Winning Strategies for Criminal Defense in Romania
What happens when your freedom is at risk in Romania’s complex legal system?
Facing legal charges is one of life’s toughest experiences.
Romania’s legal framework is unique, requiring specialized knowledge and strategic approaches.
Our team has over three decades of experience in economic crime cases.
We know the legal defense tactics that work in Romanian courts.
The system demands knowledge of laws and practical expertise in evidence assessment and procedural nuances.
Effective legal representation greatly impacts case outcomes.
Our specialists have developed methods to protect clients’ rights.
They navigate the complexities of criminal proceedings from pre-trial investigations to appeals.
This guide explores proven defense strategies in Romania’s legal framework.
It offers insights for those facing charges.
Understanding these elements is key to developing strong protection strategies and ensuring due process is followed.
For professional legal help, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Talk to attorneys who specialize in Romanian jurisprudence.
Key Takeaways
- Specialized knowledge of Romanian legal procedures is key for effective defense;
- Strategic evidence assessment can greatly impact case outcomes;
- Pre-trial investigation phase needs specific tactical approaches;
- Understanding procedural timelines affects defense strategy development;
- Professional legal representation increases the likelihood of favorable results;
- Each phase of legal proceedings demands different strategic considerations;
- Early intervention by experienced counsel often leads to better outcomes.
The Romanian Criminal Justice System Overview
The criminal justice system in Romania follows a civil law tradition.
It has safeguards to ensure fair treatment in the legal process.
The Romanian Criminal Code and the Criminal Procedure Code guide all criminal proceedings.
Romania’s justice system balances the state’s need to prosecute crimes with strong protections for defendants.
Understanding this system is key for effective defense strategies.
Legal professionals well-versed in Romanian criminal law are often needed.
Criminal proceedings have a structured progression with safeguards at each stage.
The system focuses on both procedural correctness and substantive justice.
For help navigating these complexities, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
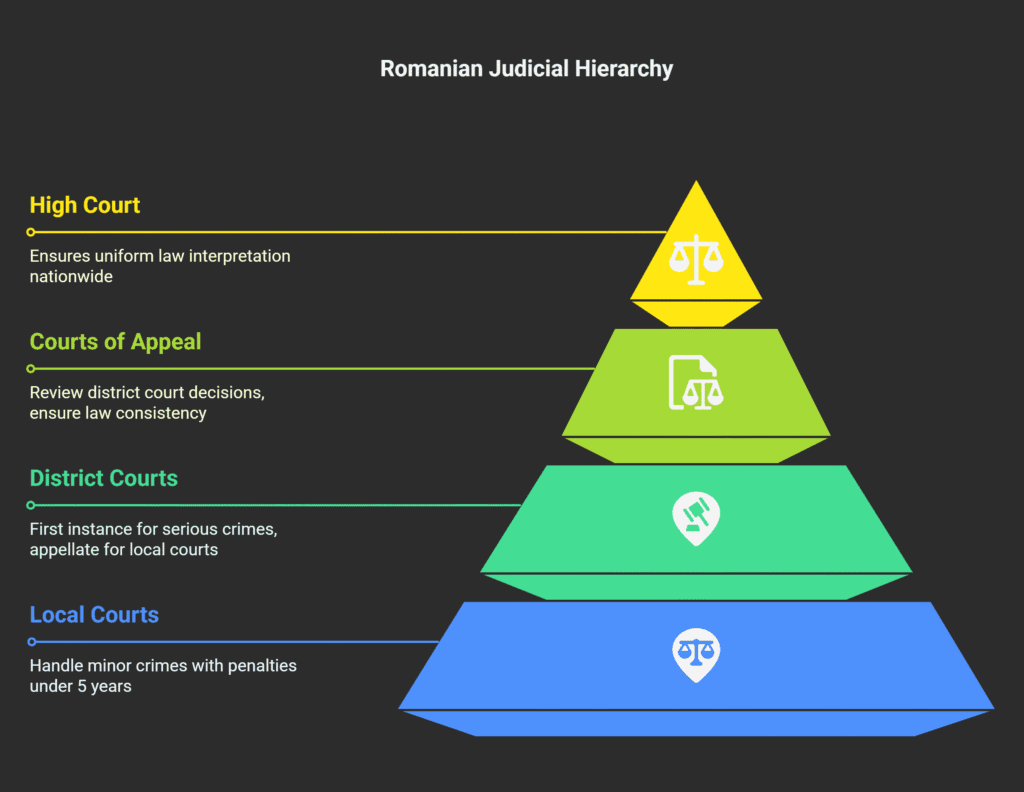
Structure of Romanian Courts
The Romanian judicial system has a hierarchical court structure.
It has specialized jurisdictions for criminal matters.
This structure offers multiple chances for case review, which can be used in defense strategies.

Local courts (Judecătorii) handle less serious crimes with penalties under 5 years.
These courts manage most criminal cases in Romania.
They are the first step for most defendants in the criminal justice system.
District courts (Tribunale) have two roles.
They act as first instance courts for serious crimes and as appellate courts for local court decisions.
Each district has one tribunal, handling complex criminal matters.
Courts of Appeal (Curți de Apel) review district court decisions.
They handle appeals in significant cases and ensure the law is applied consistently.
The High Court of Cassation and Justice is Romania’s highest court.
It ensures uniform law interpretation across the country.
It also handles appeals from Courts of Appeal in major cases.
Each court level has its own procedural rules.
Defense attorneys must navigate these rules strategically.
Knowing the right jurisdiction and procedural requirements is key for effective legal representation.
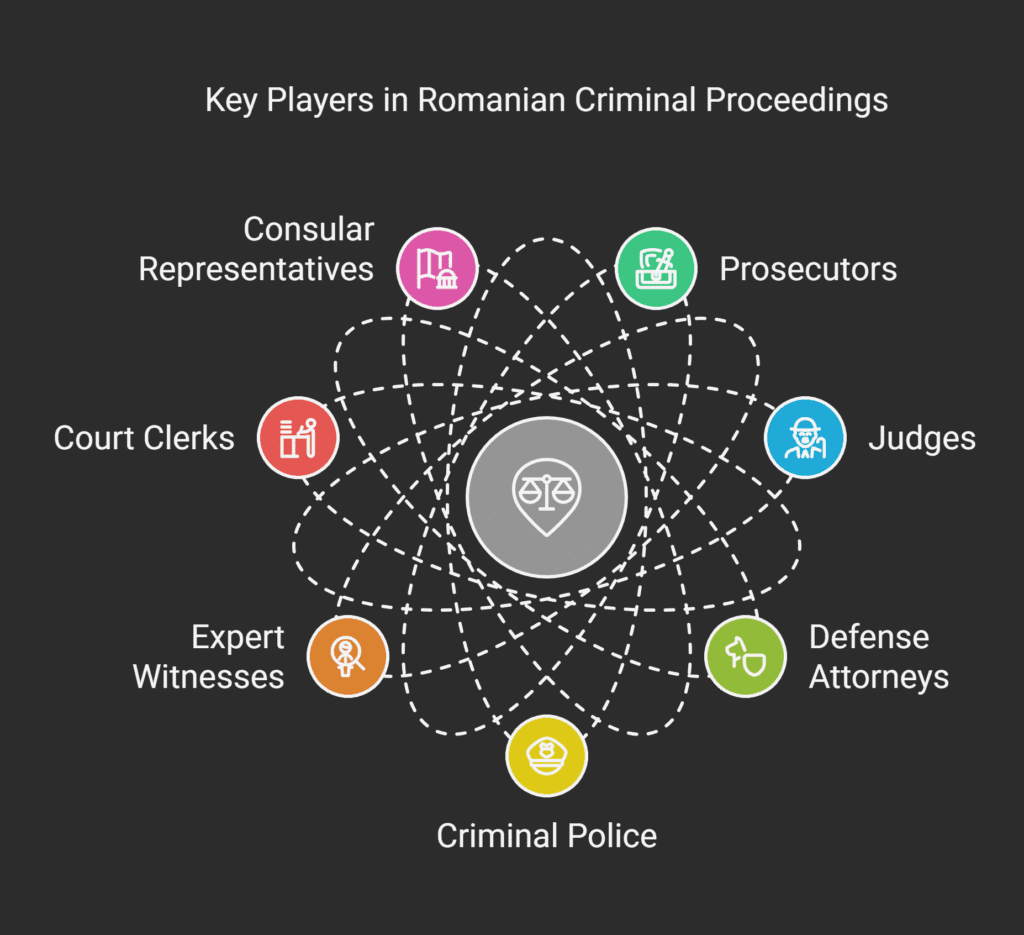
Key Players in Criminal Proceedings
Romanian criminal proceedings involve several key players.
Each has a distinct role and responsibility.
Their interaction shapes the case’s outcome.

Prosecutors (procurori) lead the prosecution.
They conduct investigations, gather evidence, and represent the state in court.
They make important decisions about charging and case progression under the Romanian Penal Code.
