Understanding Child Support Obligations in Romania
Understanding Child Support Obligations in Romania
In Romania, up to 50% of a parent’s income can go to child support.
This shows how critical child support is.
If you’re going through a divorce, knowing these laws is vital for your child’s care.
Child support in Romania is more than just money.
It’s a promise to your child’s future, no matter who they live with.
The Romanian laws make sure both parents help with their child’s needs.
Understanding how to handle child support is essential.
The Romanian Civil Code has rules for child support.
These rules help balance what the child needs with what the parents can afford.
Exploring child support in Romania can be complex.
But, getting help from a legal expert can make a big difference.
For advice tailored to your case, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Key Takeaways
- Child support can be up to 50% of a parent’s net income;
- Support obligations last until the child is 18, or 26 if they’re in school;
- Courts look at the average income from the last year;
- Not paying for 3 months can lead to criminal charges;
- Child support orders can change if there’s a big change;
- Expert legal advice is available at office@theromanianlawyers.com
What is Child Support Under Romanian Law
Child support in Romania is a key part of family law.
It makes sure parents take care of their kids, even if they’re not together.
The law says child support is money for kids’ basic needs and to help them grow well.
Legal Definition and Purpose
The Romanian Civil Code says child support is a parent’s duty.
It covers things like food, clothes, and education.
The main aim is to keep the child’s life stable and help them grow right.
Scope of Financial Support
Child support includes many costs for a child’s care.
These are:
- Housing costs;
- Educational expenses;
- Medical care;
- Extracurricular activities;
- Clothing and personal items.
Duration of Support Obligations
Support usually lasts until the child is 18.
But, it can go longer if the child keeps studying or has special needs.
The exact time depends on the situation and what the Court decides.
Child Support Obligations in Romania
In Romania, laws clearly state that parents must support their children.
Both custodial and non-custodial parents have specific duties.
These laws help ensure kids get the financial support they need for their upbringing and education.
Child support in Romania is based on the non-custodial parent’s income.
Here’s how it works:
| Number of Children | Percentage of Net Monthly Income |
|---|---|
| 1 child | Up to 25% |
| 2 children | Up to 33% |
| 3 or more children | Up to 50% |
Parents must support their children until they are 18.
If a child goes to college, support can last until they are 26.
