Dual Employment in Romania: Legal & Tax Rules Explained
Dual Employment in Romania: Legal & Tax Rules Explained
Dual employment is legal in Romania under Article 35 of the Romanian Labour Code.
Employees may hold multiple employment contracts at the same time, either with different employers or, in certain cases, with the same employer, provided work schedules do not overlap and no statutory incompatibility applies.
As a rule, employers are prohibited from penalizing employees solely for holding another job.
Expert guidance from Atrium Romanian Lawyers
1. What Is Dual Employment Under Romanian Law?
Dual employment (cumul de funcții) refers to the situation in which an individual holds two or more individual employment contracts (contracte individuale de muncă – CIM) simultaneously.
These contracts may be concluded with different employers or, subject to stricter conditions, with the same employer.
Romanian labour law adopts a contract-based approach, meaning each employment relationship is assessed independently.
There is no legal requirement for an employee to obtain consent from one employer in order to work for another, nor is there a general obligation to disclose all other employment relationships, except where disclosure is required for fiscal or compliance purposes.
The legal basis for this principle is found in the Romanian Labour Code, particularly the rules governing freedom of work and contractual autonomy.
2. Is Dual Employment Legal in Romania?
Yes. Dual employment is expressly legal under Article 35 of the Labour Code, which enshrines the employee’s freedom to work for multiple employers.
This means that Romanian law does not impose:
- A numerical limit on employment contracts;
- A hierarchy between jobs; or
- A requirement to designate a “main employer” for labour-law purposes.
3. Can an Employer Forbid an Employee From Having a Second Job?
As a general rule, no. Employers may not forbid employees from having a second job solely because they wish to work elsewhere.
Romanian law is aligned with EU standards on transparent and predictable working conditions.
These rules prohibit employers from applying unfavorable treatment—such as dismissal, demotion, or harassment—simply because an employee exercises their right to work elsewhere.
Clauses that broadly prohibit “any other paid activity” are, in most cases, unenforceable unless they are justified by a real and specific conflict of interest and are linked to a valid non-compete clause.
4. Independence of Employment Contracts
Each individual employment contract operates as a separate legal relationship.
This has several important consequences:
- Salary entitlement arises independently under each contract;
- Annual leave accrues separately for each contract;
- Social contributions are calculated per contract, subject to tax rules;
- Disciplinary liability is assessed independently by each employer.
5. Salary and Annual Leave in Dual Employment
Salary Entitlement
An employee holding multiple contracts is entitled to receive the full negotiated salary under each contract, regardless of income earned elsewhere.
Romanian labour law does not permit salary reductions based on the existence of other employment relationships.
Annual Leave
Paid annual leave is earned separately under each employment contract.
Each employer must grant leave proportionally to the duration and workload of the respective contract.
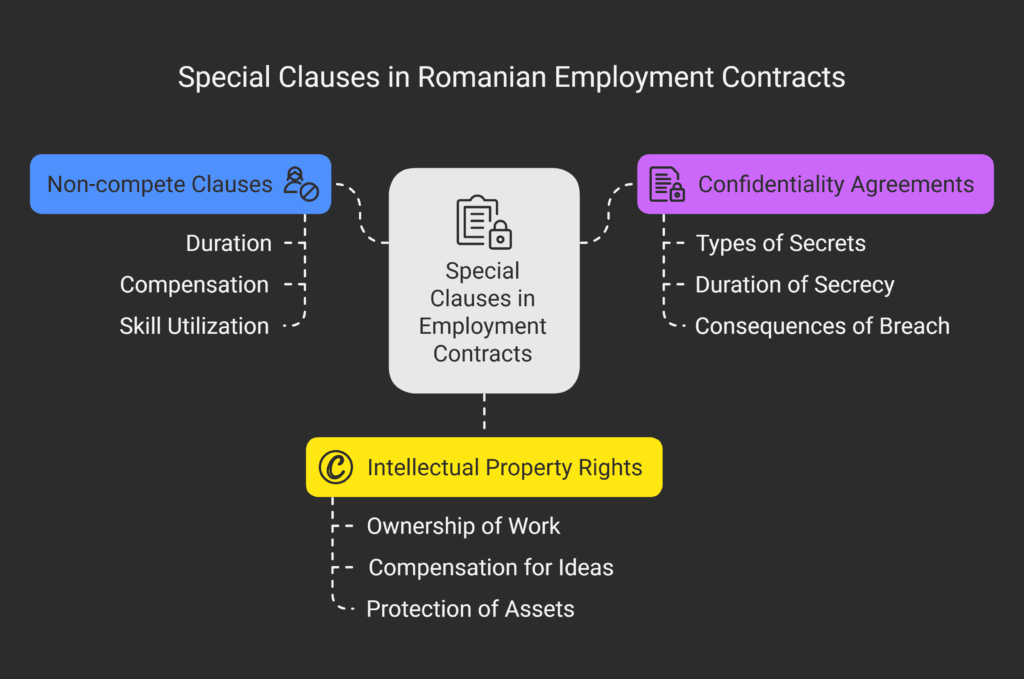
6. Loyalty, Confidentiality, and Non-Compete Obligations
Dual employment does not eliminate loyalty or confidentiality obligations.
