Appealing a Criminal Conviction in Romania: Legal Insights
Appealing a Criminal Conviction in Romania: Legal Insights
Nearly 15% of criminal verdicts in Romania face appeals, showing the importance of this legal path.
If you get a bad verdict in the Romanian justice system, knowing your right to appeal is key.
It helps protect your freedom and future.
The journey to overturn a verdict is complex, following Romanian law’s unique rules.
Courts aim to uncover the truth through strict protocols.
Knowing these rules well is crucial for a successful appeal.
The appeals process offers hope for those wrongly convicted.
But, it requires timely action, proper documents, and strong legal arguments.
Each step must meet specific criteria to increase your chances of winning.
This guide covers the basics of appealing verdicts in Romania’s courts.
While we offer detailed info, your case may need tailored advice.
For specific questions, reach out to our team at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
Key Takeaways
- Approximately 15% of criminal verdicts in Romania face appeals, showing the system’s active use;
- Romanian law guarantees the right to challenge court decisions as a safeguard against judicial errors;
- Strict procedural timelines must be followed when filing appeals;
- The appeals system operates on multiple levels within the Romanian court hierarchy;
- Professional legal representation significantly improves chances of a successful appeal;
- Each case requires a customized legal strategy based on specific circumstances.
Understanding the Romanian Criminal Appeal System
Understanding Romania’s criminal appeal system is key.
It involves knowing the court structure and appeal options.
Success in appealing a verdict depends on choosing the right court and appeal type.
This knowledge is crucial for a strong appeal strategy.
Structure of Criminal Courts in Romania
The Romanian judicial system has a four-tier hierarchy.
Each level has a specific role in criminal cases.
Knowing this structure is essential for determining your appeal path.
At the bottom are the first instance courts (judecătoria).
They handle minor crimes and contraventions.
These courts are found in towns and cities across Romania.
Next are the tribunals (tribunale).
They deal with serious crimes and appeal decisions from the judecătoria.
Each county has one tribunal, usually in the county capital.
The courts of appeal (curți de apel) are the third level.
They handle appeals from tribunals.
Romania has 15 courts of appeal, covering several counties each.
At the top is the High Court of Cassation and Justice (Înalta Curte de Casație și Justiție).
It’s Romania’s highest court.
It deals with appeals from the courts of appeal and is the final authority.
Types of Criminal Appeals Available
The Romanian legal system offers two main appeal types:
- Appeal (Apel) – This is the first appeal against a court decision. It allows a full review of your case. You can present new evidence and challenge the original court’s findings.
- Second Appeal (Recurs) – This is a further appeal after an unsuccessful first appeal. It focuses on legal matters, not facts. It checks if the law was applied correctly.
In some cases, you can also file an extraordinary appeal.
This includes a request for case review (revizuire) with new evidence or an appeal in the interest of the law (recurs în interesul legii).
However, the latter cannot change the outcome of your case.
Appeal Court Jurisdiction
Knowing which court has jurisdiction over your appeal is vital.
The jurisdiction depends on the original court and the appeal type.
For decisions from first instance courts (judecătoria), appeals go to the county tribunal.
This applies to most minor crimes.
Appeals from tribunals go to the court of appeal (curte de apel) with jurisdiction over the tribunal.
This ensures the right court reviews your case.
For cases tried by courts of appeal, the High Court of Cassation and Justice is the appellate court.
It also handles second appeals against decisions from courts of appeal.
The rules for jurisdiction in Romanian criminal appeals follow a clear hierarchical pattern.
This ensures each case gets the right review efficiently.
Your Romanian lawyer can help choose the correct appeal court for your case.
Legal Grounds for Appeal a Criminal Conviction in Romania
To overturn a criminal conviction in Romania, knowing the legal reasons for appeal is key.
Romanian law doesn’t allow appeals just because you’re not happy with the verdict.
It outlines specific situations where appeals can be made and considered by higher courts.
The Romanian Criminal Procedure Code lists legal grounds for appeals that need solid proof.
If you can’t show at least one of these grounds, your appeal might be dismissed right away.
One common reason for appealing is if there were mistakes during the trial.
These could be wrong court composition, jurisdiction issues, or breaking important rules.
For example, if the court didn’t have the right to hear your case, that’s a big mistake that can make the whole trial invalid.
Another reason is if the law was applied wrongly.