Judges ensure impartiality and procedural fairness.
They evaluate evidence, interpret laws, and make decisions based on the case’s merits.
In Romania, judges actively question witnesses.
Defense attorneys (avocați) defend the accused.
They challenge prosecution evidence and protect their clients’ rights.
Criminal lawyers in Romania develop strategies tailored to each case and guide clients through the process.
The criminal police help prosecutors with investigations.
They collect evidence and interview witnesses.
Expert witnesses provide specialized knowledge, and court clerks manage administrative tasks.
For non-Romanian citizens, consular representatives can help find legal representation.
If you don’t speak Romanian, your embassy can assist in finding a criminal defense lawyer in Romania who speaks your language.
Understanding these roles is vital for effective defense strategies.
Lawyers help and represent you in criminal proceedings.
For professional representation in Romanian criminal proceedings, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Legal Rights of the Accused Under Romanian Law
When you face criminal charges in Romania, knowing your legal rights is key.
The Romanian legal system gives defendants strong protections.
These rights are real and help build a strong defense.
Knowing these rights helps defendants defend themselves better.
It also helps lawyers spot any mistakes that could hurt your case.
Let’s look at the rights you have when accused in Romania.
Constitutional Protections
The Romanian Constitution protects you when you’re charged with a crime.
These guarantees are the foundation of your defense rights.
They keep the government from abusing its power.
The presumption of innocence is a key right.
It means the prosecution must prove your guilt.
This right is vital for your defense in Romania.
Another important right is the protection of personal liberty.
Romanian law limits how long you can be held before trial.
This ensures you’re not unfairly kept in jail before your case is heard.
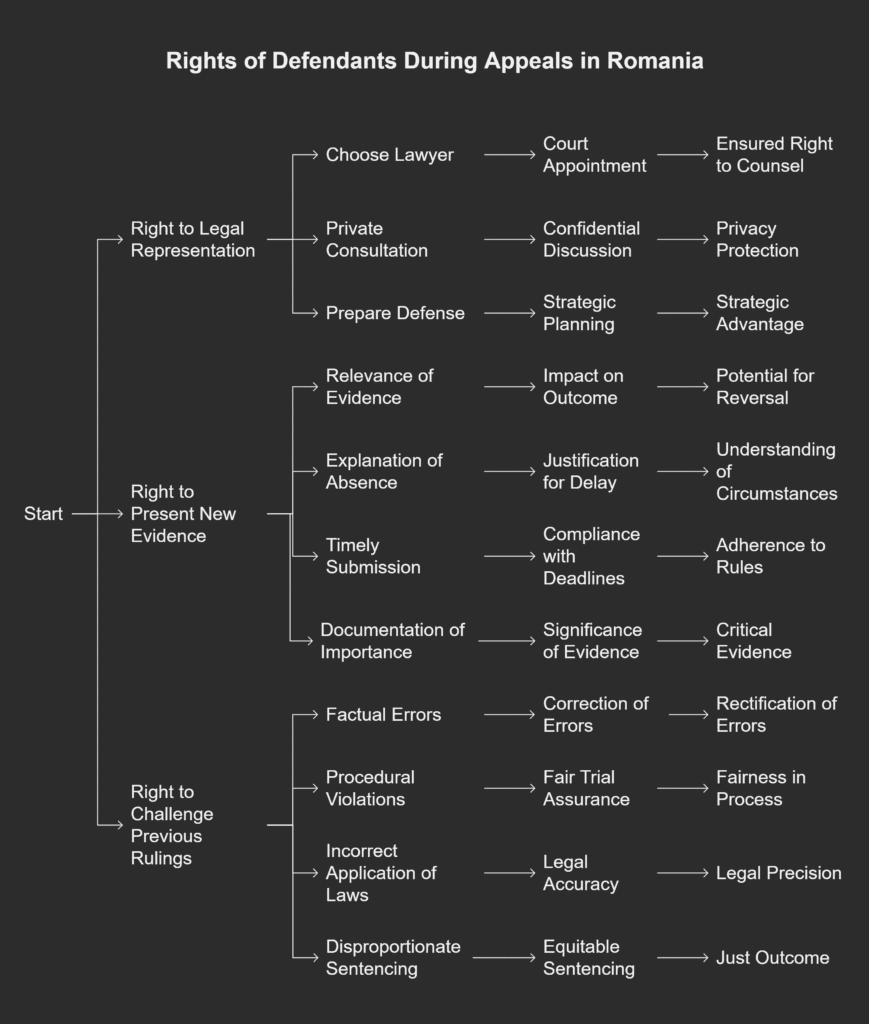
- The right to a fair trial before an independent and impartial tribunal;
- Protection against self-incrimination;
- The right to legal assistance throughout criminal proceedings;
- The principle of legality, ensuring criminal liability exists only for acts defined as offenses by law at the time of commission.
These constitutional protections are also backed by international human rights.
This gives you more ways to challenge unfair procedures.
Your Rights During Investigation and Trial
The criminal investigation process in Romania brings specific rights into play.
These rights start when you’re considered a suspect and last through the trial.
When detained, you must be told about the charges against you in a language you understand.
This includes the legal name of the crime and why you’re accused.
One key right is the right to remain silent.
Romanian law says:
- You have the right to remain silent throughout the criminal investigation.
- The authorities have to inform you on your right to remain silent, that there will be no negative consequences for your silence, and that anything you do say can be used against you.
This right is like the Miranda rights in other places.
It’s a key part of due process in Romania.
You also have the right to a lawyer.
Romanian law says:
- Once apprehended, you have the immediate right to appoint a lawyer of your choice or to be assisted by a public defender (avocat din oficiu).
- The police/prosecutor has to inform you of your right to a lawyer before you give any statement.
This right to counsel is critical. It lets you get legal advice early on.
The attorney-client privilege also protects your talks with your lawyer.
This keeps your defense plans private.
During the investigation, you also have the right to:
- Examine the case file and evidence against them (though prosecutors may temporarily restrict this access during investigations for up to 10 days after charges are filed);
- Request and propose evidence collection;
- Challenge the legality of evidence collection methods;
- File complaints against investigative measures.
As the case moves to trial, criminal trial procedures in Romania offer more rights.
These include:
- The right to be present at trial (unless you waive it);
- The ability to propose witnesses and evidence;
- The right to challenge prosecution evidence;
- The opportunity to make final statements before judgment;
- Access to an interpreter if you don’t speak Romanian;
- The right to appeal unfavorable decisions.
These safeguards make sure criminal defense rights in Romania meet European justice standards.
But using these rights well needs a lawyer’s help.
They know how to use these rights to defend you.
Understanding your rights is just the first step.
Using them well in your defense needs a lawyer’s help.
A skilled defense attorney can make sure your rights are respected and used to your advantage.
If you’re facing criminal charges, get help from a lawyer who knows Romanian criminal law.
A good lawyer can protect your rights and help you get a better outcome.
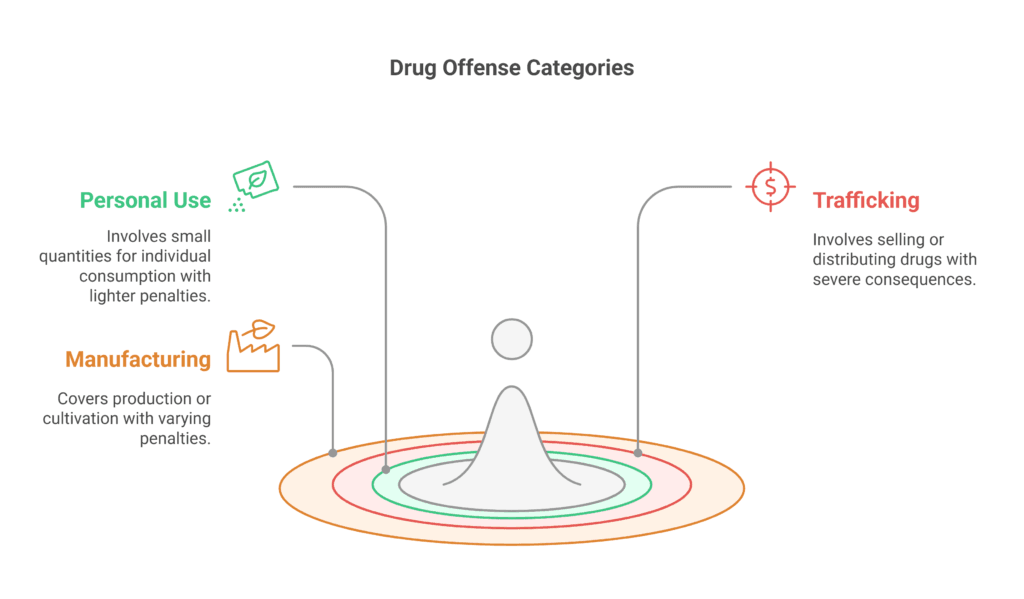
Criminal Defense Strategies in Romania
Defending against criminal charges in Romania is complex.