Romanian laws also cover extra costs like education, medical bills, and activities outside school.
If a parent doesn’t pay child support, they could face serious penalties.
Not paying for three months or more can lead to jail time or fines.
Courts can also take money from wages or seize assets to make sure kids get the support they need.
Calculating Child Support Payments
Understanding child support in Romania is key for parents.
The Romanian legal system has a clear way to figure out fair payments.
This ensures kids get the financial help they need.
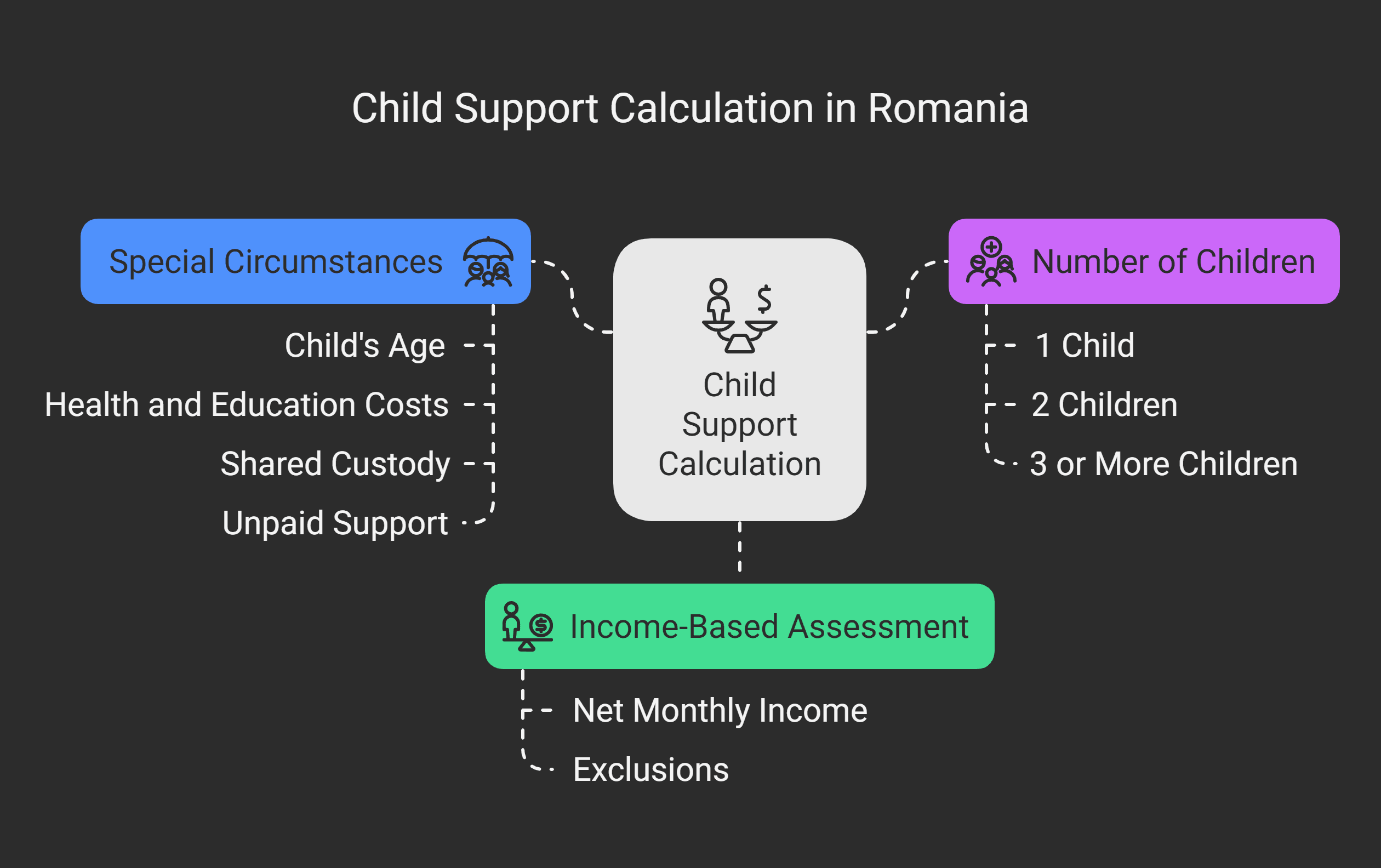
Income-Based Assessment
Child support starts with looking at the paying parent’s income.
Courts check the net monthly income, including salaries and permanent benefits.
But, they don’t count occasional incomes.
They usually look at the income over the past year.
Number of Children and Payment Percentages
The number of kids affects child support in Romania.
Here’s how it works:
| Number of Children | Maximum Percentage of Net Income |
|---|---|
| 1 child | Up to 25% |
| 2 children | Up to 33% |
| 3 or more children | Up to 50% |
It’s important to remember.
The total support a debtor owes can’t be more than 50% of their income.
Special Circumstances
Courts look at special situations when setting child support in Romania.
Things like the child’s age, health, and education costs matter.
They also consider the child’s standard of living.
If there’s shared custody or special needs, the court might change the percentages.
For unpaid child support in Romania, legal steps can be taken.
This could mean taking money from wages or seizing assets.
Keep in mind, child support orders don’t go back in time.
The obligation starts from when the court order was made or the support request was filed.
Legal Framework for Child Maintenance
Romania has a strong legal system for child support.
It’s based on Romanian family law and international agreements.
This ensures fair child support and allows for changes when needed.
Romanian Civil Code Provisions
The Romanian Civil Code is key for child support rules.
It explains who must support whom in families.
Article 513 talks about legal support duties, and Article 519 shows who comes first.
The code says child support lasts until the child is 26.
This ensures they are financially secure for a long time.
Family Law Statutes
Family laws in Romania add more details to child support rules.
They cover important points like:
- Non-transferability of maintenance obligations;
- Inclusion of essentials like food, clothing, and healthcare in support;
- Responsibilities of heirs in continuing support for minors.
International Agreements
Romania is part of important international child support agreements.