This happens when the trial court got the law wrong or applied it in the wrong way.
To appeal on this, you need to clearly say which law was misused and how it affected your case.
Evidence issues are also a big reason for appeals in Romania.
This includes:
- Not enough evidence to support the conviction;
- Conflicting evidence that wasn’t sorted out;
- Wrongly letting in or keeping out evidence;
- Not considering important evidence from the trial.
Finding new evidence not seen during the trial is another reason to appeal in Romania.
But this new evidence must be really important and could change the case’s outcome.
You also need to show it couldn’t have been found and used in the original trial, even with hard work.
Violations of defense rights are serious reasons for appeal in Romania.
These could be not being allowed legal help, not having enough time to defend yourself, or not being able to question witnesses.
Romanian courts take these very seriously because they affect the right to a fair trial.
Also, if you think the sentence is too harsh, you can appeal.
If you believe the punishment is too severe compared to the crime, you might have grounds.
You need to show the sentence is not in line with the law or past cases.
When you’re preparing your appeal, just stating the reasons isn’t enough.
You need to back up each reason with details from your case and the law.
Your appeal should clearly show how the mistakes or violations affected your case.
The strength of your appeal grounds is very important.
Romanian appellate courts focus on appeals that show clear legal mistakes or rights violations.
It’s crucial to find the strongest legal arguments for your case.
Successful appeals in Romania often use more than one reason.
For example, showing both procedural errors and wrong application of the law can make a strong case for overturning the conviction.
Knowing the legal grounds for appeals in Romania helps you focus on the best arguments for your case.
With the right legal advice, you can figure out which grounds apply to you and how to support them in your appeal.
Time Limits and Deadlines for Filing Appeals
Knowing the appeal deadlines in Romania is key to protecting your rights.
The Romanian courts have strict rules.
If you miss these deadlines, you might lose your chance to appeal a conviction.
Standard Appeal Filing Deadlines
In Romania, you have a short time to file an appeal.
For ordinary appeals (apel), you have 10 days after the judgment is communicated.
This means you need to act fast.
For second appeals (recurs), the deadline is also 10 days.
But, some cases have different rules.
For example, you have just 48 hours to challenge a pretrial detention order.
The court must hold a hearing within 5 days of your appeal.
This shows how crucial it is to prepare your appeal quickly.
Your lawyer in Romania should start working on it right away after a bad verdict.
Extensions and Exceptions
While deadlines are strict, there are exceptions.
These are rare and need strong reasons.
Courts might extend deadlines in cases of:
- Force majeure – unexpected events that stopped you from filing on time;
- Serious medical conditions that made it hard to act legally;
- Documented communication failures in the judicial system;
- Absence of proper legal notification about your appeal rights.
To ask for an extension, you must file a motion with evidence.
The court will decide if your situation was truly exceptional.
These requests are carefully reviewed, and extensions are rare.
Consequences of Missing Deadlines
Missing appeal deadlines in Romania has serious effects.
If you don’t file on time, you lose your right to appeal.
This makes the original conviction final and unchangeable.
Courts are strict about these deadlines.
If you file late, your appeal is dismissed, no matter its merit.
This means the court won’t look at your case’s arguments.
Having a final conviction can impact your future.
It can affect your job prospects, criminal record, and civil rights.
After missing a deadline, your only option might be an extraordinary remedy like revision, which is rarely successful.
Because of these serious consequences, you must take deadlines very seriously.
Get legal advice quickly after a bad verdict to protect your appeal rights.
Remember, these deadlines are set to keep the justice system efficient, but they require careful attention from defendants and their lawyers.
Essential Documentation for Criminal Appeals
When you want to appeal a criminal conviction in Romania, getting the right documents is key.
The Romanian courts focus a lot on following the rules. So, having the right documents is crucial for your appeal to be considered.
Under Romanian law, all documents need to be made very carefully.
The court will look at these documents closely before they even start on your case.
Here’s what you need for a criminal appeal in Romania.
The Appeal Petition
The appeal petition is the main part of your appeal.
It must follow strict rules under Romanian law.
Your petition should clearly say:
- The court decision you’re challenging;
- Why you’re appealing;
- The legal reasons for your appeal;
- What you want to happen next;
- Your name and signature.
Your appeal petition must clearly state what parts of the judgment you’re contesting.
This could be the whole decision or just parts of it.