It requires a deep understanding of the law.
Lawyers must tailor their defense to each case, knowing the criminal justice system well.
Defense strategies often involve pointing out legal mistakes and questioning evidence.
Success often depends on the attorney’s ability to identify weaknesses in the prosecution’s case and build a strong defense.
Our law firm specializes in various criminal cases.
We offer detailed legal help from the start to appeals.
This includes cases like financial fraud and intellectual property crimes.
Procedural Defense Approaches
Procedural defense focuses on legal mistakes that can harm the prosecution.
It starts with checking the legality of searches and evidence collection.
One key strategy is to question the court’s jurisdiction.
If successful, this can exclude illegal evidence and weaken the prosecution.
During the preliminary chamber phase, defense attorneys can challenge evidence gathering. Successfully contesting these elements can lead to case dismissal before reaching trial on the merits, saving clients time and resources.
Effective procedural defense tactics also include:
- Challenging the formulation of charges for lack of precision or legal basis;
- Requesting specialized expert opinions to counter prosecution evidence;
- Filing interlocutory appeals against adverse procedural rulings;
- Contesting the validity of witness statements based on procedural irregularities;
- Challenging the chain of custody for physical evidence.
During trial, it’s important to watch for legal mistakes.
Defense counsel must object to any legal errors to protect the case for appeal.
Substantive Defense Approaches
Substantive defense strategies challenge the prosecution’s story and offer alternative views.
They focus on the crime’s legal elements and defend against guilt.
A key strategy is to question if the prosecution can prove the crime beyond doubt.
Defense attorneys may argue the defendant’s actions don’t meet the crime’s legal definition.
In some cases, defenses like self-defense or necessity can clear the defendant.
Character evidence and reputation witnesses can also help in certain situations, like for first-time offenders.
For financial crimes, defenses often involve complex financial transactions.
Expert witnesses are key in these cases, providing knowledge to counter prosecution claims.
| Defense Strategy Type | Primary Focus | Typical Timing | Success Factors |
| Procedural Defense | Legal protocols and procedural rights | Pre-trial and preliminary chamber | Identifying procedural violations and technical errors |
| Substantive Defense | Elements of the offense and factual narrative | Trial on merits | Challenging prosecution evidence and presenting alternatives |
| Hybrid Approach | Combination of procedural and substantive elements | Throughout all proceedings | Comprehensive legal knowledge and strategic flexibility |
| Negotiation Strategy | Securing favorable plea agreements | Any stage before final judgment | Understanding prosecution priorities and case weaknesses |
We offer legal help for all criminal law matters.
Our attorneys provide strategic advice for each client’s situation.
This includes help during investigations and complex cases before Romania’s top courts.
We’re proud of our successes in tough cases.
Choosing a lawyer from our firm can greatly impact your case’s outcome.
For specialized legal help, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Our experienced criminal defense attorneys are ready to assist.
The Criminal Procedure Timeline in Romania
Understanding the Romanian criminal justice system is key.
It involves knowing the timeline and each stage’s opportunities.
The criminal procedure in Romania has a set sequence, each with its own rules and time limits.
This knowledge helps defendants and their lawyers defend their rights effectively at every step.
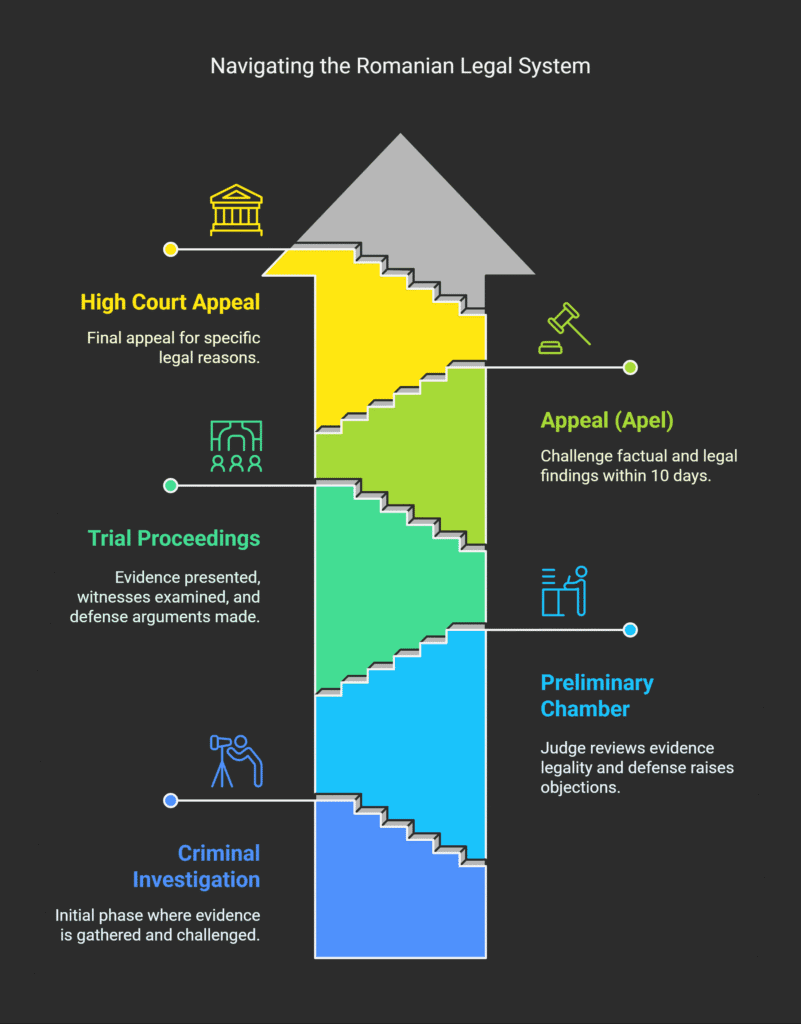
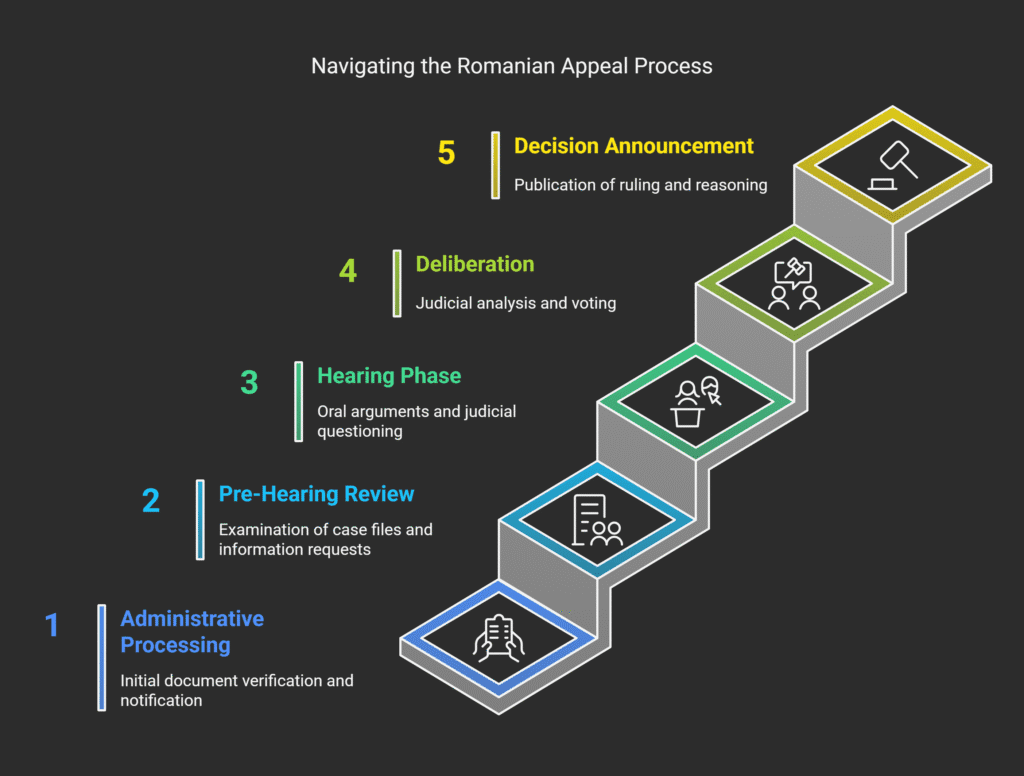
The process includes four main phases: criminal investigation, preliminary chamber, trial, and appeals.
Each phase has its own challenges and opportunities.
Lawyers need to adapt their strategies for each stage.
