Business Transfers in Romania: Fiscal and Legal Insights
Business Transfers in Romania: Fiscal and Legal Insights
In Romania, only 14 Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs) were active by the end of 2020.
This shows how complex business transfers can be.
To navigate these, you need to understand the legal and fiscal rules well.
Thinking about buying a company in Romania?
You’ll face a complex set of rules.
Romania doesn’t have one law for all mergers and acquisitions.
Instead, it uses the civil code and many special laws.
To smoothly transfer ownership in Romania, you must know the local laws, taxes, and strategies.
Getting help from experts is key to understanding the complex world of Romanian business transfers.
Key Takeaways
- Romanian business transfers require sophisticated legal and fiscal expertise;
- No uniform M&A regulation exists in Romanian legislation;
- Civil code serves as primary legal framework for transactions;
- Complex tax and pricing documentation is mandatory;
- Professional consultation is essential for successful transfers.
Understanding the Romanian M&A Landscape
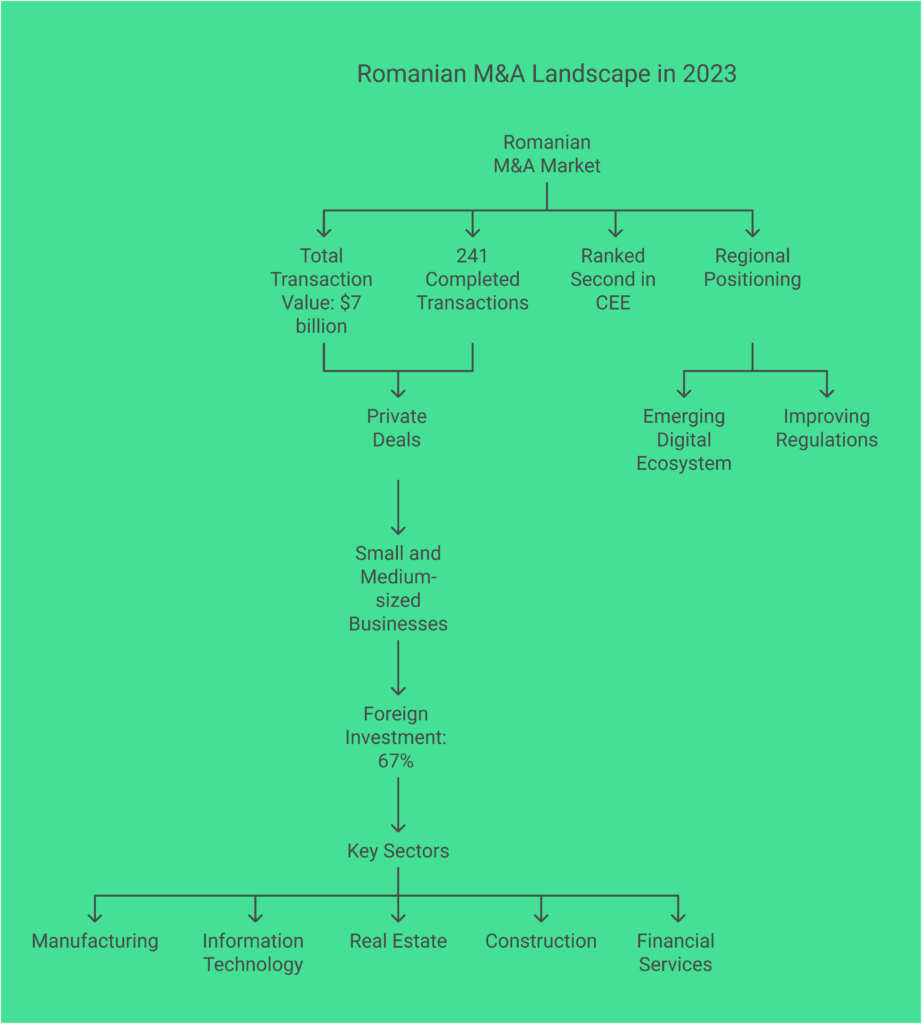
The Romanian mergers and acquisitions scene is growing fast.