Court Decision Documentation
You need to include certified copies of the court decision you’re appealing.
This includes:
- The full text of the judgment;
- The reasons for the decision;
- Any dissenting opinions.
Romanian courts need these documents to understand your case fully.
If you can’t get these documents yourself, your lawyer can ask the court for them.
Supporting Evidence
You need to document any evidence that supports your appeal.
This could be:
| Type of Evidence | Documentation Required | Certification Needed |
| Witness Testimony | Written statements or transcripts | Notarized copies |
| Expert Opinions | Full expert reports with credentials | Original or certified copies |
| Physical Evidence | Detailed descriptions and photographs | Authentication certificates |
| New Evidence | Explanation of why it wasn’t presented earlier | Certification of authenticity |
All documents supporting your claims must be given to the court and the other parties in certified copies.
Sometimes, the court might ask for the original documents.
Legal Representation Documentation
If you have a lawyer in Romania, which is recommended, you need to include:
- A power of attorney (procură) for your lawyer;
- Proof of your lawyer’s membership in the Romanian Bar Association;
- Authorization for special procedural acts, if needed.
These documents show your lawyer’s right to represent you in the appeal process.
Document Preparation Requirements
The appeal process in Romania has specific rules for preparing documents.
Each document must be:
- Written in Romanian or have a certified translation;
- Certified or notarized when needed;
- Given in enough copies for the court and all parties;
- Organized according to court standards.
Documents that don’t follow these rules might be rejected.
This could harm your appeal.
Documents from outside Romania might need extra legalization or apostille certification.
Record Keeping and Filing Proof
Keeping detailed records is important during the appeal process.
Always:
- Save copies of all documents;
- Get official proof of filing (dovada depunerii);
- Keep a record of all submissions in order;
- Ask for confirmations of receipt for all documents.
This record helps if there are questions about filing or receiving documents.
Accessing Court Records
Getting the right court records can be hard in Romania.
If you’re having trouble, try these:
- Write a formal request for access;
- Have your lawyer use legal rules to get access;
- Ask for judicial help if access is denied;
- File a complaint with the Superior Council of Magistracy if access is blocked.
You have the right to see the case file (dosar) under Romanian law.
This is key for preparing a strong appeal.
Getting the right documents is not just a formality in Romania’s appeal system.
It’s the base of your appeal.
Making sure all documents are complete, properly prepared, and filed on time can greatly improve your chances of a fair appeal.
Role of Defense Lawyers in the Appeals Process
Defense lawyers are key in criminal appeals in Romania.
They know how to handle legal steps and make strong arguments.
Criminal defense lawyers in Romania help you through tough legal times.
Your lawyer speaks for you in court, making your story sound right in law.
They look for mistakes in the trial and find flaws in the evidence.
They use Romanian law to make your appeal strong.
Selecting an Appeals Attorney
Finding the right lawyer for your appeal is important.
Appeals need special knowledge of court rules and past cases.
Look for someone with experience in appeals courts.
When picking your Romanian lawyer, think about:
- Experience with cases like yours;
- Success in changing convictions or sentences;
- Knowledge of the courts;
- How they communicate;
- Clear fees and payment plans.
Ask for a first meeting to see if they understand your case.
Many Romanian criminal lawyers offer free talks to discuss your appeal chances.
Firms like Atrium Romanian Lawyers (office@theromanianlawyers.com) offer advice tailored to you.
Legal Representation Rights
In Romania, you have rights to legal help during appeals.
These rights help ensure you get a fair chance to defend yourself.
You can talk privately with your lawyer from Romania and have time to plan your defense.
Your rights include:
- Choosing your lawyer;
- Private talks with your lawyer;
- Your lawyer being there for all hearings;
- Enough time to prepare.
These rights are important from start to finish.
Legal representation in Romania is key to fair justice, especially when appealing court decisions.
Courts usually agree to reasonable requests about your rights.
Public Defender Options
If you can’t afford a lawyer, Romania offers public defenders.
They make sure everyone gets legal help.
Public defenders are crucial in the justice system.
Public defenders are needed in:
- Minor criminal cases;
- Detained or arrested people;
- Crimes that could mean life in prison;
- Offenses with sentences over 5 years.
To get a public defender, apply to the court handling your appeal.
Show you can’t afford a lawyer.
Public defenders handle many cases, which might mean less time for yours.