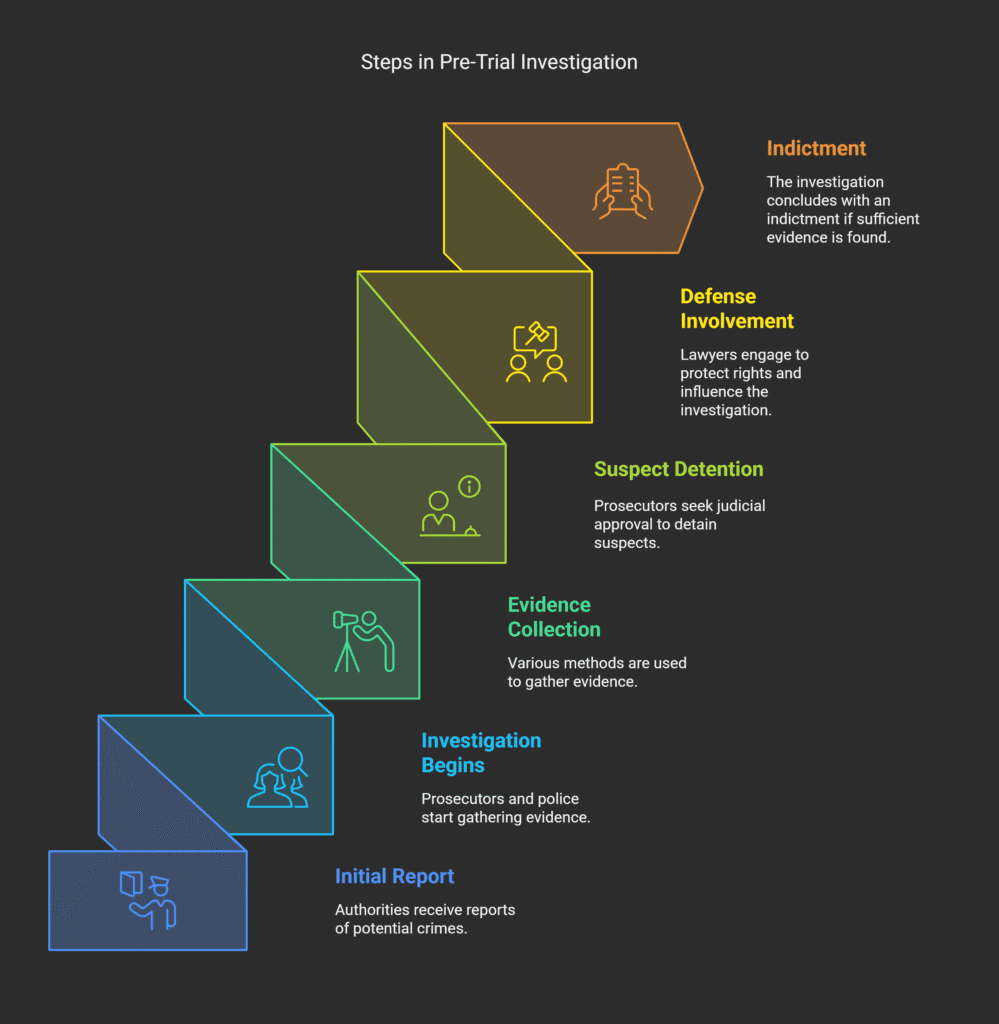
Pre-Trial Investigation Phase
The pre-trial investigation is the first and most critical phase of criminal proceedings in Romania.

It starts when authorities notice a possible crime.
This can be through direct observation, victim reports, or witness statements.
Prosecutors lead the investigation with help from judicial police.
For certain crimes, like corruption, specific bodies handle the case.
The National Anticorruption Directorate (DNA) deals with corruption, while the Directorate for Investigating Organized Crime and Terrorism (DIICOT) handles organized crime.
During this phase, investigators use many methods to gather evidence.
These include:
- Interviewing witnesses and suspects;
- Collecting and analyzing documents;
- Searching properties and seizing items;
- Using technical surveillance;
- Conducting expert examinations and forensic analysis.
If prosecutors want to detain a suspect, they must bring them before a judge.
The judge decides if detention is necessary.
Suspects can challenge this decision within 48 hours, with appeals heard within 5 days.
Suspects usually have the right to see their case file during criminal investigations.
But prosecutors can limit this access for up to 10 days after charges are filed.
Defense lawyers always have access to their clients’ statements, no matter the restrictions.
The investigation ends with an indictment if there’s enough evidence.
Early defense involvement is vital to protect rights and influence the investigation.
Trial Proceedings and Appeals

After an indictment, the case goes to the preliminary chamber.
Here, a judge checks if the evidence was gathered legally.
This is a key chance for the defense to challenge any irregularities.
The trial proceedings in Romania follow a set format for fairness.
The trial starts with preliminary matters, then the indictment is read.
Evidence is then presented by both sides.
During the trial, defendants have important rights:
- They can actively participate;
- Question witnesses and experts;
- Present evidence that clears their name;
- Make statements, though not under oath;
- Have the last word before the court deliberates.
After evidence is presented, closing arguments are made.
The defendant always gets to speak last before the court decides.
The judgment must explain the court’s reasoning clearly.
If arrested, you can challenge the decision within 48 hours.
The appeal must be heard within 5 days after filing.
The appeals process in Romanian criminal cases protects against judicial mistakes.
After a verdict, parties can appeal within 10 days.
This triggers a thorough review by a higher court.
This appeal is not just a review but a full trial continuation.
The appellate court can re-examine evidence and make new conclusions.
In rare cases, there’s a further appeal called “recurs în casație” before the High Court of Cassation and Justice.
This appeal is for specific legal reasons, not factual reassessment.
| Procedural Stage | Key Defense Opportunities | Time Limitations |
| Criminal Investigation | Challenge evidence gathering methods, request additional evidence | Varies by case complexity |
| Preliminary Chamber | Contest legality of evidence, raise procedural violations | 5 days to file objections |
| Trial Proceedings | Present defense evidence, cross-examine witnesses | Determined by court schedule |
| Appeal (Apel) | Challenge factual and legal findings | 10 days from verdict |
Effective defense strategies must adapt to each stage while keeping a consistent defense narrative.
Knowing the specific timeframes and requirements at each phase is key to protecting defendants’ rights and achieving good outcomes.
For professional help through criminal proceedings in Romania, from investigation to appeals, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
They offer expert legal representation tailored to your case.
Building an Effective Defense Team
Understanding Romania’s criminal justice system is key.
You need a defense team that fits your case perfectly.
The right team can change the outcome of your case, from guilty to not guilty.
They protect your rights and create strategies for Romanian courts.
Finding the right professionals is the first step.
They should know Romanian law well.
In serious cases, teamwork is vital for a strong defense.
Selecting the Right Criminal Defense Attorney
Choosing a criminal defense lawyer in Romania is critical.
Look for someone with experience in your type of case.
This could be anything from theft to violent crimes.
Lawyers with similar case experience know the law and prosecution tactics.
Their reputation in Romania’s legal world shows their skill.
Peers, judges, and clients can give you a good idea of their ability.
If you’re not from Romania, language is important.
Some criminal defense lawyers in Romania speak multiple languages.
Your embassy can help find a lawyer who speaks your language and knows the law.
Registered lawyers are listed in the Lawyers’ Yearly Register.
You can hire any lawyer in Romania, even if they’re not in your region’s bar association.
Good communication with your lawyer is essential.
They should explain things clearly and keep you updated.
Your lawyer’s strategy should match your goals, whether it’s to win your case or get a good plea deal.
Before choosing, talk to several lawyers.
Discuss your case, how they’ll communicate, and their fees.
For help finding a criminal defense attorney in Romania for your case, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Working with Expert Witnesses and Specialists
Expert witnesses are key in criminal defense, for complex cases.
They provide analysis and testimony that can help your case.
This can include challenging evidence or giving new insights.
In Romania, experts can be court-appointed, requested by the defense, or hired privately.
Common experts include:
- Forensic specialists who analyze physical evidence;
- Digital forensic experts who examine electronic data;
- Financial analysts who review complex transactions in economic crime cases;
- Medical professionals who address issues related to injuries, cause of death, or mental state;
- Psychological experts who provide insights into a defendant’s mental condition.
Specialized legal assistance is vital for investigations by special directorates.
Working with experienced attorneys is critical, as these investigations can be serious.
Defense attorneys and experts must work well together.
They need to share case details, ask the right questions, and prepare for testimony.
The attorney must choose experts who are qualified, credible, and can explain complex information to judges.
It’s best to get expert witnesses early in your case.
This gives them time to analyze and prepare their findings.
Remember, your lawyer helps and represents you, but they don’t investigate.
Choosing the right experts is key.
Building a strong defense team also means having investigators.
They can find evidence and witnesses that help your case.
For help finding and working with expert witnesses, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Evidence Strategies in Romanian Criminal Cases
Effective evidence strategies in Romanian criminal cases need a deep understanding of legal rules and principles.
The way evidence is managed and presented can greatly affect the outcome of a case.
Romanian defense attorneys must create detailed plans to handle both the prosecution’s evidence and the defendant’s exculpatory materials.
In Romanian criminal procedure, evidence must meet strict standards to be allowed in court.