It’s becoming a top spot for companies looking to change their structure.
The market is full of chances for growth and strategic moves.
In 2023, the Romanian M&A market showed it’s strong.
Key signs point to its bright future:
- Total transaction value reached approximately 7 billion dollars;
- 241 completed ownership transition transactions;
- Ranked second in Central and Eastern European M&A activity.
Market Dynamics and Trends
Most deals in Romania are private. Small and medium-sized businesses lead the way.
About 67% of deals come from outside, showing investors’ keen interest.
Sectoral Breakdown
The top sectors for mergers and acquisitions in Romania are:
- Manufacturing;
- Information Technology;
- Real Estate;
- Construction;
- Financial Services.
Regional Positioning
Romania is a major player in Central and Eastern Europe’s M&A scene.
Its location, emerging digital ecosystem, and improving rules attract investors.
They see great chances for restructuring their businesses here.
Legal Framework Governing Business Transfers in Romania
Understanding the legal side of business transfers in Romania is key.
The rules are based on both national laws and EU directives.
This makes the process for handing over a business in Romania quite detailed.
Important legal parts of business transfers in Romania include:
- Directive (EU) 2017/1132 on company law aspects;
- Directive (EU) 2019/2121 addressing cross-border conversions;
- Romanian Companies Law (Law 31/1990);
- Financial Services Authority Regulation No. 5/2018.
Your plan for transferring a business must follow certain rules.
The Romanian laws set important rules and steps for business deals:
- Controlling interest is defined as holding 50% plus one voting right;
- Public takeovers become mandatory when an investor holds over 33% voting rights;
- Shareholders with more than 5% ownership can propose valuation methods;
- Mandatory notifications are required at specific ownership thresholds.
When you plan to transfer a business, you must follow strict rules.
Filings related to business combinations must be submitted within 24 hours of triggering events.
Also, merger plans need to be published in the Official Gazette of Romania.
International investors should know about recent changes.
Government Emergency Ordinance No. 108/2023 has made rules for foreign direct investment clearer.
This adds more complexity to business transfers in Romania.
Types of Business Transfers and Acquisitions
When thinking about company ownership changes in Romania, it’s key to know the different ways to transfer businesses.
Business leaders face complex choices between mergers, acquisitions, and other transfer methods.
These choices can greatly affect their business strategies.
In Romania, business succession planning mainly focuses on two main types: share deals and asset deals.
Each type has its own legal, financial, and operational implications for corporate transfers.
Mergers and Their Characteristics
Mergers are a complex way to join two companies into one. In Romania, mergers often mean:
- Combining corporate structures;
- Shared leadership and strategy;
- Benefits in taxes and operations.
Acquisition Structures
Acquiring a business in Romania can be complex, with many strategies for different goals.
The main acquisition types are:
- Buying the whole target company;
- Buying a part of it;
- Making a strategic minority investment.
Asset vs. Share Deals
| Characteristic | Asset Deals | Share Deals |
|---|---|---|
| Transferable Elements | Specific assets and some liabilities | Whole company ownership |
| Tax Implications | Seller pays taxes | 16% capital gains tax for locals |
| Complexity | More complex due to asset-by-asset transfers | Smaller complexity in ownership change |
For commercial enterprise transfer in Romania, knowing these detailed strategies helps businesses pick the best one.
This choice should match their goals and the market situation.
Foreign Direct Investment Regulations
Romania is a great place for business ownership change.
It has a solid framework for foreign direct investment (FDI).
This framework helps attract international investors.
It also guides foreign buyers on how to start or grow their business here.
Here are some important points about Romania’s FDI rules:
- Mandatory screening for investments over €2 million;
- Comprehensive national security and public order checks;
- Environmental protection compliance requirements;
- Specific sector-specific investment scrutiny.