Hiring an appeals lawyer in Romania can give you more focus and help.
Whether you choose a private lawyer or a public defender, good legal help is key.
Your lawyer is your advocate and partner in seeking justice.
Evidence Presentation in Appeal Courts
When you appeal a criminal conviction in Romania, knowing how to present evidence is key.
The rules for presenting evidence in appeals are different from the first trial.
They cover what evidence you can show, how to submit it, and when new evidence is considered.
Appeals in Romania mainly review the evidence from the first trial.
Your strategy must focus on this.
The appeals court checks if the lower court applied the law correctly to the evidence.
Key Differences in Evidence Handling
In appeals, you can’t just bring back all the evidence from the first trial.
You need to pick and highlight evidence that supports your appeal.
This means analyzing the trial record and finding issues with the evidence.
To challenge evidence, show why the first court made mistakes.
This could be because of evidence that was wrongly admitted or evaluated.
Romanian law allows new evidence in appeals under certain conditions.
But, this right is not unlimited.
To introduce new evidence, you must show it was not available during the first trial.
You also need to explain its relevance and submit it on time.
- Demonstrate why the evidence couldn’t have been presented during the original trial;
- Establish clear relevance to your specific grounds for appeal;
- Submit a formal request to the court explaining the significance of the new evidence;
- Present the evidence within procedural timeframes established by law.
After looking at the evidence, you can ask for more evidence or statements.
The court will decide if this evidence is relevant and could change the case outcome.
Effective Strategies for Evidence Presentation
To effectively challenge a verdict, make clear summaries of evidence issues.
Your appeal should focus on legal errors that need correction, not just repeat original arguments.
Working with a skilled defense attorney is vital.
They can help you make strong evidence-based arguments that follow Romanian appeal rules.
This increases your chances of winning.
| Evidence Aspect | First Instance Court | Appeal Court | Strategic Considerations |
| New Evidence | Broadly admissible | Limited to unavailable/unknown evidence | Must justify why evidence wasn’t presented earlier |
| Witness Testimony | Primary evidence gathering | Rarely heard unless new | Focus on inconsistencies in original testimony |
| Expert Opinions | Commissioned by court | New opinions possible if justified | Challenge methodology or conclusions of original experts |
| Documentary Evidence | Comprehensive collection | Selective review of key documents | Highlight documents overlooked or misinterpreted |
Remember, appeals in Romania are not about retrying your case.
They focus on legal or procedural errors with evidence that affected the verdict.
By understanding these differences and preparing well, you can improve your appeal’s chances of success.
Rights of Defendants During Appeals
Knowing your rights during appeals is key to challenging a criminal conviction in Romania.
The Romanian legal system offers many protections.
These ensure fair proceedings and due process throughout the appeal.
The Romanian Constitution and Criminal Procedure Code outline specific protections for appealing criminal convictions.
Knowing these rights and how to use them can greatly impact your appeal’s outcome.
Let’s look at the main rights you have during this important legal process.
Right to Legal Representation
One of the most important defense rights in Romania is having legal representation during appeals.
This right means you get professional help with complex legal steps.
Legal help is crucial during appeals because rules are strict.
You have the right to:
- Choose your own lawyer or get one from the court if you can’t afford one;
- Speak privately with your lawyer before and during hearings;
- Have enough time to prepare your defense with your lawyer;
In serious cases, you must have a lawyer.
The court will appoint one if you don’t have one.
This ensures your right to counsel is protected, no matter your financial situation.
Right to Present New Evidence
You have the right to introduce new evidence during appeals under certain conditions.
This right is key when new evidence was not available or known during the trial.
To use this right, you must meet specific conditions:
- The new evidence must be relevant and could change the case’s outcome;
- You must explain why this evidence wasn’t presented in the original trial;
- The evidence must be submitted on time;
- You need to document why the new evidence is important.
The appeals court decides if new evidence is accepted.
But, presenting strong reasons for its inclusion can help.
This right is a key way to prevent wrongful convictions in Romania by correcting overlooked facts.
Right to Challenge Previous Rulings
In the Romanian appeals system, you can challenge specific parts of the lower court’s decision.
This is a key right of the accused in appeals and is the basis of the appeals process.
You can challenge rulings on several grounds:
- Factual errors or misinterpretation of evidence by the lower court;
- Procedural violations that affected your right to a fair trial;
- Incorrect application of laws to your case;
- Disproportionate sentencing compared to similar cases.