The 2007 Hague Protocol helps decide which laws apply for support in EU countries.
This makes sure support is enforced across borders.
The European Judicial Network has created standard forms for maintenance issues.
These forms are in 23 languages.
They help make recovering support easier and more efficient for everyone.
Rights and Responsibilities of Parents
In Romania, parents have more than just financial duties.
The law, mainly Law no. 272/2004, puts the child’s needs first.
This rule applies to all kids with Romanian citizenship, both in Romania and abroad, and to non-citizen kids living in Romania.
Parents must work together to care for their child.
This includes helping with their health and growth.
Even if they live apart, both parents are responsible for the child’s upbringing.
When parents split up, they must agree on where the child will live.
If they can’t agree, a court will decide what’s best for the child.
Parents also have to pay for things like school, medical bills not covered by insurance, and activities outside of school.
The law makes sure they do this.
It also says kids should keep in touch with both parents, unless it’s not good for them.
- Parents must register children immediately after birth;
- Birth certificates must be issued within 24 hours;
- Parents must notify police within 24 hours if a child goes missing;
- Both parents have the right to participate in decisions affecting the child.
Knowing these rights and duties helps parents meet their obligations.
It’s important for both parents to be involved in their child’s life and financial support, no matter who has custody.
Enforcement of Child Support Orders
Romania takes child support very seriously.
The country has strong laws to make sure parents pay up.
This part talks about how Romania enforces child support orders, including legal actions, wage garnishment, and criminal penalties.
Legal Consequences of Non-Payment
If a parent doesn’t pay child support in Romania, they face big problems.
The laws allow for strict measures.
Parents who don’t pay can get sued and have to pay fines.
Wage Garnishment Procedures
Wage garnishment is a common way to enforce child support.
Courts can tell employers to take money from the non-paying parent’s paycheck.
The amount taken depends on how many kids there are:
- 25% of net monthly income for one child;
- 33% for two children;
- 50% for three or more children.
Criminal Penalties
For those who keep not paying, Romania has harsh penalties.
Article 305 of the Romanian Penal Code says parents who don’t pay for three months can get jailed for 6 months to 3 years or fined.
This shows how serious Romania is about child support.
| Number of Children | Maximum Garnishment | Criminal Penalty for Non-Payment |
|---|---|---|
| One | 25% of net income | 6 months – 3 years imprisonment or fine |
| Two | 33% of net income | 6 months – 3 years imprisonment or fine |
| Three or more | 50% of net income | 6 months – 3 years imprisonment or fine |
These steps help make sure kids get the money they need.
Romania’s efforts to enforce child support show its commitment to kids’ rights and well-being.
Modification of Support Orders
Child support orders in Romania can change.
Life events can affect your financial duties.
It’s important to know when and how to update these orders.
Changed Circumstances
Big life changes can mean you need to adjust child support payments.
Losing a job, getting a new one, or changes in your child’s needs can all require updates.
For example, if you lose your job, you might ask for lower payments.
Court Petition Process
To change a support order, you must ask the court.
You’ll need to show evidence of your new situation.
The court will look at your income and your child’s needs.
Documentation Requirements
Having the right documents is essential when asking for changes.
You’ll need to show proof of income changes, like pay stubs or tax returns.
For shared custody, you might also need to prove changes in parenting time or expenses.
Remember, not paying child support in Romania can lead to serious penalties.
This includes fines or even jail time.
It’s better to handle changes legally than to stop payments yourself.
Even with international child support, you can make changes with the right documents and legal advice.
Cross-Border Child Support Cases
Cross-border child support cases in Romania are complex.
They happen when one parent lives outside Romania.
This makes it hard to enforce child support orders.
Romania works with other countries to help with this through international agreements.
Romania is part of global treaties that make handling child support easier.
These agreements help make sure children get the financial support they need, no matter where their parents are.
The Romanian legal system helps keep child custody and support orders in place, even across international borders.
Family law in Romania understands the challenges of these cases.
It offers ways for parents to deal with legal systems in other countries.
Romanian courts can make orders that work in other countries, and they can also enforce orders from other countries.
Parents in cross-border cases should get legal advice to know their rights.