Foreign investors need to understand Romania’s detailed rules when considering a business transfer here.
The investment screening process makes sure investments fit with national interests.
At the same time, it keeps the country open to investors.
| FDI Regulation Highlights | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Screening Fee | €10,000 (refundable under certain conditions) |
| Maximum Review Duration | 135 days |
| Penalty for Unauthorized Investments | Up to 10% of worldwide turnover |
The Romanian FDI regime strikes a good balance.
It attracts foreign investments while safeguarding national interests.
Investors need to look closely at sector-specific rules, like in energy, telecommunications, and critical infrastructure.
Foreign investors should know about the detailed screening process for ownership changes.
The rules ensure transparency and national security.
They don’t block international business investments.
Business Transfer in Romania: Process and Requirements
Starting a commercial enterprise succession in Romania needs careful planning.
The process involves many important steps.
These steps focus on legal and financial details.
Understanding the framework for business transfers in Romania is key.
The process aims for transparency, legal compliance, and a smooth transfer of ownership.
Pre-Transfer Assessment
The first step is a detailed pre-transfer evaluation.
This phase is critical and includes:
- Comprehensive financial review;
- Valuation of company assets;
- Identification of legal risks;
- Verification of contracts.
Documentation Requirements
Business transfers need careful documentation.
You’ll need:
- Detailed financial statements;
- Shareholder agreements;
- Corporate registration documents;
- Tax compliance certificates.
| Document Type | Legal Requirement | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|
| Share Transfer Approval | 75% Share Capital Consent | 7-14 Days |
| Registration Certificate | Romanian Companies Law | 10 Days |
| Tax Clearance | Mandatory Verification | 5-7 Days |
Legal Compliance Steps
Legal compliance is essential for a smooth transfer.
Key steps are:
- Notifying authorities;
- Getting Competition Council approvals;
- Completing registration processes.
Seeking expert legal advice is recommended.
For professional help, call our recommended Romanian legal experts at +40765366887.
Due Diligence in Romanian Business Transfers
When buying a company in Romania, due diligence is key.
It helps lower risks and makes sure the transfer goes well.
This step checks the investment in many ways.
When planning mergers and acquisitions in Romania, focus on several important areas:
- Financial review of historical performance;
- Legal compliance verification;
- Operational infrastructure assessment;
- Commercial and market analysis.
Business sales in Romania need careful checking.
Investors should look closely at financial reports, legal papers, and any rules that might affect the business.
| Due Diligence Category | Key Focus Areas | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Revenue streams, profit margins | Hidden liabilities |
| Legal | Contractual obligations | Pending litigation |
| Operational | Technology infrastructure | Inefficient processes |
Experts say using new tech and getting help from experts is smart.
Good planning can really cut down on risks.
With a thorough due diligence, you’ll have a better shot at making a successful deal in Romania’s fast-changing market.
Tax Implications and Fiscal Considerations
Understanding tax laws in Romania is key for corporate transactions.
When you’re handling ownership changes, you’ll face many financial issues.
These can greatly affect your business strategy.
Romanian tax laws are complex for financial transfers.
Knowing the main tax points is vital.
It helps avoid risks and get the best financial results from your deal.
Transfer Pricing Requirements
The Romanian Fiscal Code requires strict rules for deals between related parties.
There’s been a rise in tax audits on these issues.
- Mandatory documentation for related-party transactions;
- Comprehensive reporting requirements;
- Potential penalties for non-compliance.
VAT Implications
VAT is a big deal in business transfers.
Romania has its own VAT rules that businesses must follow:
- Standard VAT rate: 19%
- Reduced VAT rates: 9% and 5% for specific supplies
- VAT registration threshold: RON 300,000 annually
Corporate Tax Aspects
Corporate tax strategies are important for business transfers.
You need to think about tax liabilities, exemptions, and new laws.
Tax planning is essential to optimize your financial position during ownership transitions in Romania.