When challenging rulings, be specific.
Your appeal should clearly state which parts of the ruling you’re challenging and why.
General complaints without legal grounds are unlikely to succeed.
You also have the right to be present at hearings, speak last before deliberations, and have an interpreter if needed.
These rights ensure you can fully participate in the appeals process.
Understanding and using these rights is crucial for a fair appeal.
The legal system is complex, but these protections are in place to prevent errors and give you a chance to correct unjust outcomes.
Appeal Court Procedures and Hearings
Understanding the appeal court procedures in Romania is key.
The process is structured to ensure fairness and thorough review.
Knowing these steps can make your appeal journey smoother.
When you file an appeal, the court checks if your documents are complete.
They make sure you’ve included everything needed.
Then, they tell everyone involved in the case about your appeal.
The court’s first step is to review your case.
They look at the main points and see if they need more information.
They might ask for more details or documents from you or the other side before the hearing.
In Romania, appeal panels usually have three judges.
For more complex cases, five judges may be involved.
This way, decisions are made with the input of several judges.
Hearings follow a set format.
The judge checks if everyone is there and gives a quick summary of the case.
You or your lawyer will then explain why you’re appealing.
The prosecutor will argue against your appeal.
You have the right to respond to their arguments.
Judges might ask questions to clarify things.
Most hearings are open to the public.
But, some cases involving minors or national security are closed. Only the parties involved are there.
The time it takes to finish an appeal varies.
Simple cases might take 2-3 months.
More complex ones could take 6 months or more.
Your lawyer can give a better idea of when it might end.
After hearing everything, judges go off to decide.
They vote on the decision, and any dissenting opinions are noted.
The court’s final decision must explain why they accepted or rejected your appeal.
It’s important to know how to act in court.
Wear professional clothes and show respect.
Turn off your phone and only speak when the judge invites you.
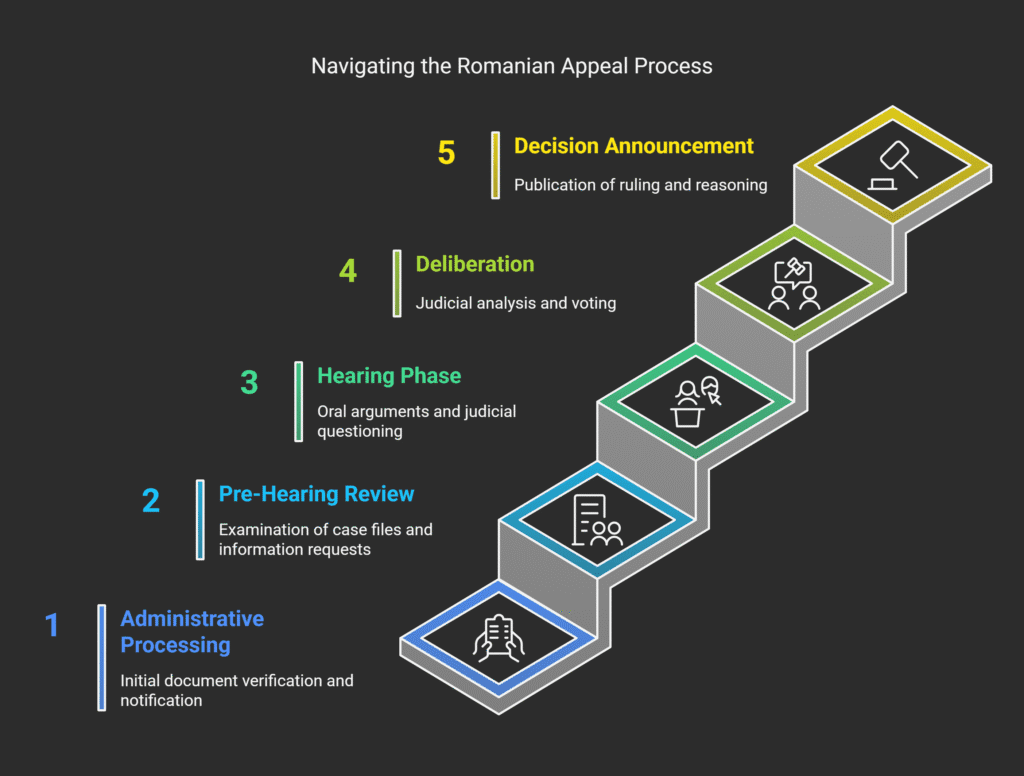
| Appeal Stage | Key Activities | Your Role | Timeframe |
| Administrative Processing | Document verification, party notification | Submit complete documentation | 1-2 weeks |
| Pre-Hearing Review | Case file examination, additional information requests | Respond promptly to court inquiries | 2-4 weeks |
| Hearing Phase | Oral arguments, judicial questioning | Present your case clearly or through counsel | 1-3 sessions |
| Deliberation | Judicial analysis, voting on decision | Await ruling | 1-4 weeks |
| Decision Announcement | Ruling publication, reasoning provided | Receive and review decision | Within 30 days of deliberation |
The appeal process in Romania focuses on being thorough, not fast.