Defense lawyers must carefully analyze all case materials and develop strategies to protect the defendant’s rights.
The Romanian Criminal Procedure Code gives defendants and their lawyers the right to see the entire case file.
Prosecutors can limit this access during investigations, but only for 10 days after charges are filed.
This is a key chance for defense preparation.
Challenging Prosecution Evidence

A systematic assessment of prosecution evidence is key to effective defense in Romania.
Defense attorneys must check the evidence’s content and how it was obtained.
They look for ways to exclude or reduce the impact of damaging evidence.
The main challenge is questioning the legality of evidence collection.
Romanian courts can exclude evidence gathered improperly.
If authorities break constitutional or procedural rules, the evidence can be thrown out.
Defense lawyers should also question the chain of custody for physical evidence.
Issues with preservation and contamination can weaken prosecution exhibits.
This is very effective with forensic evidence like fingerprints or DNA samples.
Witness testimony reliability is another key challenge.
Defense attorneys can use cross-examination to show inconsistencies or bias in witness statements.
Romanian courts are starting to recognize the flaws in eyewitness testimony, giving defense teams chances to challenge it.
Prosecution expert testimony needs careful scrutiny.
Defense teams can challenge experts by questioning their qualifications, methods, and findings.
They can also present opposing expert opinions to counter prosecution claims.
The preliminary chamber phase is a critical time to challenge evidence legality before trial.
Defense attorneys must raise objections quickly.
Failing to do so may limit their ability to challenge evidence later.
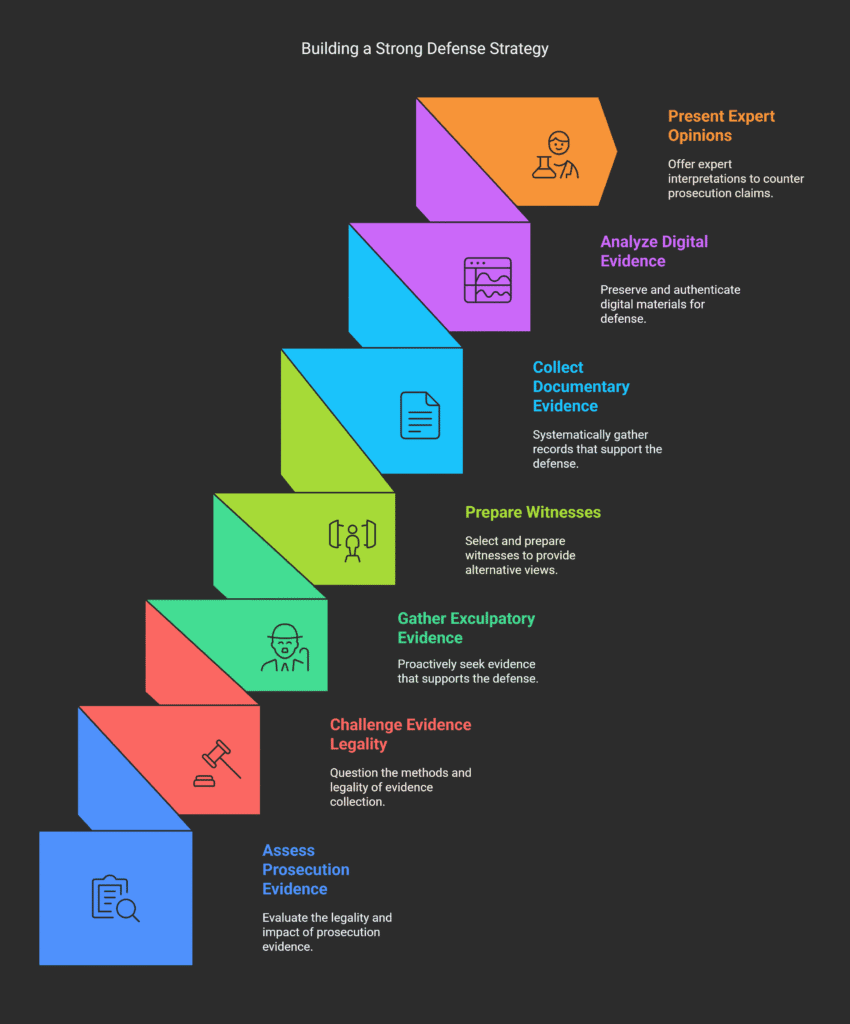
Gathering Exculpatory Evidence
While prosecutors lead investigations, defense attorneys must actively seek out favorable evidence.
This proactive approach strengthens the defendant’s case.
Defense counsel should ask for specific investigative actions to find exculpatory information.
This can include interviewing witnesses, getting surveillance footage, or electronic records.
Prosecutors have discretion but must consider these requests.
Choosing and preparing witnesses is key to effective evidence gathering.
Defense teams can propose witnesses during investigations and trials.
Strategic witness selection can provide alternative views, alibis, or contradict prosecution claims.
Collecting documentary evidence supporting the defense requires systematic effort.
This includes records that establish alibis, financial documents in economic crimes, communications that contradict prosecution claims, medical records, and employment or educational records.
In some cases, defense-commissioned expert examinations can offer alternative views of technical evidence.
While courts often favor prosecution experts, well-qualified defense experts can challenge prosecution conclusions, which is important in complex cases.
Digital evidence is increasingly important in criminal cases.
Social media, electronic communications, location data, and other digital materials can support defense claims.
Defense teams must know how to preserve and authenticate such evidence.
| Evidence Strategy | Prosecution Approach | Defense Response | Strategic Timing |
| Witness Testimony | Presenting multiple corroborating witnesses | Cross-examination highlighting inconsistencies | Preliminary hearing and trial |
| Physical Evidence | Establishing chain of custody and relevance | Challenging collection methods and preservation | Preliminary chamber phase |
| Expert Analysis | Presenting technical findings supporting guilt | Offering alternative expert interpretations | Pre-trial and trial phases |
| Documentary Evidence | Selective presentation supporting charges | Providing context and additional documentation | Throughout proceedings |
| Digital Evidence | Extracting incriminating digital materials | Authentication challenges and contextual analysis | Preliminary chamber and trial |
Throughout the evidence gathering process, defense attorneys must keep detailed records and ensure evidence is properly authenticated.
Romanian courts have strict standards for evidence admissibility, requiring careful attention to procedural rules.
After reviewing the evidence, defendants can ask for more evidence collection or witness statements.
Prosecutors must consider these requests and decide whether to include them in the case file.
If new evidence is added or charges change, defendants must be informed promptly.
For professional help in creating detailed evidence strategies for your case, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Our experienced team offers expert advice on challenging prosecution evidence and developing strong exculpatory materials.
Negotiation and Plea Bargaining Tactics
In Romania, plea bargaining is a key strategy for defendants and their lawyers.
It’s called “acordul de recunoaștere a vinovăției” in Romanian.
This method is part of recent judicial reforms to make the system more efficient.
Plea bargaining lets defendants talk to prosecutors about charges and sentences in exchange for admitting guilt.
This can lead to better outcomes than going to trial.
It’s a strategic choice to consider.
“Effective plea bargaining requires not just legal knowledge, but strategic foresight—the ability to accurately assess case strengths and weaknesses while understanding the prosecutor’s motivations and constraints.”
Deciding on a plea agreement involves many factors.
These include looking at the evidence, the severity of the charges, and possible sentences.
Getting professional legal advice is key for these negotiations.
Our team of criminal defense attorneys creates custom negotiation plans for each client.
When to Consider a Plea Agreement
Choosing a plea agreement needs careful thought.
It starts with looking at the evidence.
If the prosecution has strong evidence, a plea might reduce the sentence.
But, if the evidence is weak or there were procedural mistakes, going to trial might be better.
The seriousness of the charges also plays a big role.
More serious crimes might offer bigger sentence reductions through negotiation.
A defendant’s criminal history is important in negotiations.
First-time offenders usually get better deals than those with past crimes.
This is true, even in DUI cases, where a clean record can help.
Other things also affect plea decisions.
These include:
- Emotional and financial costs of long trials;
- Potential effects of a conviction;
- The defendant’s personal and work life;
- When in the process the decision is made.
Romanian law has rules about plea agreements.
They can’t be used for crimes with sentences over 7 years.
Knowing these rules is important when thinking about pleas.
A DUI lawyer in Romania from our team can help decide if a plea is right for you.
We look at all the details to find the best strategy.
For advice, email us at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Negotiation Strategies with Prosecutors
Good negotiation with prosecutors in Romania needs smart strategies.
Defense attorneys start by preparing well, analyzing the evidence.
This helps them know the prosecution’s weak points.
This prep lets them talk about possible charge reductions or sentences.
Building a good relationship with prosecutors helps negotiations.
Experienced Romanian lawyers can be firm but respectful, fighting for their clients’ best interests.