Strategic Sectors and Special Regulations
When you’re doing commercial transfers in Romania, knowing about strategic sectors is key.
The Romanian government watches business deals in important areas closely.
These areas affect national security and public order.
Foreign investors face a tough approval process in sensitive sectors.
The Commission for the Examination of Foreign Direct Investments (CEISD) checks these deals carefully.
Key Strategic Sectors Requiring Special Approval
- Energy infrastructure;
- Transport systems;
- IT and communication networks;
- Financial and banking services;
- Critical national infrastructure;
- Security-related industries.
For sales of companies in these key sectors, investors need special approvals.
The rules require a close look at deals over 2 million euros.
Recently, laws have changed, like the updates to Emergency Ordinance 46/2022.
These changes help protect national interests but also keep the investment climate good.
Investment Approval Considerations
- Comprehensive security assessment;
- Evaluation of national security risks;
- Check on the investor’s background;
- Look at how the deal affects key sectors.
Knowing these rules is vital for smooth business transfers in Romania’s strategic sectors.
Investors should team up with local legal advisors to get through these complex steps.
Role of Regulatory Bodies and Authorities
When you transfer business ownership in Romania, knowing the role of key regulatory bodies is key.
Your journey in corporate restructuring will meet several important authorities.
They oversee and validate business transactions.
Romanian business transfers need several regulatory frameworks for transparency and compliance.
These key institutions are vital in monitoring and approving corporate changes.
Competition Council Oversight
The Competition Council is a key watchdog in firm handovers. It has main duties:
- Preventing anti-competitive market practices;
- Reviewing merger and acquisition impacts;
- Evaluating economic concentration transactions;
- Protecting fair market competition.
When you transfer business ownership in Romania, you must tell the Competition Council for certain transactions.
This keeps the market transparent and stops monopolies.
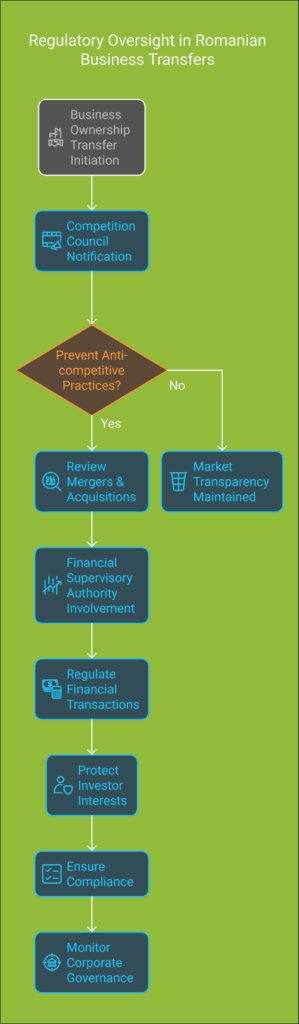
Financial Supervisory Authority Functions
The Financial Supervisory Authority (ASF) is key in corporate restructuring in Romania, mainly for financial institutions and listed companies. Its main tasks are:
- Regulating financial market transactions;
- Protecting investor interests;
- Ensuring compliance with financial regulations;
- Monitoring corporate governance standards.
Your business transfer plan must meet these regulatory needs for smooth, legal transactions in various sectors.
Knowing these regulatory frameworks helps you confidently and strategically navigate Romanian business transfers.
Cross-Border Transaction Considerations
Foreign investors must grasp the complex world of corporate takeovers in Romania.
The country has a strong legal setup to help with ownership changes.
It also protects national interests.