Courts look at all parts of your case to ensure justice.
This careful approach might take longer but helps avoid quick, wrong decisions.
If you can’t make it to a hearing, tell the court right away.
Give a good reason.
Not showing up without a good reason can hurt your appeal.
Your lawyers in Romania can usually represent you.
Keep talking to your lawyer throughout the appeal.
They can explain what’s happening, help you understand the judges’ comments, and prepare you for each step.
Working together can make navigating the appeal system easier.
Possible Outcomes of Criminal Appeals
Understanding the possible results of your criminal appeal in Romania is key.
The appeals court has several options when reviewing your conviction.
The outcome depends on the strength of your legal arguments, the evidence, and your case’s specifics.
When the appeals court makes a decision, it will issue a ruling.
This ruling can be one of several outcomes.
The court’s decision is based on a detailed look at your case’s procedural and substantive aspects.
Conviction Overturned
The most favorable outcome is having your conviction overturned.
This occurs when the appeals court finds significant legal errors in the original trial.
When this happens, the court declares the original judgment flawed.
Several reasons can lead to a conviction being reversed.
These include new evidence, procedural violations, or insufficient evidence to support a guilty verdict.
If a conviction is overturned, the court might declare you not guilty.
Or, it might stop the criminal trial if it shouldn’t have started.
This means you regain your legal presumption of innocence.
If you were in jail, you would likely be released.
This is unless there are other charges or legal reasons for detention.
Sentence Modification
In some cases, the appeals court might keep the conviction but change the sentence.
This happens when the punishment was seen as too harsh or not in line with legal standards.
Sentence modifications can include reducing the prison term, converting a custodial sentence to a suspended one, or adjusting penalties.
- Reduction in prison term length;
- Conversion of a custodial sentence to a suspended sentence;
- Alteration of additional penalties (such as fines or probation terms);
- Adjustment of legal classification of the offense to a less severe category.
When seeking to modify a sentence, your lawyer will argue the punishment was too harsh.
The appeals court has a lot of discretion in modifying sentences.
They consider the crime’s nature, your personal situation, and similar cases.
A successful sentence modification can greatly improve your situation.
For example, a reduced prison sentence or a change to probation can help you keep your job and family ties.
Appeal Rejection
The least favorable outcome is having your appeal rejected.
This happens when the appeals court finds no merit in your arguments.
When this occurs, the original verdict and sentence remain in effect.
Appeal rejections usually happen when the court sees no procedural errors, the evidence supports the conviction, and the sentence is fair.
The court will explain its reasoning in writing, addressing each of your appeal’s arguments.
After an appeal rejection, you must follow the original sentence.
However, this doesn’t mean you’ve run out of legal options.
You might still have the right to appeal further or explore other post-appeal remedies.
The appeals court can also make more nuanced decisions.
Partial reversals occur when some charges are overturned while others are kept.
This can lead to a revised sentence based on the remaining convictions.
The court might also issue a remand decision, sending your case back to the lower court.
This happens when the appeals court finds procedural errors but can’t make a final decision.
Roughly 30% of criminal appeals in Romania result in some form of modification to the original verdict or sentence.
Complete reversals occur in about 15% of cases.
These figures vary by year and by the type of offense involved.
Regardless of the outcome, the appeals court will provide a detailed written decision.
This document is crucial for understanding the court’s reasoning and determining if further legal action is needed.
Post-Appeal Legal Options
After the usual appeal process, Romania offers special legal paths for those who think justice was not done.