Romanian authorities make sure a child’s right to support is not affected by distance.
They always focus on what’s best for the child in legal matters.
Conclusion
Understanding child support in Romania is key for parents going through divorce or unmarried parents wanting to know their rights.
The Romanian legal system puts children’s well-being first.
It has clear rules for what parents owe their kids.
Romanian law says child support is money parents give to their kids until they’re 18.
How much they pay depends on their income, how many kids they have, and other special cases.
The laws in the Romanian Civil Code and Family Law make sure child support is fair and the same for everyone.
Not paying child support in Romania is taken very seriously.
If someone doesn’t pay, they might have their wages taken or face criminal charges.
Parents can ask to change how much they pay if their situation changes.
But, they must go through the right court steps and show the needed documents.
If you’re dealing with child support in Romania and it’s complicated, getting help from a lawyer is a good idea.
For expert advice on child support in Romania, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
They can help based on your specific situation.
FAQ
What is the legal definition of child support in Romania?
In Romania, child support means the money parents must give to their kids for basic needs.
This includes food, clothes, and education.
It’s part of the family law to help kids grow up well.
How long do child support obligations typically last in Romania?
In Romania, child support usually lasts until a child is 18.
But, if a child keeps studying or has special needs, support can go longer.
How are child support payments calculated in Romania?
Payments in Romania depend on how much the paying parent earns.
The court looks at income, how many kids there are, and what the kids need.
Payments are usually 16% to 25% of the parent’s income, based on the number of kids.
Can child support orders be modified in Romania?
Yes, orders can change in Romania if things like income or needs change.
To ask for a change, a court petition is needed.
What are the consequences of not paying child support in Romania?
Not paying child support in Romania can lead to big problems.
You might face wage garnishment, fines, or even jail.
The law takes child support very seriously.
How are cross-border child support cases handled in Romania?
Romania deals with child support across borders through treaties.
Courts try to enforce orders, but it can be tricky because of legal and money differences.
What rights do non-custodial parents have regarding child support in Romania?
Non-custodial parents in Romania can ask for support changes if their situation changes.
They also have the right to be involved in their child’s life and have a relationship with them.
Are there special considerations for child support in cases of shared custody?
Yes, shared custody changes how child support is figured out in Romania.
The court looks at how much time each parent spends with the child.
But, the main goal is to make sure the child’s needs are met.
How does Romanian law handle child support for children with special needs?
Romanian law knows kids with special needs might need more money.
The court might order more support or keep it going longer to meet their needs.
Can parents make their own child support agreements in Romania?
Parents in Romania can make their own agreements, but the court must approve it.
The court checks if it’s good for the child and follows the law before saying yes.
What are the basic child support laws in Romania?
In Romania, child support (known as “pensie de întreținere” in Romanian) is regulated by the Romanian Civil Code and family law provisions.
According to Romanian law, both parents have a legal obligation to provide financial support for their minor child, regardless of whether they have child custody.
The Romanian Civil Code (Law no. 287/2009) specifically addresses child support obligations in Articles 499-531, emphasizing that supporting one’s children is both a moral and legal duty.
The principle underlying child support in Romania is always the best interests of the child, ensuring their proper development and well-being.
This obligation to provide financial support continues until the child reaches 18 years of age, but may extend if the child continues their education or has special needs.
Even when parents divorce or separate, their financial responsibilities toward their children remain unchanged under Romanian family law.
How is the amount of child support calculated in Romania?
The amount of child support in Romania is determined based on several factors, primarily the child’s needs and the parents’ financial circumstances.
Generally, the Romanian Civil Code establishes that child support payments should be approximately 1/4 of the paying parent’s net income for one child, 1/3 for two children, and 1/2 for three or more children.
However, these percentages are not strictly binding, as courts have discretion to adjust the amount of child support based on specific circumstances.
When determining the appropriate amount, courts consider the child’s age, educational needs, health requirements, and standard of living before the parents’ separation.
Additionally, the courts examine both parents’ income, earning capacity, and other financial obligations.
A child support lawyer in Romania can help navigate these calculations and ensure that the support order reflects fair consideration of all relevant factors.
The court may also periodically review and adjust the amount of child support if there are significant changes.