decision, or just want to know your rights, Romania’s system has your back.
It offers many ways to seek help.
Protection of Fundamental Rights through Judicial Control
Romania’s courts protect your constitutional rights and freedoms.
They act as guardians when your rights are broken.
The constitutional right to a fair trial is key, ensuring legal processes are fair and respect your rights.
Courts also check if the state acted unfairly.
If a government decision harmed your rights, you can challenge it.
They can cancel bad decisions and order fixes, like paying for damages.
A new law helps those who speak out against wrongdoings.
Law no. 361/2022 on whistleblower protection gives strong support.
It protects those who report corruption or other wrongs from being punished.
Navigating the Court System as an Individual
The Romanian courts system has four levels: local courts, tribunals, courts of appeal, and the High Court of Cassation and Justice.
Knowing which court to go to is the first step.
Civil cases start in local courts, while bigger cases begin at the tribunal.
When you start a legal case, you must follow certain rules and deadlines.
For civil cases, you have three years to act.
Criminal complaints have a two-month limit, but serious crimes give you more time.
Court documents in Romania are standard but hard to understand without a Romanian lawyer.
Your first step, the complaint, must include who you are, what happened, why it’s wrong, and what you want.
If you miss these details, your case might be thrown out.
Legal Remedies Available to Citizens
Romania has many ways to fix rights issues.
Constitutional complaints let you question laws that affect your case.
These complaints start in your court case and then go to the Constitutional Court.
Administrative appeals are another key option.
Before going to court, you must try to fix the problem with the authority first. If they don’t help, you can go to court.
If Romanian courts can’t help, you can try the European Court of Human Rights.
But, you must have tried everything in Romania first.
You also have four months to apply after the last decision in Romania.
Seeking Legal Assistance for Judicial Control Matters
Getting help from a Romanian lawyer for judicial control is often a good idea.
They can help plan your case and speak for you in court.
For criminal cases, a criminal lawyer in Bucharest or Romania can be very helpful.
Legal aid is for those who can’t afford a lawyer.
The National Legal Aid Bureau can assign a lawyer if you qualify. You need to show you can’t afford one.
You can apply at your court or local bar association.
For complex cases, like administrative or constitutional issues, a Romanian law office for judicial control can help.
Services like Atrium Romanian Lawyers (contact: office@theromanianlawyers.com) offer the needed expertise.
The Romanian Criminal Code also protects those who report corruption.
Reporting a bribe before it’s known can give you special protection.
This shows Romania’s commitment to constitutional democracy and the rule of law.
Conclusion: The Future of Judicial Control in Romania
Romania’s judicial control system is changing.
It’s balancing old traditions with new European rules.
To have a clear justice system, everyone in Romania must keep working together.
When dealing with your rights, remember that judicial control is key.
Recent reforms have made public authorities more accountable.
They’ve also tackled some big challenges.
Digital changes offer chances to make justice better in Romania.
These technologies can make justice more accessible.
They also protect human rights, which are vital for democracy.
The success of judicial control relies on public involvement.
Your active role ensures reforms strengthen, not weaken, judicial independence.
If you have legal questions about judicial control in Romania, help is available at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
With active citizens and dedicated Romanian lawyers, Romania’s justice system can protect democracy and rights.
FAQ
What is judicial control in Romania?
How is the Romanian court system structured?
What is the difference between judicial control and judicial review in Romania?
What role does the Constitutional Court play in Romania’s judicial control system?
How does Romania ensure judicial independence?
What types of judicial control exist in criminal proceedings in Romania?
How has EU membership influenced Romania’s judicial control system?
What is the role of the Superior Council of Magistracy in Romania?
How can Romanian citizens challenge unconstitutional laws?
How does administrative judicial control work in Romania?
What legal assistance is available for judicial control matters in Romania?
How does the Romanian Constitutional Court interact with European courts?
What reforms have been implemented to strengthen judicial control in Romania?
How can individuals navigate Romania’s court system effectively?
What constitutional safeguards protect the judiciary in Romania?
What is judicial control in Romania and how does it function?
Judicial control in Romania represents a system of checks and balances through which the courts oversee the legality of actions taken by public administration and other authorities.
This control mechanism is fundamental to the rule of law in the Romanian legal framework.
At its essence, judicial control ensures that administrative actions comply with the Constitution and applicable laws.
The Romanian system of judicial review operates through specialized administrative courts that have the power to examine and potentially invalidate administrative acts that are found to be contrary to higher legal norms.
This system serves as a guarantee of citizens’ rights against potential abuses by state institutions.