Good negotiation strategies include:
| Mitigating Factor | Potential Impact | Strategic Approach |
| Lack of criminal history | Significant positive influence | Emphasize rehabilitation |
| Cooperation with authorities | Demonstrates good faith | Document all cooperative actions |
| Restitution to victims | Shows responsibility | Present a restitution plan |
| Personal circumstances | Contextualizes behavior | Provide supporting documentation |
Defense attorneys use case weaknesses to their advantage.
This includes evidence problems, procedural errors, or different ways to look at the facts.
The timing of negotiations is also key, with different chances at different stages.
During talks, lawyers must keep clients informed about offers and their risks.
They should also be ready for trial, keeping their clients’ options open.
This strengthens their negotiating position.
A crime lawyer in Romania from our team offers tailored legal help for each case.
We focus on getting good results through negotiation when it’s smart.
For help with negotiations in your case, email us at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Trial Preparation and Courtroom Strategies

In Romanian criminal trials, the outcome often depends on how well the defense prepares and strategizes.
The trial is the key moment where defense theories face off against prosecution evidence.
Good preparation and smart strategy are key to a successful defense.
Good trial prep means analyzing the case well, organizing evidence, and making strong legal arguments.
Romanian trials have strict rules that defense lawyers must follow.
Successful strategies mix legal knowledge with the ability to persuade, pay attention to details, and be ready for surprises.
In Romanian trials, both sides give their final arguments.
The defendant gets to speak last, which can really sway the judge.
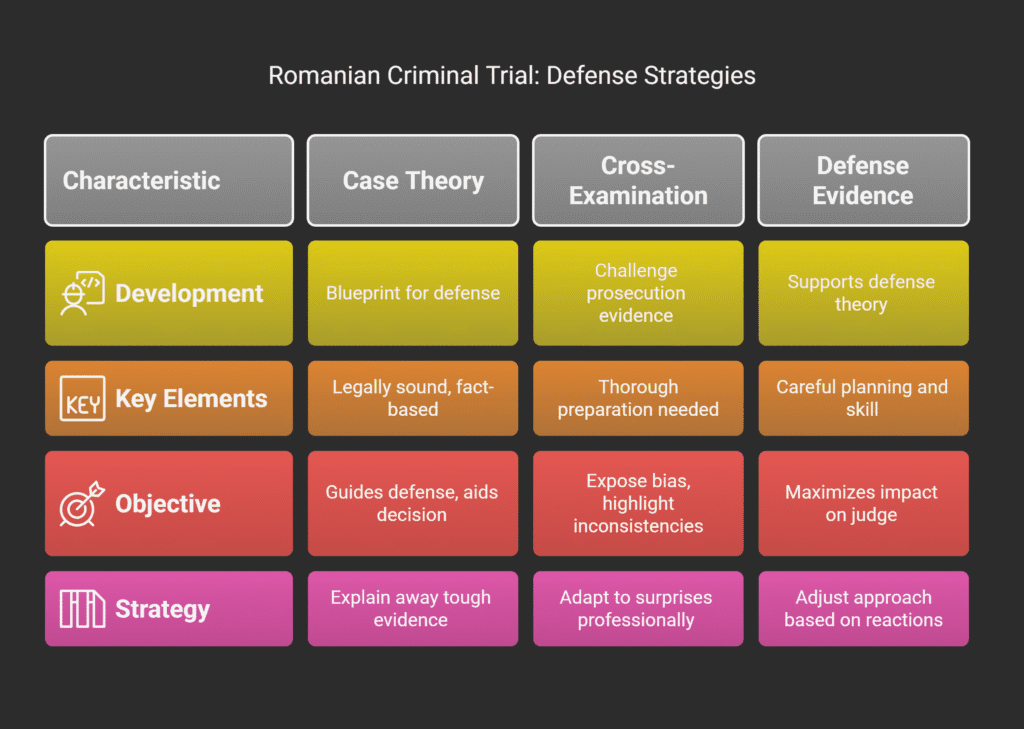
Developing a Compelling Case Theory
A strong case theory is like a blueprint for your defense.
It organizes your evidence and arguments into a clear story.
This is what guides your defense and helps the judge make a decision.
Good case theories need to be legally sound, based on facts, emotionally engaging, and easy to understand.
They start with a deep look at the prosecution’s evidence and finding weaknesses.
Then, defense lawyers come up with alternative stories that support their side.
Instead of ignoring tough evidence, a good case theory explains it away.
This makes your case stronger and more believable.
The theory should be clear in every part of your defense.
Effective Cross-Examination Techniques
Cross-examination is a chance to challenge the prosecution’s evidence in Romanian trials.
Even though the system is not purely adversarial, defense lawyers can question witnesses and challenge their testimony.
Good cross-examination starts with thorough prep, including looking at past statements and documents.
Defense lawyers plan their questions carefully to achieve their goals.
They use leading questions to guide the witness’s answers.
When questioning prosecution witnesses, defense lawyers should focus on:
- Highlighting inconsistencies with prior statements;
- Exposing bias or motivation to testify falsely;
- Demonstrating perceptual limitations or memory issues;
- Establishing facts that support the defense theory.
For expert witnesses, defense lawyers should question their qualifications, methods, and the facts behind their opinions.
Good questioning can show the limits of the expert’s analysis or suggest other ways to look at the evidence.
During cross-examination, defense lawyers need to stay professional and adapt to any surprises.
The order and timing of questions are very important.
Save your strongest points for when they will have the most impact.
Presenting Defense Evidence Persuasively
Presenting defense evidence well requires careful planning and skill.
Start by choosing evidence that supports your theory and prepares for challenges from the prosecution.
How you order your evidence can make a big difference.
Use the first and last pieces of evidence to make the biggest impact.
This is because people remember what comes first and last best.
When using witnesses, defense lawyers should ask questions that get clear, helpful answers.
Make sure witnesses stick to their story during cross-examination.
For documents, explain them well and show how they fit into your case.
During trial proceedings, parties present their closing arguments, with the defendant always having the final word before deliberation. The court then issues its judgment, which must contain detailed reasoning for its decision on both factual and legal matters.
Visual aids and demonstrative exhibits can help explain complex evidence when used right.
They’re great for technical or financial evidence that’s hard for judges to understand.
While presenting evidence, defense lawyers should watch how the judge reacts.
Adjust your approach as needed to keep your evidence connected to your theory.
Showing you’ve thought of possible weaknesses makes your case stronger.
A DUI lawyer in Romania or a crime lawyer in Romania from our team offers personalized help for each case.
We focus on professional court work and aim for the best results for our clients through careful prep and strategy.
For help with trial prep and courtroom strategies in your case, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Sentencing Mitigation Strategies
In Romania, sentencing mitigation strategies can change harsh penalties into more manageable ones.
Even when a guilty verdict seems likely, skilled lawyers can help.
They do this by using their knowledge of Romanian law and advocating for their clients.
These strategies are key in both plea deals and contested cases.
The goal is to get the best possible sentence under Romanian law.
Factors Affecting Sentencing in Romania

The Romanian Criminal Code sets a framework for sentencing.
It guides judges with specific factors.
For each crime, there are sentencing ranges based on the case’s details.
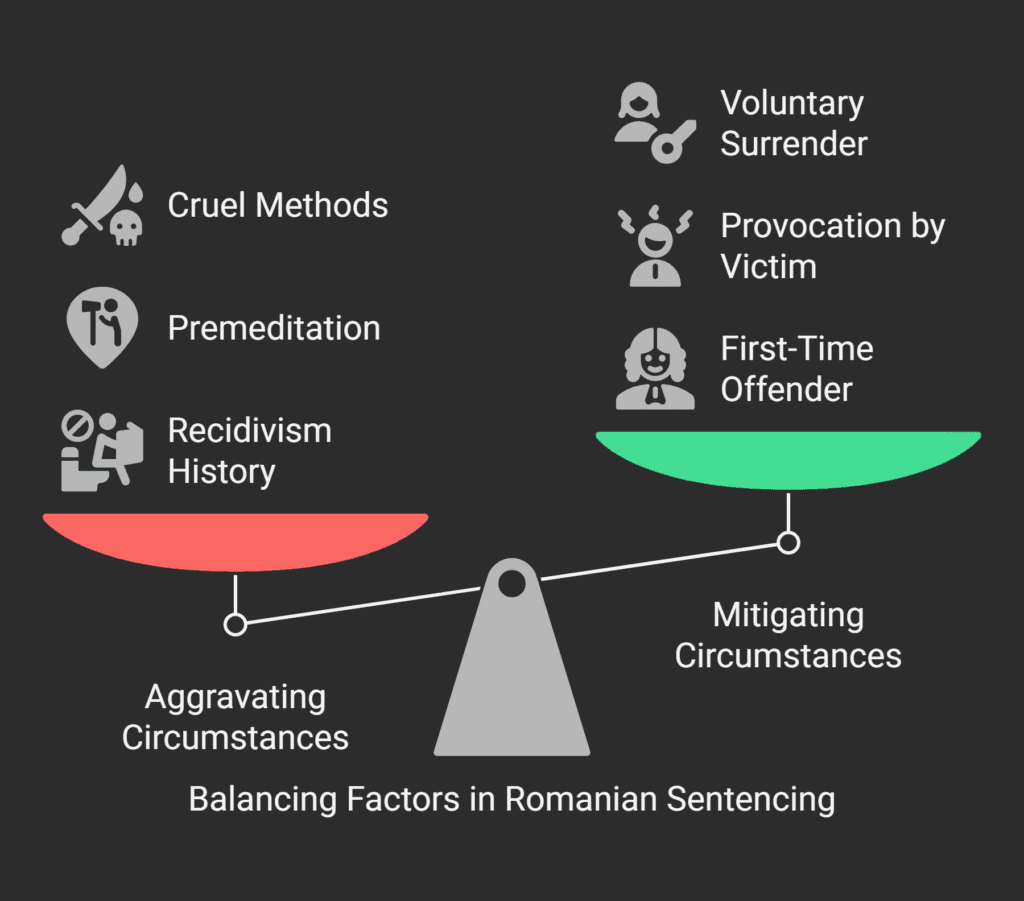
Aggravating circumstances that can increase sentences include:
- Recidivism or prior criminal history;
- Commission of multiple offenses;
- Premeditation or careful planning;
- Particularly cruel methods of commission;
- Exploitation of victim vulnerability;
- Commission by organized criminal groups.