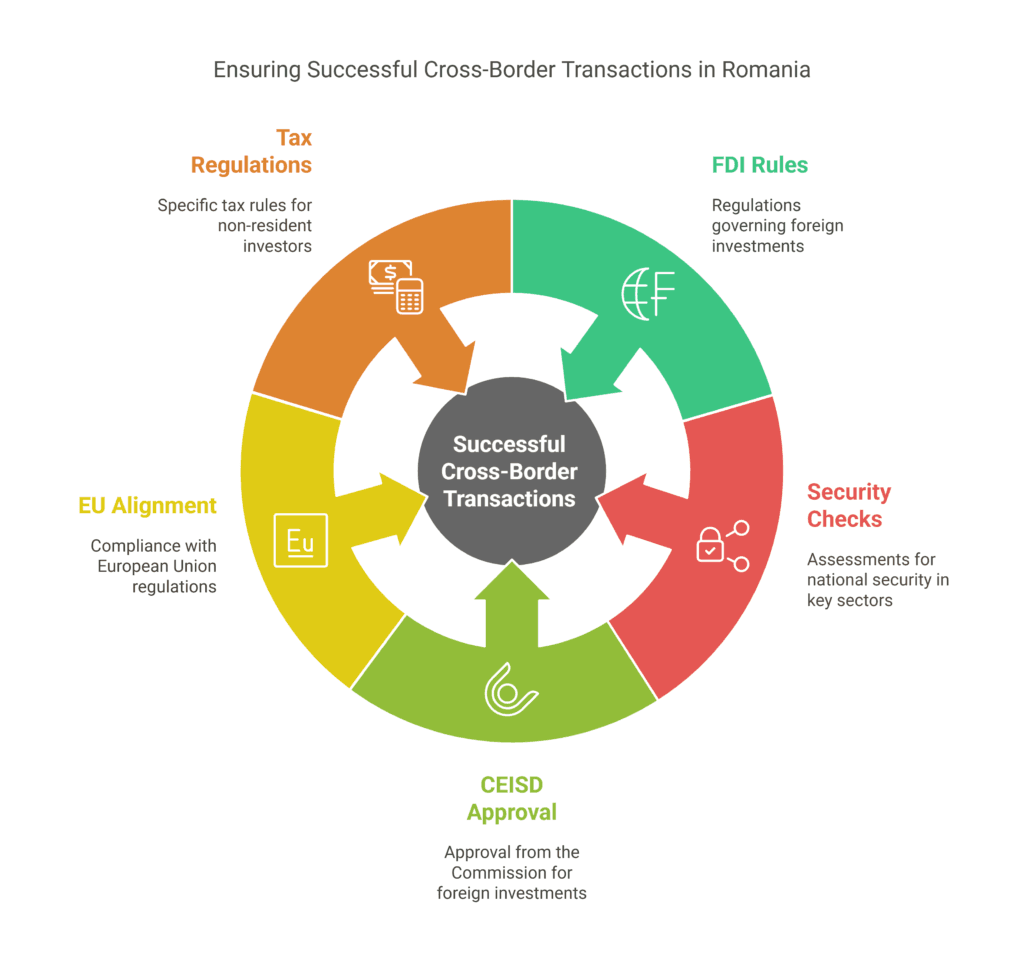
Key points for cross-border deals include:
- Following Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) rules;
- Security checks for key sectors;
- Getting approval from the Commission for the Examination of Foreign Direct Investments (CEISD);
- Aligning with EU rules.
The Romanian government has rules to attract foreign investment safely.
Foreign buyers need to know a few important things:
- They must report investments in sensitive areas;
- There could be a 5-8 month wait for FDI approval;
- They need to show detailed ownership details.
Taxes are very important in cross-border deals. Non-resident investors should know about specific tax rules:
| Transaction Type | Withholding Tax Rate | Special Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Dividends | 8% | 0% for EU companies with 10%+ shareholding |
| Interest | 16% | Potential exemptions under EU directives |
| Royalties | 16% | Reduced rates for specific agreements |
It’s vital to understand these detailed rules for successful deals in Romania.
You must look at legal, financial, and regulatory aspects.
This ensures a smooth change in ownership.
Recent Legislative Changes and Future Outlook
Romania’s business world is changing a lot in 2024.