These options help protect against unfair convictions.
But, they have strict rules to follow.
Extraordinary Appeals to the High Court
If regular appeals fail, you can ask Romania’s top court for help.
The High Court of Cassation and Justice looks at special appeals in certain cases:
- Appeal in Cassation – For serious mistakes in applying the law;
- Appeal in Annulment – When there were big mistakes in how the case was handled;
- Review of Final Decisions – For new evidence that changes everything.
These appeals have tight deadlines, from 30 days to 1 year.
Winning is rare, with success rates often under 15%.
Case Revision Based on New Evidence
Case revision is another chance for justice in Romania.
It’s for new evidence that came up after your case was closed.
This includes:
- New witnesses or evidence;
- Forensic findings that contradict the trial;
- Proof that evidence was faked;
- Proof that judges did something wrong.
Constitutional Court Applications
If you think your conviction was because of bad laws, you can ask the Constitutional Court.
Your lawyer needs to:
- Find laws that were wrongly applied;
- Show how these laws hurt your case;
- Apply within 45 days of your last appeal.
The Constitutional Court only looks at laws, not the facts of your case.
If they agree, your case might be retried without the bad laws.
European Court of Human Rights Applications
After trying everything in Romania, the European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) is an international option.
They check if your rights were broken.
To use this option, you must:
- Exhaust all domestic remedies – Try all appeals in Romania;
- File within 4 months – You have 4 months after your last appeal;
- Identify specific rights violations – Clearly say which rights were broken.
The ECHR process takes 3-5 years.
If they find in your favor, they might give you money and make Romania fix the problem, possibly by reopening your case.
Practical Considerations
Keep these things in mind when thinking about post-appeal options:
- Winning is rare, with success rates under 10%;
- You need a lawyer who knows these complex rules;
- It can cost a lot, especially for international options;
- It takes a long time, often years.
Recent changes in Romania’s justice system aim to improve these options.
But, winning is still hard.
Your lawyer should tell you the chances before you start.
Remember, these special remedies are not for everyday appeals.
They are for protecting against big mistakes in justice.
Conclusion
The Romanian criminal appeals process gives a second chance to those wrongly convicted.
Appeal success rates in Romania depend on the case’s complexity.
But, with the right preparation, your chances improve a lot.
Looking at successful criminal appeals cases in Romania shows a pattern.
Those with skilled lawyers do much better.
Hiring a criminal appeals lawyer in Romania is key.
They know how to meet deadlines and find good reasons to appeal.
Choosing the right lawyer can change your outcome.
A top Romanian law firm knows the law and how courts work.
Many find that good legal help is worth the investment in appeals.
Every appeal is judged on its own.
Courts look at mistakes in the process and legal issues.
A Romanian law office with experience can create a plan just for you.
If you’re facing a criminal conviction, act fast.
For help with your appeal, contact Atrium Romanian Lawyers at office@theromanianlawyers.com.
They can guide you through your options and what to do next.
FAQ
What is the time limit for filing a criminal appeal in Romania?
In Romania, you have 10 days to file a regular appeal after the judgment is communicated.
For second appeals, the deadline is 30 days.
Missing these deadlines usually means losing your right to appeal.
However, in rare cases like serious illness, you might get an extension.
What are the main grounds for appealing a criminal conviction in Romania?
You can appeal if there were procedural errors or if the law was applied wrongly.
If the evidence was not enough or was contradictory, you can also appeal.
New evidence, violations of your rights, or a harsh sentence are other valid reasons.
Your appeal must clearly state why you’re appealing and provide legal arguments.
Can I present new evidence during my appeal?
Yes, but with some restrictions.
Romanian appeal courts mainly review existing evidence.
New evidence is only accepted if it was not available during the trial.
You must explain why this evidence couldn’t be presented earlier and show its relevance.
Do I need a lawyer to file a criminal appeal in Romania?
While not mandatory, having a lawyer is highly recommended.
Appeals are complex and require specialized knowledge.
A lawyer can help identify strong grounds for appeal, ensure deadlines are met, and present your case effectively.
For serious cases, legal representation is often required.
What documents are required to file a criminal appeal in Romania?
You’ll need the appeal petition, copies of the original judgment, evidence supporting your appeal, and a power of attorney.
All documents must be properly prepared and translated if necessary.
Keeping copies and proof of filing is also important.