On the other hand, mitigating circumstances that support reduced sentences include:
- First-time offender status;
- Provocation by the victim;
- Exceeding the limits of legitimate self-defense;
- Voluntary surrender to authorities;
- Cooperation with investigators;
- Genuine remorse demonstrated through concrete actions.
Personal circumstances are also considered during sentencing.
Judges look at age, health, family, job history, and community involvement.
These help paint a fuller picture of the defendant.
The way the crime was committed also matters.
Courts look at the defendant’s role and contribution.
A smaller role can lead to a lighter sentence.
Romanian courts aim for sentences that match the crime’s gravity but avoid being too harsh.
They must explain their reasoning in detail.
This makes the sentencing process clear.
Rehabilitation is another key factor.
Judges consider if alternatives to jail might help the defendant more.
This is often the case for first-time offenders or those with strong community support.
Effective Arguments for Reduced Sentences
Creating strong arguments for lighter sentences requires a mix of legal knowledge and persuasive presentation.
Defense lawyers should start by studying the sentencing laws.
They look for minimum penalties and alternatives to jail.
Highlighting the defendant’s limited role in a crime can also help.
This is true in cases where there are multiple people involved.
It shows the defendant’s level of responsibility.
Showing there’s no prior criminal history is another strong point.
It suggests the current crime is an isolated incident.
This makes the defendant seem less of a risk to society.
Remorse shown by the defendant is also important.
This can include:
- Public apologies to victims or communities;
- Voluntary compensation to those harmed;
- Participation in restorative justice programs;
- Other concrete actions demonstrating acceptance of responsibility.
Rehabilitation chances are a strong argument.
Defense lawyers should show evidence of:
- Stable employment history or educational pursuits;
- Strong family support systems;
- Willingness to participate in relevant treatment programs;
- Concrete plans for future law-abiding behavior.
Hardships caused by jail time can also justify alternative sentences.
This includes effects on family members or health issues that worsen in jail.
Defense lawyers should also show the defendant’s positive side.
This can include letters, testimony, and volunteer work.
It helps show the defendant’s value to society.
Highlighting harsh consequences of a conviction can also help.
This includes job loss, license revocation, or immigration issues that add to the punishment.
The court then explains its decision in detail.
This transparency helps defendants understand their sentence.
It also gives grounds for appeals if there were mistakes.
For help with sentencing mitigation strategies in Romania, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Our team can help find and present the best arguments for your case.
Post-Conviction Remedies and Appeals

In Romania, understanding the appeals and remedies after a conviction is key.
The legal system offers ways to challenge judgments, fix mistakes, or introduce new evidence.
These steps help ensure justice is served.
After a court makes a decision, there are options.
The Romanian law sets up a clear appeals process and special remedies.
Knowing these can help in planning a strong defense.
Grounds for Appeal in Romanian Law
Romanian law lists specific reasons to appeal a court’s decision.
These include mistakes in how the case was handled or errors in the decision itself.
Successful appeals show these mistakes changed the outcome.
Some common reasons for appeal include:
- Improper court composition or lack of jurisdiction;
- Violations of public trial requirements;
- Infringement of defense rights during proceedings;
- Improper handling or admission of evidence;
- Failure to address key defense arguments.
Appeals can also challenge how the law was applied or facts were found.
The court checks if the law was correctly applied to the facts.
To appeal, you must do so within 10 days of the judgment.
You need to clearly state what you’re challenging and why.
This helps the court know what to review.
The court will look at all the evidence again.
They might even consider new evidence.
This is a chance to fix mistakes from the first trial.
For help finding grounds for appeal, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
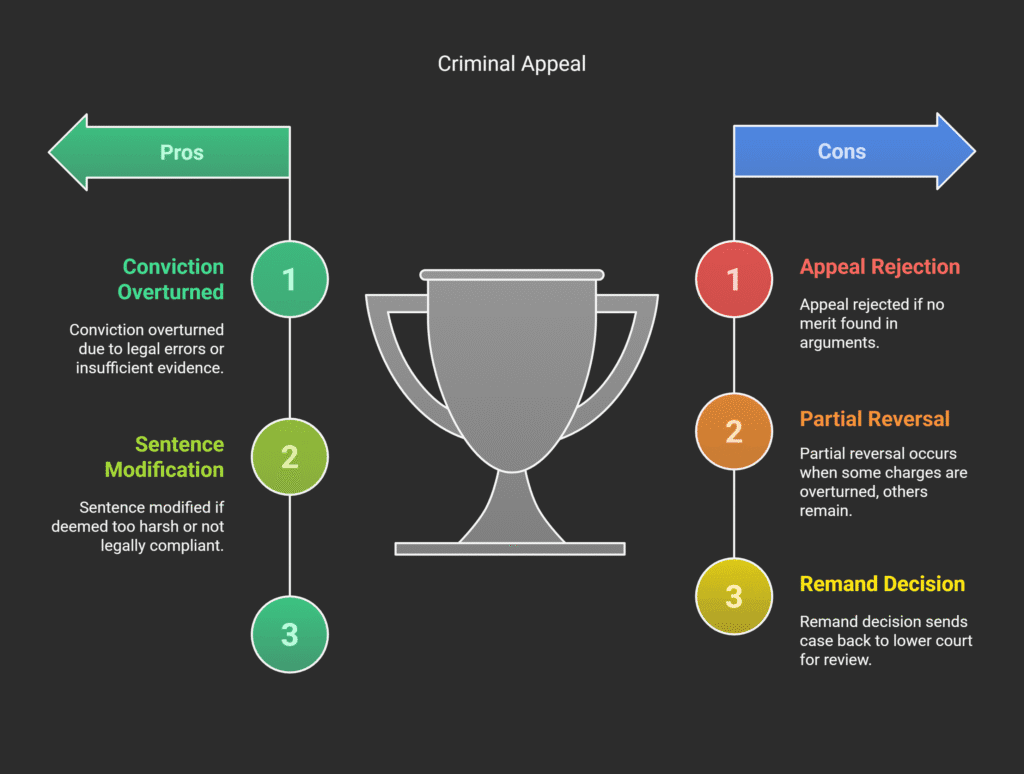
The outcome of an appeal can be:
- Confirmation of the original decision;
- Modification regarding legal classification or sentencing;
- Retrial orders in cases of serious procedural violations;
- Complete reversal with acquittal.
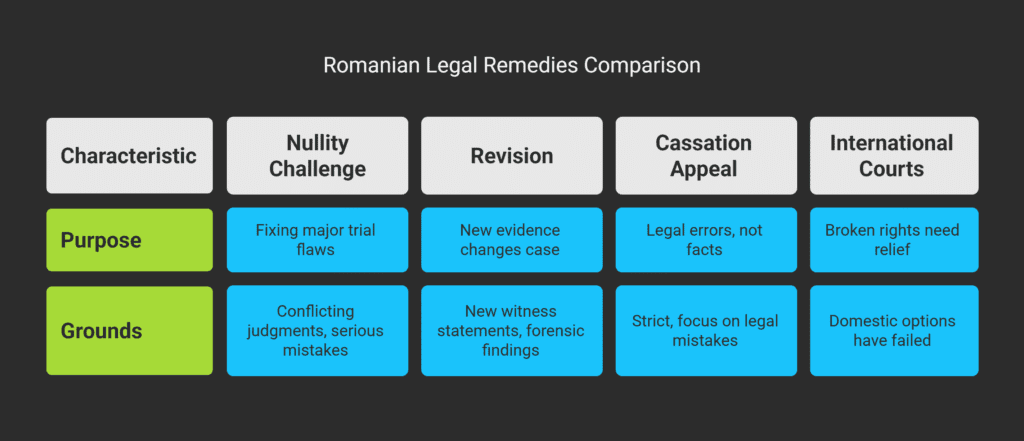
Extraordinary Legal Remedies

Romania also offers special remedies for challenging final decisions.