This brings new chances for selling businesses and changing how companies work.
The rules for buying and selling companies are getting clearer.
Important changes are making the Romanian business scene different.
These changes affect how businesses operate:
- Government Decision 300/2024 makes it easier to invest;
- Emergency Ordinance 32/2024 changes how money is handled;
- New rules for foreign investments.
2024 Regulatory Updates
Romania wants to make it easier for investors to come in.
If you’re thinking about selling your business in Romania, you’ll find it easier to start a new one.
The rules are clearer now.
Anticipated Changes
Romania’s economy is looking good, with a 3% GDP growth forecast for 2024-2025.
The government plans to make things better for businesses by:
- Making it easier to transfer businesses;
- Following EU rules;
- Welcoming more foreign investments.
If you’re looking to buy a business in Romania, now is a great time.
The mix of EU money and economic changes makes it a good place to invest.
Conclusion
Business divestment in Romania is complex and needs careful planning and legal knowledge.
When looking at corporate acquisitions, you must understand the detailed rules for business ownership changes in Romania.
This process includes legal steps, financial checks, and making strategic choices.
Your success in Romanian business transfers depends on thorough preparation and expert advice.
With about 690,000 small and medium-sized enterprises possibly changing hands soon, knowing the legal details is key.
The rules, like Law no. 31/1990, require focus on things like share transfer agreements and shareholder approvals.
Getting professional legal help is vital for these complex deals.
Romanian corporate law asks for accurate documents, like share transfer agreements and updated Articles of Association.
Working with skilled corporate lawyers can help avoid risks and make sure your business moves smoothly and legally.
For expert help with your business transfer, call Romania business transfer expert at tel. +40765366887.
Your careful planning will be key to the success of your corporate deal or business sale in Romania’s fast-changing market.
FAQ
What are the main types of business transfers in Romania?
In Romania, you can transfer businesses through mergers, acquisitions, asset deals, or share deals.
Mergers combine two companies into one.
Acquisitions mean one company buys another.
Asset deals transfer specific business assets, and share deals change who owns the company.
What are the key regulatory bodies involved in business transfers in Romania?
Several key groups watch over business transfers in Romania.
The Competition Council stops unfair competition.
The Financial Supervisory Authority looks after financial sector deals.
The Commission for the Examination of Foreign Direct Investments (CEISD) checks foreign investments.
What additional requirements exist for foreign investors in Romanian business transfers?
Foreign investors face extra rules, like national security checks under Emergency Ordinance 46/2022.
They must get extra approvals in key areas like energy and IT.
The CEISD reviews these deals to protect Romania’s interests and welcome foreign money.
How important is due diligence in Romanian business transfers?
Due diligence is very important in Romanian business transfers.
It checks the target business’s finances, laws, operations, and sales.
A good due diligence helps avoid risks and makes the transfer smooth.
It’s best to get experts to do a detailed check.
What tax considerations are critical in Romanian business transfers?
Important tax issues include following the arm’s length principle, VAT, and corporate taxes.
With more audits on transfer pricing, it’s key to document and justify prices.
You should also think about tax breaks, delays, and new tax laws that might affect your deal.
What are the primary challenges in cross-border business transfers in Romania?
Dealing with international rules is a big challenge in cross-border transfers in Romania.
You face issues like currency, legal systems, security checks, and taxes.
Getting help from Romanian legal and financial experts is vital for these complex deals.
How has the Romanian M&A landscape changed in recent years?
The Romanian M&A market has seen big changes, like the COVID-19 pandemic and global tensions.
Romania is a strong player in Central and Eastern Europe, with more interest in tech, green energy, and finance.
New laws aim to make it easier for foreign investors to come in.
What documentation is typically required for a business transfer in Romania?
You’ll need lots of documents for a business transfer in Romania.
These include financial statements, legal papers, shareholder agreements, and tax certificates.
Depending on the deal, you might also need environmental reports, security clearances, and more.