What happens during an appeal hearing in Romania?
The hearing starts with verification of the parties and a summary of the case.
Your lawyer will present arguments, and the prosecutor will respond.
Judges may ask questions.
You can make a final statement before the decision is made.
The court may decide immediately or schedule a later date.
What are the possible outcomes of my criminal appeal?
The appeals court can overturn your conviction, modify your sentence, or reject your appeal.
They might also partially reverse the conviction or remand the case for reconsideration.
The outcome depends on the strength of your appeal and the evidence.
If my appeal is rejected, what other legal options do I have?
After exhausting standard appeals, you might consider extraordinary appeals or case revision based on new evidence.
You could also apply to the Romanian Constitutional Court or the European Court of Human Rights.
These options require specialized legal expertise and have high thresholds for acceptance.
How is the jurisdiction determined for my criminal appeal?
The jurisdiction depends on the original court and the offense type.
Appeals from first instance courts go to tribunals, while appeals from tribunals go to courts of appeal.
The High Court of Cassation and Justice hears appeals from courts of appeal and special cases.
This ensures appeals are heard by higher courts.
Can I be released from detention while my appeal is pending?
You can request release, but it’s at the court’s discretion.
The court will consider factors like risk of flight and danger to public safety.
In some cases, they might replace detention with less restrictive measures.
Your lawyer can request these measures on your behalf.
What is the difference between a regular appeal (apel) and a second appeal (recurs) in Romania?
A regular appeal is a comprehensive review of your case.
It allows reassessment of evidence and legal interpretations.
A second appeal focuses more on legal matters and doesn’t reassess evidence.
Regular appeals offer broader grounds for challenging a conviction.
How long does the criminal appeals process typically take in Romania?
The time varies based on case complexity and court workload.
Simple appeals might take 3-6 months, while complex ones can take a year or more.
Factors like additional evidence and court backlog affect the timeline.
Your lawyer can give a more accurate estimate based on your case.
Can I represent myself in a criminal appeal in Romania?
While possible, self-representation is rarely advisable.
Appeals require complex legal procedures and specialized knowledge.
Without proper expertise, you risk procedural errors or failing on substantive issues.
For serious cases, legal representation is often mandatory.
What costs are associated with filing a criminal appeal in Romania?
Costs include court fees, attorney fees, and expenses for documentation and expert opinions.
In cases of financial hardship, reduced fees or public defender representation might be available.
Discuss fees with your attorney before proceeding, as costs vary.
How can I find a qualified criminal appeals lawyer in Romania?
Look for lawyers with experience in criminal appeals, not just general criminal law.
Check their track record, familiarity with courts, and knowledge of appellate procedure.
Contact the Romanian Bar Association for referrals or seek recommendations.
Ask about their experience with similar cases during initial consultations.
What are the grounds for appealing a criminal conviction in Romania?
Under Romanian law, specifically the Criminal Procedure Code, there are several grounds for appealing a criminal conviction.
The main grounds include: errors in the application of substantive law, procedural irregularities, incorrect assessment of evidence, disproportionate sentencing, or new evidence that wasn’t available during the initial trial.
The Romanian Criminal Code of Criminal Procedure provides comprehensive frameworks for these appeals.
It’s important to note that your appeal must clearly specify which aspects of the judgment you’re challenging and provide legal arguments supporting your position.
The appellate court will only examine those aspects of the judgment that you’ve specifically challenged in your appeal.
If you’re considering an appeal based on new evidence, you must demonstrate that this evidence wasn’t available during the original trial and that it could substantively change the outcome of your case.
Under Romanian jurisdiction, the right to appeal is considered fundamental and is protected both by domestic legislation and the European Convention on Human Rights.
What is the time limit for filing an appeal against a criminal conviction in Romania?
In Romania, the time limit for filing an appeal against a criminal conviction is strictly regulated by the Criminal Procedure Code.
Typically, you have 10 days from the communication of the written judgment to file a standard appeal (known as “apel” in Romanian).
For extraordinary appeals (such as “recurs în casație” which goes to the High Court of Cassation and Justice), the timeframe is 30 days from the final decision.
Missing these deadlines can result in your appeal being declared inadmissible, although in exceptional circumstances, you may be able to request reinstatement of the time limit if you can prove that you missed the deadline due to circumstances beyond your control.