These are used when regular appeals are not possible or have failed.
Contestația în anulare (nullity challenge) is for serious mistakes like conflicting judgments.
It’s about fixing major flaws in the trial, not the case itself.
Revizuirea (revision) is for new evidence that could change the case.
This includes new witness statements, forensic findings, or evidence tampering.
Recurs în casație (cassation appeal) is a rare option before the High Court of Cassation and Justice.
It’s for legal errors, not facts.
The grounds are strict and focus on legal mistakes.
Each remedy has its own rules and time limits.
It’s important to get legal advice to see which one fits your case.
International courts can also offer relief.
If rights were broken, you can go to the European Court of Human Rights.
This is a long process but can help if domestic options failed.
Challenging laws through the excepție de neconstituționalitate procedure is another option.
Presidential pardons and amnesty laws can also offer relief, but these are political, not judicial.
Understanding post-conviction remedies in Romania needs legal help.
For advice on appeals or special remedies, email office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Conclusion: Securing the Best Possible Outcome
Understanding the Romanian criminal justice system is complex.
It needs strategic planning and strong legal support.
The defense strategies in this guide are proven to protect defendants’ rights at every step.
Our law firm has a strong track record in complex cases across Romania.
We focus on detailed case preparation, managing evidence, and strong courtroom arguments.
Getting experienced defense counsel early can greatly improve your chances of a good outcome.
Specialized criminal defense lawyers in Romania can change the outcome of a case.
Our team knows the best tactics and Romanian laws well.
This gives clients a big advantage in court, whether it’s dismissing a case, negotiating a plea, or defending at trial.
Each case in Romania needs a custom defense strategy.
Our lawyers are experts in white collar and financial crimes.
They bring up-to-date legal knowledge and experience to each case, helping to improve the outcome.
If you need help with criminal matters in Romania, contact office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Our experienced Romanian attorneys are ready to assist.
FAQ
What are the main courts handling criminal cases in Romania?
Romania has a clear court structure for criminal cases.Local courts handle minor offenses with penalties under 5 years.District courts deal with more serious crimes and review local court decisions.Courts of Appeal review district court decisions. The High Court of Cassation and Justice is the top court, ensuring laws are applied uniformly.What rights do defendants have during criminal investigations in Romania?
Defendants in Romania have key rights.They must be told of accusations in a language they understand.Defendants have the right to legal help, to remain silent, and to see case files.They can propose evidence and witnesses.Defendants can challenge prosecution evidence and make final statements before judgment.They also have the right to appeal.What is the presumption of innocence in Romanian criminal law?
The presumption of innocence is a key principle in Romanian law. It’s in the Constitution.It means the prosecution must prove guilt, not the defendant.This principle requires all doubts to be in favor of the accused. It stops authorities from treating someone as guilty before a final decision.What procedural defense strategies are most effective in Romanian criminal cases?
Effective strategies include challenging the legality of searches and seizures.Contesting court jurisdiction or prosecutorial competence is also key.Filing motions to exclude illegally obtained evidence is important.Challenging imprecise charge formulations and questioning evidence legality during the preliminary chamber phase are also effective.Monitoring procedural compliance, requesting specialized expert opinions, and filing interlocutory appeals are also important.How can defense attorneys gather exculpatory evidence in Romanian criminal cases?
Defense attorneys can gather exculpatory evidence by submitting specific requests for investigative actions.They can propose witnesses for examination during both investigation and trial.Collecting documentary evidence supporting the defense position is also important.Commissioning independent expert examinations and securing digital evidence are key.Maintaining records of all evidence gathered is essential.What is plea bargaining in Romania and when was it introduced?
Plea bargaining in Romania allows defendants to negotiate with prosecutors.It was introduced recently as part of reforms to increase judicial efficiency.It’s available for offenses punishable by up to 7 years imprisonment.It requires judicial approval of all negotiated terms.When should a defendant consider a plea agreement in Romania?
A defendant should consider a plea agreement when facing strong prosecution evidence.When the sentence reduction is significant, it’s also a good time.Being a first-time offender or wanting to avoid the costs of a long trial are reasons.Personal circumstances that would be worsened by incarceration are also important.Each case needs a careful assessment with defense counsel.What negotiation strategies are effective with Romanian prosecutors?
Effective strategies include thorough case preparation and establishing rapport with prosecutors.Highlighting mitigating factors and leveraging case weaknesses are key.Timing negotiations strategically and maintaining clear communication are important.Preparing for trial while negotiating keeps leverage.Ensuring agreements meet judicial approval requirements is also important.How should a defense attorney develop a compelling case theory in Romanian criminal proceedings?
A defense attorney should analyze prosecution evidence and identify weaknesses.Assessing defense evidence and formulating alternative explanations is important.Ensuring consistency with legal standards and available evidence is key.Acknowledging problematic evidence and reinforcing the theory consistently are important.This creates a clear narrative for judges.What techniques make cross-examination effective in Romanian criminal trials?
Effective techniques include thorough preparation and strategic planning. Maintaining control through careful use of leading questions is important.Employing impeachment techniques and focusing on qualifications and methodology when examining experts are key. Adapting to unexpected responses and considering the timing and sequence of questions are important.What factors affect sentencing decisions in Romanian criminal cases?
Sentencing decisions are influenced by statutory ranges and aggravating circumstances. Mitigating circumstances, the defendant’s personal circumstances, and the manner of offense commission are also important.The consequences and harm caused, proportionality principles, and rehabilitation prospects are also considered.What arguments are most effective for securing reduced sentences in Romania?
Effective arguments include highlighting the defendant’s limited role in the offense. Emphasizing the absence of prior criminal history is also important.Demonstrating genuine remorse through actions like victim compensation is key. Presenting evidence of rehabilitation and personal hardship is also important. Highlighting disproportionate collateral consequences of conviction can also be effective.What are the main grounds for appeal in Romanian criminal cases?
Main grounds for appeal include procedural violations and substantive errors. Appeals must be filed within 10 days of judgment communication.They must specify the challenged decision components and specific grounds for appeal.What extraordinary legal remedies are available after exhausting ordinary appeals in Romania?
Extraordinary remedies include “contestația în anulare” for serious procedural errors. “Revizuirea” is available when new evidence emerges. “Recurs în casație” addresses specific legal errors.Petitions to the European Court of Human Rights for convention rights violations are also available. Constitutional challenges and presidential pardons or amnesty laws are sometimes options.How does the Romanian criminal investigation phase work?
The investigation starts when authorities become aware of a possible offense.Prosecutors lead investigations with judicial police assistance.They gather evidence through witness interviews, document collection, searches, surveillance, and expert examinations. Suspects have the right to remain silent and to legal representation during questioning.The investigation concludes with either an indictment if evidence is sufficient or case closure if evidence is insufficient.What role do prosecutors play in Romanian criminal proceedings?
Prosecutors lead investigations, gather evidence, and determine whether to file charges. They prepare indictments and represent the state’s interests in court.Prosecutors present evidence and arguments during trial, question witnesses and the accused, and respond to defense motions. They participate in plea negotiations and file appeals against unfavorable decisions.What are the most effective strategies for building a strong defense in criminal cases in Romania?
Building a strong defense in criminal cases in Romania requires a comprehensive approach that begins from the moment you’re aware of being under investigation.
First and foremost, securing representation from an experienced criminal defense lawyer or criminal defense attorney familiar with Romanian law is crucial.
The best defense lawyers in Romania will immediately work to analyze the specifics of your case, identify procedural errors, and develop a tailored defense strategy.
One of the most effective strategies involves a thorough examination of evidence gathering procedures.
The Romanian Criminal Procedure Code contains strict rules about how evidence can be collected and what can be admitted in court.
A skilled criminal lawyer in Romania will scrutinize whether your rights were respected during searches, interrogations, and evidence collection.
Any violation of these rules can lead to evidence being excluded, which can significantly weaken the prosecution’s case.
Another winning strategy involves challenging the legal classification of the alleged offense.
Often, criminal charges may be improperly framed under a more serious category than warranted by the facts.
Criminal defense lawyers in Romania with deep legal expertise in the nuances of criminal law can sometimes succeed in having charges reduced to less severe offenses, resulting in lighter penalties.
Additionally, effective defense in the Romanian courts often involves bringing forward expert witnesses, conducting independent investigations, and presenting alternative explanations for the evidence presented by prosecutors.
The most successful criminal defense attorneys in Romania leave no stone unturned when building their clients’ defense cases.
How does the criminal investigation phase work in Romania and what are my rights during this period?
The criminal investigation phase in Romania is a critical period that begins when authorities suspect a crime has been committed. During this phase, the prosecution, led by a prosecutor, collects evidence to determine whether there are grounds to send the case to trial.