Employees must continue to:
- Protect confidential information belonging to each employer;
- Avoid unfair competition;
- Comply with any valid non-compete clauses.
Under Romanian law, a non-compete clause is enforceable only if it is paid and proportionate.
Courts frequently invalidate unpaid or overly broad clauses.
7. Working Time Limits and Rest Periods
General Working Time Rule
Romanian labour law sets a general maximum of 48 working hours per week, including overtime.
According to current practice of the Labour Inspectorate (Inspecția Muncii), this limit is generally applied per contract, not per individual, when different employers are involved.
As a result, under current national practice, an employee may lawfully hold two full-time contracts with different employers, provided work schedules do not overlap.
Same Employer vs. Different Employers
When multiple contracts exist with the same employer, the rules are stricter. In such cases:
- Roles must be distinct;
- Schedules must not overlap;
- Total daily working time may not exceed 12 hours;
- The mandatory 12-hour daily rest period must be respected cumulatively.
European Perspective
EU case law, including decisions of the Court of Justice of the European Union on rest periods, increasingly emphasizes cumulative rest protection.
While Romanian law has not yet fully adopted this approach across different employers, future alignment cannot be excluded.
8. Special Rules for Minors
For employees aged 15 to 18, the law is strict:
- Maximum 6 working hours per day;
- Maximum 30 working hours per week;
- Limits apply cumulatively across all contracts.
These protections are mandatory and reflect Romania’s obligations under EU and international labour standards.
9. Fiscal Framework for Dual Employment
Minimum Wage Threshold
As of 2026, the gross minimum wage in Romania is 4,050 RON, according to regulations issued by the Romanian Government and Ministry of Labour.
This threshold is central to the taxation of part-time contracts and the calculation of social contributions.
10. Part-Time Over-Taxation: The Core Issue
Under Romanian fiscal rules introduced through tax emergency ordinances adopted by the Ministry of Finance, part-time contracts with salaries below the minimum wage are generally subject to social contributions calculated at the full minimum-wage level.
This rule was designed to discourage artificial fragmentation of employment but has significant implications for dual-employed individuals.
11. How to Avoid Part-Time Over-Taxation
An exemption applies where the employee’s total gross income across all contracts reaches at least the minimum wage.
To benefit from this exemption:
- The employee must submit a declaration on own responsibility;
- The declaration must be submitted monthly;
- According to current fiscal regulations issued by the Romanian Ministry of Finance, the deadline is generally the 5th day of the following month;
- The declaration must be submitted to each employer.
If the declaration is not submitted on time, the employer is generally required to calculate and pay full social contributions.
12. Categories Automatically Exempt From Over-Taxation
Certain categories benefit from automatic exemption under Romanian tax law, including:
- Students and pupils under 26;
- Apprentices under 18;
- Parents or legal guardians of at least two children;
- Persons with recognized disabilities;
- Old-age pensioners.
13. The “Base Function” (Funcția de Bază)
Every employee must designate one and only one employment contract as their base function.
The base function determines:
- Entitlement to personal income-tax deductions;
- Eligibility for meal tickets.
The employee may change the base function at any time by notifying employers in writing. Receiving base-function benefits from more than one employer constitutes a fiscal irregularity.
14. Sector-Specific Restrictions and Incompatibilities
Public Sector
Civil servants are subject to strict incompatibility rules under Romanian public integrity legislation, with limited exceptions for teaching, research, or artistic activities. Contractual staff in public institutions generally enjoy greater flexibility.
Medical Professionals
Doctors frequently combine public hospital work with private practice. However, private activity must not overlap with public schedules, and leaving a hospital during mandatory on-call shifts is prohibited under healthcare-specific regulations.
Company Administrators
In joint-stock companies, an administrator cannot simultaneously be an employee of the same company under Romanian company law. Such contracts are null and void from the outset.
15. Administrative Monitoring and Transparency
All employment contracts must be registered in the national employee registry system administered by the Labour Inspectorate. Employees may access their registry extract to verify registered contracts, salaries, and seniority.
This transparency significantly reduces the risk of undeclared or overlapping work.
16. Impact on Pension Rights
Overlapping employment periods count once toward seniority in years. However, social contributions paid on multiple incomes increase pension points, which may result in a higher future pension.
17. Employer Risk Management in Dual Employment
Employers hiring dual-employed workers should, as part of their general health-and-safety and compliance obligations:
- Verify that work schedules do not overlap;
- Monitor fatigue risks;
- Ensure accurate registry reporting;
- Properly remunerate any non-compete clauses.
Failure to manage these aspects may expose employers to sanctions during inspections by the Labour Inspectorate or to liability in the event of workplace incidents.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, provided work schedules do not overlap and no statutory incompatibility applies.
As a rule, no, unless a valid non-compete clause or a statutory incompatibility is breached.
No. Meal tickets may be granted only by the base-function employer.
Generally, yes, because contributions are paid on multiple incomes, increasing pension points.
Key Compliance Rule: Transparency. Employees must declare their base function and applicable tax exemptions correctly, employers must register contracts accurately, and work schedules must never overlap.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Specific situations may require individual legal assessment. Professional legal guidance should be obtained before taking action based on this content.